栈是一种特殊的表,只在表首进行插入和删除操作,表首称之为栈顶,表尾称为栈底;栈的核心原则是先进后出,简称Last In First Out(LIFO表);常用的运算有:1、是否为空栈判断;2、栈是否满判断;3、返回栈顶元素;4、插入栈顶元素;5、删除栈顶元素;
## 用数组实现栈代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct astack *Stack;
typedef struct astack
{
int top;
int maxtop;
int *data; //栈元素数组,可以是int型也可以是其他数据类型比如char;
}Astack;
Stack StackInit(int size,Stack S)
{
S->data=(int*)malloc(size*sizeof(int));
S->maxtop=size;
S->top=-1; //当top为1的时候,代表栈为空;
return S;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack S)
{
return S->top<0;
}
int StackFull(Stack S)
{
return S->top>=S->maxtop; //当top=maxtop时,代表当前栈满
}
int StackTop(Stack S)
{
return S->data[S->top]; //默认认为用户在使用栈时,需要考虑栈为空时无法返回栈顶元素
}
void Push(int x, Stack S)
{
S->top++;
S->data[S->top]=x; //默认用户所使用的栈空间(即在最开始用户开栈时需要提前考虑数组data大小)够大;
}
int Pop(Stack S)
{
S->top--;
return S->data[S->top]; //默认此时栈不为空,否则是非法操作;
}
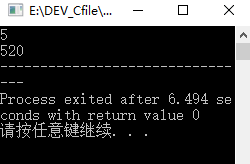
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
scanf("%d",&n);
Stack S=new Astack;
StackInit(n,S);
Push(0,S);
Push(5,S);
printf("%d",StackTop(S));
// printf("%d",Pop(S));
Pop(S);
Push(2,S);
while(StackEmpty(S)!=1) //当栈不是空的时候,返回0,是空栈返回1;
{
printf("%d",StackTop(S));
Pop(S);
}
return 0;
}
栈的指针实现代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct node* link;
typedef struct node //自定义栈内节点数据类型 ;
{
int element;
link next;
}Node;
typedef struct astack* Stack;
typedef struct astack //定一个栈指针,有一个top顶点指针;
{
link top;
}Astack;
Stack StackInit(Stack S)
{
S->top=0;
return S;
}
int StackEmpty(Stack S) //判断top指针是不是空指针;
{
return S->top==0;
}
int StackFull(Stack S) //通过指针实现的栈每次都是直接新开辟一个节点指针,所以只是看这个指针是否开辟成功;
{
link p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(p==NULL)return 1;
else
{
free(p);
return 0;
}
}
int StackTop(Stack S)
{
return S->top->element;
}
void Push(int x,Stack S) //直接插入x;
{
link p;
p=new Node;
p->element=x;
p->next=S->top;
S->top=p;
}
int Pop(Stack S) //每次删除的元素都能够输出此时删除的元素是哪一个;
{
link p;
int x;
x=S->top->element;
p=S->top;
S->top=p->next;
free(p);
return x;
}
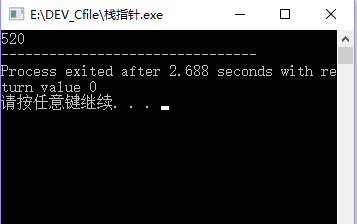
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
Stack S=new Astack;
StackInit(S);
// link p=new Node;
Push(0,S);
Push(5,S);
printf("%d",Pop(S));
Push(2,S);
while(StackEmpty(S)!=1)
{
printf("%d",StackTop(S));
Pop(S);
}
return 0;
}
上面描述的都是通过自定义实现的栈的使用,其实还有直接可以使用的STL中的栈(即已经有直接可以使用的栈,比较方便,需要包括头文件stack);
STL中的栈的使用简单介绍使用代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stack> //使用STL中已有的栈需要包括该文件
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
stack<int>s;
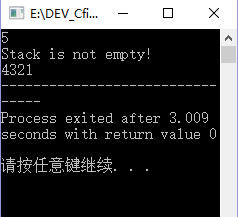
int main()
{
int i,j,n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s.push(i); //将1~n的数字存储到栈中,直接使用s.push(元素);
}
if(s.empty()!=1) //如果栈空,则s.empty()返回1,否则返回0;
{
printf("Stack is not empty!\n");
s.pop(); //此时如果使用s.pop()函数不能同时输出其删除元素,可先使用s.top()得到之后再删除;
}
else
{
printf("Stack is empty!\n");
}
while(s.empty()!=1)
{
printf("%d",s.top());
s.pop();
}
return 0;
} 
第三次作业:
1、(栈的基本运算操作:入栈出栈等):可以直接使用STL中的栈(比较懒就这样使用),也可以自定义栈实现(耗时当然比较少);对于题目中的字符串代表不同操作,可以直接针对其首字母处理,会方便一点;
2、(栈的应用:计算中缀表达式结果,包含括号等操作符比如计算{3*(6+9/3-4)+8}的结果):大致思路是使用两个栈,一个存储操作数,一个存储操作符,自定义操作符的优先级处理函数,然后对输入的表达式入栈、判断是否需要出栈、运算等操作;
题目实现代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
stack<int> Num_Stk;
stack<char>Oper_Stk;
int Oper_Big(char ch)
{
if (Oper_Stk.empty() || ch == '(' || (Oper_Stk.top() == '('&&ch != ')'))
{
return 0;
}
else if ((Oper_Stk.top() == '+' || Oper_Stk.top() == '-') && (ch == '*' || ch == '/'))
{
return 0;
}
else if (Oper_Stk.top() == '('&&ch == ')')
{
Oper_Stk.pop(); return 1;
}
else return -1;
}
void Deal_num()
{
int num1 = Num_Stk.top(); Num_Stk.pop();
int num2 = Num_Stk.top(); Num_Stk.pop();
int ans = 0;
if (Oper_Stk.top() == '+') ans = num1 + num2;
else if (Oper_Stk.top() == '-') ans = num2 - num1;
else if (Oper_Stk.top() == '*') ans = num1*num2;
else if (Oper_Stk.top() == '/')ans = num2 / num1;
Num_Stk.push(ans);
Oper_Stk.pop();
}
int main()
{
int num = 0;
char str[1000] = "";
cin >> str;
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (str[i] != '\0')
{
char expre[1005]; j = 0;
while (str[i] >= '0'&&str[i] <= '9')
{
expre[j] = str[i]; i++;
j++; expre[j] = '\0';
}
if (str[i] != '(')
{
num = atoi(expre);
Num_Stk.push(num);
}
while (1)
{
k = Oper_Big(str[i]);
if (k == 0)
{
Oper_Stk.push(str[i]);
break;
}
else if (k == 1)
{
i++;
}
else if (k == -1)
{
Deal_num();
}
}
i++;
}
cout << Num_Stk.top() << endl;
return 0;
}




 本文详细介绍了栈数据结构的概念、特点及应用,包括栈的基本操作如入栈、出栈等,并提供了使用数组和指针实现栈的具体代码示例,还讲解了如何利用标准模板库(STL)中的栈进行操作。
本文详细介绍了栈数据结构的概念、特点及应用,包括栈的基本操作如入栈、出栈等,并提供了使用数组和指针实现栈的具体代码示例,还讲解了如何利用标准模板库(STL)中的栈进行操作。
















 1568
1568

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








