多对多双向映射关系,比如一个医生可以为多个病人看病,一个病人也可以找不同的医生看病。在数据库中只要找到这个医生就可以找到他所看过的病人信息,相反,如果找到病人的信息也可以反过来找到为其看过病的医生信息。
多对多映射关系通常要通过中间表来建立联系,中间表中保存的是医生表和病人表的外键信息。
Doctor.java:
public class Doctor { private String id; private String name; private String subject; private Set<Patient> patients = new HashSet<Patient>(); public Doctor() { } public Doctor(String id, String name, String subject, Set<Patient> patients) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.subject = subject; this.patients = patients; } //getter,setter…… }
Patient.java:
public class Patient { private String id; private String name; private String caseForPatient; private Set<Doctor> doctors = new HashSet<Doctor>(); public Patient() { } public Patient(String id, String name, String caseForPatient, Set<Doctor> doctors) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.caseForPatient = caseForPatient; this.doctors = doctors; } //getter,setter…… }
配置文件:
Doctor.hbm.xml:
1 <hibernate-mapping> 2 <class name="com.sunflower.yuan.pojo.Doctor" table="doctor"> 3 <id name="id" type="string" column="id"> 4 <generator class="uuid"></generator> 5 </id> 6 7 <property name="name" type="string" column="name"></property> 8 <property name="subject" type="string" column="subject"></property> 9 10 <set name="patients" cascade="save-update" table="doctor_patient" inverse="true"> 11 <key column="doctor_id" not-null="true"></key> 12 <many-to-many column="patient_id" class="com.sunflower.yuan.pojo.Patient"></many-to-many> 13 </set> 14 15 </class> 16 </hibernate-mapping>
Patient.hbm.xml:
1 <hibernate-mapping> 2 <class name="com.sunflower.yuan.pojo.Patient" table="patient"> 3 <id name="id" type="string" column="id"> 4 <generator class="uuid"></generator> 5 </id> 6 7 <property name="name" type="string" column="name"></property> 8 <property name="caseForPatient" type="string" column="caseFP"></property> 9 10 <set name="doctors" cascade="save-update" table="doctor_patient" inverse="false"> 11 <key column="patient_id" not-null="true"></key> 12 <many-to-many column="doctor_id" class="com.sunflower.yuan.pojo.Doctor"></many-to-many> 13 </set> 14 15 </class> 16 </hibernate-mapping>
Doctor.hbm.xml中的第10行中inverse="true",Patient.hbm.xml中的第10行inverse="false",表明数据库的关系由Doctor来维护,如果都设为inverse="false",那么会出现重复插入,系统报错。第11行是中间表中对应于doctor表、patient表中的外键,用来联系两个表。
建表语句(SQL):
alter table doctor_patient drop foreign key FK667B93E5BF142721
alter table doctor_patient drop foreign key FK667B93E5FB820CF3
drop table if exists doctor
drop table if exists doctor_patient
drop table if exists patient
create table doctor (id varchar(255) not null, name varchar(255), subject varchar(255), primary key (id))
create table doctor_patient (doctor_id varchar(255) not null, patient_id varchar(255) not null, primary key (patient_id, doctor_id))
create table patient (id varchar(255) not null, name varchar(255), caseFP varchar(255), primary key (id))
alter table doctor_patient add index FK667B93E5BF142721 (patient_id), add constraint FK667B93E5BF142721 foreign key (patient_id) references patient (id)
alter table doctor_patient add index FK667B93E5FB820CF3 (doctor_id), add constraint FK667B93E5FB820CF3 foreign key (doctor_id) references doctor (id)
测试:
Test.java:
