Problem Description
A simple mathematical formula for e is
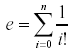
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using
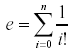
where n is allowed to go to infinity. This can actually yield very accurate approximations of e using
relatively small values of n.
Output
Output the approximations of e generated by the above formula for the values of n from 0 to 9. The
beginning of your output should appear similar to that shown below.
Sample Output
n e
- -----------
0 1
1 2
2 2.5
3 2.666666667
4 2.708333333
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double e[10] = {1};
double sum = 1;
double ans = 0;
int i;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
sum *= (double)i;
e[i] = 1 / sum;
}
printf("n e\n");
printf("- -----------\n");
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ans += e[i];
if (i <= 2)
printf("%d %g\n", i, ans);
else
printf("%d %.9f\n", i, ans);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一种使用简单数学公式计算自然常数e的方法,通过允许n趋向于无穷大来获得e的精确近似值。文章提供了一个C语言程序示例,该程序计算并输出了当n从0到9时,e的近似值。
本文介绍了一种使用简单数学公式计算自然常数e的方法,通过允许n趋向于无穷大来获得e的精确近似值。文章提供了一个C语言程序示例,该程序计算并输出了当n从0到9时,e的近似值。
















 643
643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








