关于树的层遍历,记得设置保存每一层的tmp和保存所有层的res
1、从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
思路:利用queue,第一层节点全部压进queue,进入下一层时先弹出保存然后再压下一层的节点。
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int> > vec;
if(pRoot == NULL) return vec;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(pRoot);
while(!q.empty())
{
int lo = 0, hi = q.size();
vector<int> c;
while(lo++ < hi)
{
TreeNode *t = q.front();
q.pop();
c.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
vec.push_back(c);
}
return vec;
}
};
2、请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
思路:定义从左到右用的stackL和从右到左用的stackR,先把root节点压进stackL,进入下一层时先利用tmp保存好该层节点,再在stackR中压入下一层的节点,具体是从该层节点的右节点开始压,迭代这个过程。
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int> > res;
if(pRoot == nullptr) return res;
stack<TreeNode*> stackL;
stack<TreeNode*> stackR;
TreeNode* popNode;
vector<int> tmp;
tmp.push_back(pRoot->val);
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
stackL.push(pRoot);
while(!stackL.empty() || !stackR.empty()){
while(!stackL.empty()){
popNode = stackL.top();
stackL.pop();
if(popNode->right){
stackR.push(popNode->right);
tmp.push_back(popNode->right->val);
}
if(popNode->left){
stackR.push(popNode->left);
tmp.push_back(popNode->left->val);
}
}
if(!tmp.empty()) {
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
}
while(!stackR.empty()){
popNode = stackR.top();
stackR.pop();
if(popNode->left){
stackL.push(popNode->left);
tmp.push_back(popNode->left->val);
}
if(popNode->right){
stackL.push(popNode->right);
tmp.push_back(popNode->right->val);
}
}
if(!tmp.empty()){
res.push_back(tmp);
tmp.clear();
}
}
return res;
}
};
3、给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
思路: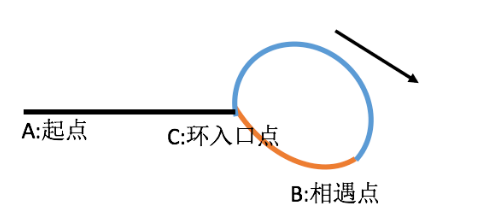
当快慢指针相遇的时候:
此时慢指针走的路程为Sslow = x + m * c + a
快指针走的路程为Sfast = x + n * c + a
2 Sslow = Sfast
2 * ( x + m*c + a ) = (x + n *c + a)
从而可以推导出:
x = (n - 2 * m )*c - a
= (n - 2 *m -1 )*c + c - a
即环前面的路程 = 数个环的长度(为可能为0) + c - a
什么是c - a?这是相遇点后,环后面部分的路程。(橙色路程)
所以,我们可以让一个指针从起点A开始走,让一个指针从相遇点B开始继续往后走,
2个指针速度一样,那么,当从原点的指针走到环入口点的时候(此时刚好走了x)
从相遇点开始走的那个指针也一定刚好到达环入口点。
所以2者会相遇,且恰好相遇在环的入口点。
最后,判断是否有环,且找环的算法复杂度为:
时间复杂度:O(n)
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* pslow=pHead;
ListNode* pfast=pHead;
ListNode* pfinal=pHead;
if(pHead==NULL|| pHead->next==NULL|| pHead->next->next==NULL) return NULL;
do
{
pslow=pslow->next;
pfast=pfast->next->next;
}while(pslow!=pfast);
while(pfinal!=pslow)
{
pslow=pslow->next;
pfinal=pfinal->next;
}
return pfinal;
}
};
4、请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"g"。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符“google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是"l"。
思路:
//思路:先排序,然年后保存0的个数,跟数字间隔相抵消,能抵消则返回true
/*import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public boolean isContinuous(int[] numbers) {
int numOfZero = 0;
int numOfInterval = 0;
int length = numbers.length;
if(length == 0){
return false;
}
Arrays.sort(numbers);
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// 计算癞子数量
if (numbers[i] == 0) {
numOfZero++;
continue;
}
// 对子,直接返回
if (numbers[i] == numbers[i + 1]) {
return false;
}