1 public class Test { 2 // 保存测试 3 public void save() { 4 Session session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); 5 Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); 6 7 try { 8 Doctor doctor = new Doctor(); 9 doctor.setName("华佗"); 10 doctor.setSubject("骨科"); 11 12 Doctor doctor2 = new Doctor(); 13 doctor2.setName("扁鹊"); 14 doctor2.setSubject("外科"); 15 16 Patient patient = new Patient(); 17 patient.setName("曹操"); 18 patient.setCaseForPatient("头骨痛了三四年,剧烈"); 19 20 Patient patient2 = new Patient(); 21 patient2.setName("关羽"); 22 patient2.setCaseForPatient("肩膀中箭,有剧毒"); 23 24 doctor.getPatients().add(patient); 25 doctor.getPatients().add(patient2); 26 27 patient.getDoctors().add(doctor); 28 patient2.getDoctors().add(doctor2); 29 30 session.save(patient); 31 session.save(patient2); 32 33 ts.commit(); 34 } 35 catch (Exception e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 ts.rollback(); 38 } 39 finally { 40 HibernateUtil.closeSession(session); 41 } 42 } 43 44 // 查询测试 45 public void get() { 46 Session session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); 47 Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); 48 49 try { 50 Patient patient = (Patient) session.get(Patient.class, 51 "8a85f4eb395e288f01395e2890380002"); 52 System.out.println("Patient name:" + patient.getName()); 53 System.out.println("Patient's Doctor:" 54 + ((Doctor) patient.getDoctors().toArray()[0]).getName()); 55 ts.commit(); 56 } 57 catch (Exception e) { 58 e.printStackTrace(); 59 ts.rollback(); 60 } 61 finally { 62 HibernateUtil.closeSession(session); 63 } 64 } 65 66 // HQL语句测试 67 public void getHQL() { 68 Session session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); 69 Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); 70 71 try { 72 // Query query = session 73 // .createQuery("select p.name,d.name from Patient as p,Doctor as d"); 74 // List list = query.list(); 75 // for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 76 // Object[] obj = (Object[]) list.get(i); 77 // for (int j = 0; j < obj.length; j++) { 78 // if (j + 1 == obj.length) 79 // System.out.println(obj[j]); 80 // else 81 // System.out.print(obj[j] + ","); 82 // } 83 // } 84 85 // Query query = session 86 // .createQuery("select new list(p.name,d.name) from Patient as p,Doctor as d"); 87 // List list = query.list(); 88 // for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 89 // List list2 = (List) list.get(i); 90 // for (int j = 0; j < list2.size(); j++) { 91 // if (j + 1 == list2.size()) 92 // System.out.println(list2.get(j)); 93 // else 94 // System.out.print(list2.get(j) + ","); 95 // } 96 // } 97 98 } 99 catch (Exception e) { 100 e.printStackTrace(); 101 ts.rollback(); 102 } 103 finally { 104 HibernateUtil.closeSession(session); 105 } 106 } 107 108 // 删除测试 109 public void delete() { 110 Session session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); 111 Transaction ts = session.beginTransaction(); 112 113 try { 114 Patient patient = new Patient(); 115 patient.setId("8a85f4eb395e288f01395e2890380003"); 116 117 session.delete(patient); 118 ts.commit(); 119 } 120 catch (Exception e) { 121 e.printStackTrace(); 122 ts.rollback(); 123 } 124 finally { 125 HibernateUtil.closeSession(session); 126 } 127 } 128 129 public static void main(String[] args) { 130 Test test = new Test(); 131 // test.save(); 132 // test.get(); 133 // test.delete(); 134 test.getHQL(); 135 } 136 }
第72至83行中,将两个不同表中的两个字段查询出来,这里的List list = query.list()返回的多行数据的集合,而每一行数据都是一个Object[]类型数据,参考文档说明如下:
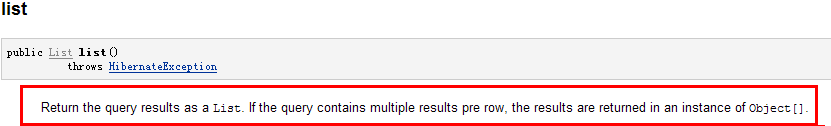
所以要进行转换:Object[] obj = (Object[]) list.get(i);
HQL语句中也可以对查询出来的每行语句进行封装,例如第85至86行中Query query = session
.createQuery("select new list(p.name,d.name) from Patient as p,Doctor as d");将每行信息封装成List对象,也可以封装在自定义对象中,不过这个自定义对象要有包含所查询属性的构造函数,并且顺序一致。
详细的HQL语句,请查看HQL语句大全一文。







 本文详细介绍了多对多映射关系的概念及其在数据库设计中的实现方式,通过Java类和XML配置文件展示了如何使用Hibernate框架来建立这种关系。包括创建表、配置映射关系、保存、查询及HQL语句测试等内容。
本文详细介绍了多对多映射关系的概念及其在数据库设计中的实现方式,通过Java类和XML配置文件展示了如何使用Hibernate框架来建立这种关系。包括创建表、配置映射关系、保存、查询及HQL语句测试等内容。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








