题目:
Description
In this problem, you are given a sequence S1, S2, ..., Sn of squares of different sizes. The sides of the squares are integer numbers. We locate the squares on the positive x-y quarter of the plane, such that their sides make 45 degrees with x and y axes, and one of their vertices are on y=0 line. Let bi be the x coordinates of the bottom vertex of Si. First, put S1 such that its left vertex lies on x=0. Then, put S1, (i > 1) at minimum bi such that
- bi > bi-1 and
- the interior of Si does not have intersection with the interior of S1...Si-1.
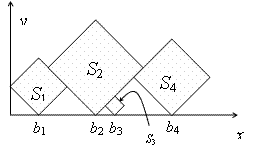
The goal is to find which squares are visible, either entirely or partially, when viewed from above. In the example above, the squares S1, S2, and S4 have this property. More formally, Si is visible from above if it contains a point p, such that no square other than Si intersect the vertical half-line drawn from p upwards.
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line of each test case is n (1 ≤ n ≤ 50), the number of squares. The second line contains n integers between 1 to 30, where the ith number is the length of the sides of Si. The input is terminated by a line containing a zero number.
Output
For each test case, output a single line containing the index of the visible squares in the input sequence, in ascending order, separated by blank characters.
Sample Input
4
3 5 1 4
3
2 1 2
0
Sample Output
1 2 4
1 3
题意:依次给出n个正方形的边长 每个正方形在x轴上呈45°摆放并且尽可能放的紧凑 问从上方看时能看见哪些正方形
思路:对于第i个正方形 判断前i-1个正方形如果和它相交的话左端点的位置 最后取一个最大值作为整个正方形的左端点位置
对于j<i的正方形 如果i的边长大于j 那么j的最右能看到的部分就不会比i的最左端点大 反之 i的最左能看到的部分就不会比j最右端点小
再将最左能看到的端点比最右能看到的端点去掉
为了避免浮点数 将每条边乘上sqrt(2)然后约掉 效果等于将正方形投影到x轴上
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=110;
int n;
struct node{
int l,r,len;
}kk[maxn];
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
if(n==0) break;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&kk[i].len);
kk[i].l=0;
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
kk[i].l=max(kk[i].l,kk[j].r-abs(kk[i].len-kk[j].len));
}
kk[i].r=kk[i].l+2*kk[i].len;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
if(kk[i].l<kk[j].r && kk[i].len<kk[j].len)
kk[i].l=kk[j].r;
}
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){
if(kk[i].r>kk[j].l && kk[i].len<kk[j].len)
kk[i].r=kk[j].l;
}
}
int flag=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(kk[i].l<kk[i].r){
if(flag) flag=0;
else printf(" ");
printf("%d",i);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}




 本文介绍了一种算法,用于确定当多个不同大小的正方形按特定规则放置在平面上时,从上方视角哪些正方形是可见的。通过计算每个正方形的左、右边界,并考虑它们之间的相对位置和大小,该算法能够找出所有可见正方形的索引。
本文介绍了一种算法,用于确定当多个不同大小的正方形按特定规则放置在平面上时,从上方视角哪些正方形是可见的。通过计算每个正方形的左、右边界,并考虑它们之间的相对位置和大小,该算法能够找出所有可见正方形的索引。
















 91
91

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