numOfInterval += numbers[i + 1] - numbers[i] - 1;
}
if (numOfZero >= numOfInterval) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
*/
//思路:map,然后保存最大最小值,条件满足max-min<5则成功;
class Solution {
public:
/*顺子满足的条件:max-min<5;
除0外其他的数字都不能重复
传入的数组放5个元素*/
bool IsContinuous( vector<int> numbers ) {
if(numbers.empty()) return 0;
int count[14]={0};//记录每个元素出现的次数;以numbers中的元素作为下标(最大K,对应13)
int len=numbers.size();
int max=-1;
int min=14;
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
{
count[numbers[i]]++;
if(numbers[i]==0) continue;
if(count[numbers[i]]>1) return 0;
if(numbers[i]>max) max=numbers[i];
if(numbers[i]<min) min=numbers[i];
}//end for
if(max-min<5) return 1;
return 0;
}//end IsContinuous()
};
5、LL今天心情特别好,因为他去买了一副扑克牌,发现里面居然有2个大王,2个小王(一副牌原本是54张^_^)...他随机从中抽出了5张牌,想测测自己的手气,看看能不能抽到顺子,如果抽到的话,他决定去买体育彩票,嘿嘿!!“红心A,黑桃3,小王,大王,方片5”,“Oh My God!”不是顺子.....LL不高兴了,他想了想,决定大\小 王可以看成任何数字,并且A看作1,J为11,Q为12,K为13。上面的5张牌就可以变成“1,2,3,4,5”(大小王分别看作2和4),“So Lucky!”。LL决定去买体育彩票啦。 现在,要求你使用这幅牌模拟上面的过程,然后告诉我们LL的运气如何, 如果牌能组成顺子就输出true,否则就输出false。为了方便起见,你可以认为大小王是0。
思路:
第一种:先排序,然年后保存0的个数,跟数字间隔相抵消,能抵消则返回true(比如1和3就需要两个0才能抵消)
第二种:map计数,相同数字的直接返回false;然后保存最大最小值,条件满足max-min<5则成功;
//思路:先排序,然年后保存0的个数,跟数字间隔相抵消,能抵消则返回true
/*import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public boolean isContinuous(int[] numbers) {
int numOfZero = 0;
int numOfInterval = 0;
int length = numbers.length;
if(length == 0){
return false;
}
Arrays.sort(numbers);
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// 计算癞子数量
if (numbers[i] == 0) {
numOfZero++;
continue;
}
// 对子,直接返回
if (numbers[i] == numbers[i + 1]) {
return false;
}
numOfInterval += numbers[i + 1] - numbers[i] - 1;
}
if (numOfZero >= numOfInterval) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
*/
//思路:map,然后保存最大最小值,条件满足max-min<5则成功;
class Solution {
public:
/*顺子满足的条件:max-min<5;
除0外其他的数字都不能重复
传入的数组放5个元素*/
bool IsContinuous( vector<int> numbers ) {
if(numbers.empty()) return 0;
int count[14]={0};//记录每个元素出现的次数;以numbers中的元素作为下标(最大K,对应13)
int len=numbers.size();
int max=-1;
int min=14;
for(int i=0;i<len;++i)
{
count[numbers[i]]++;
if(numbers[i]==0) continue;
if(count[numbers[i]]>1) return 0;
if(numbers[i]>max) max=numbers[i];
if(numbers[i]<min) min=numbers[i];
}//end for
if(max-min<5) return 1;
return 0;
}//end IsContinuous()
};
6、一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了偶数次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。
思路:捕获关键词,可以联想到位操作,进一步可用异或。如果将所有所有数字相异或,则最后的结果肯定是那两个只出现一次的数字异或的结果,所以根据异或的结果1所在的最低位,把数字分成两半,每一半里都还有只出现一次的数据和成对出现的数据这样继续对每一半相异或则可以分别求出两个只出现一次的数字
class Solution {
public:
void FindNumsAppearOnce(vector<int> data,int* num1,int* num2) {
if(data.size() < 2)
return;
int resultExclusiveOR = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++){
resultExclusiveOR ^= data[i];
}
unsigned int indexOf1 = FindFirstBitIs1(resultExclusiveOR);
*num1 = *num2 = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < data.size(); j++){
if(IsBit1(data[j], indexOf1))
*num1 ^= data[j];
else
*num2 ^= data[j];
}
}
//两个数字最低位开始从右到左不同的位是多少,算出间隔index
unsigned int FindFirstBitIs1(int num){
int indexBit = 0;
while(((num & 1) == 0) && (indexBit < 8*sizeof(int))){
num = num >> 1;
indexBit++;
}
return indexBit;
}
bool IsBit1(int num, unsigned int indexBit){
num = num >> indexBit;
return (num&1);
}
};
7、在数组中的两个数字,如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数P。并将P对1000000007取模的结果输出。 即输出P%1000000007
思路:归并排序
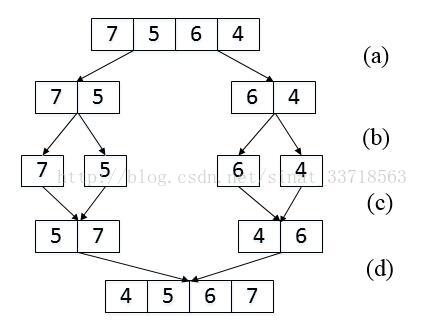
class Solution {
public:
int InversePairs(vector<int> data) {
int length=data.size();
if(length<=0)
return 0;
//vector<int> copy=new vector<int>[length];
vector<int> copy;
for(int i=0;i<length;i++)
copy.push_back(data[i]);
long long count=InversePairsCore(data,copy,0,length-1);
//delete[]copy;
return count%1000000007;
}
long long InversePairsCore(vector<int> &data,vector<int> ©,int start,int end)
{
if(start==end)
{
copy[start]=data[start];
return 0;
}
int length=(end-start)/2;
long long left=InversePairsCore(copy,data,start,start+length);
long long right=InversePairsCore(copy,data,start+length+1,end);
int i=start+length;
int j=end;
int indexcopy=end;
long long count=0;
while(i>=start&&j>=start+length+1)
{
if(data[i]>data[j])
{
copy[indexcopy--]=data[i--];
count=count+j-start-length; //count=count+j-(start+length+1)+1;
}
else
{
copy[indexcopy--]=data[j--];
}
}
for(;i>=start;i--)
copy[indexcopy--]=data[i];
for(;j>=start+length+1;j--)
copy[indexcopy--]=data[j];
return left+right+count;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector<int> array) {
int cursum=array[0];
int maxsum=array[0];
for(int i=1;i<array.size();i++){
cursum+=array[i];
if(cursum<array[i])
cursum=array[i];
if(cursum>maxsum)
maxsum=cursum;
}
return maxsum;
}
};
class Solution {
public://别人的代码就是精简,惭愧啊,继续学习。
int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if (index < 7)return index;
vector<int> res(index);
res[0] = 1;
int t2 = 0, t3 = 0, t5 = 0, i;
for (i = 1; i < index; ++i)
{
res[i] = min(res[t2] * 2, min(res[t3] * 3, res[t5] * 5));
if (res[i] == res[t2] * 2)t2++;
if (res[i] == res[t3] * 3)t3++;
if (res[i] == res[t5] * 5)t5++;
}
return res[index - 1];
}
};
class Solution {
public:
string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) {
int len = numbers.size();
if(len == 0) return "";
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), cmp);
string res;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
res += to_string(numbers[i]);
}
return res;
}
static bool cmp(int a, int b){
string A = to_string(a) + to_string(b);
string B = to_string(b) + to_string(a);
return A < B;
}
};
11、输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
思路:按外部顺序遍历,相同字母跳过,不相同的字母则交换,进入遍历内部顺序(递归),退出内部遍历时记得交换外部遍历的字母。外部遍历完成时排序成字典顺序后输出。
这种排序通常都是双遍历的。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> Permutation(string str) {
//可以用递归来做
vector<string> array;
if(str.size()==0)
return array;
Permutation(array, str, 0);
sort(array.begin(), array.end());
return array;
}
//注意array是取引用
void Permutation(vector<string> &array, string str, int begin)//遍历第begin位的所有可能性
{
if(begin==str.size()-1)
array.push_back(str);
for(int i=begin; i<=str.size()-1;i++)
{
if(i!=begin && str[i]==str[begin])//有重复字符时,跳过
continue;
swap(str[i], str[begin]);//当i==begin时,也要遍历其后面的所有字符;
//当i!=begin时,先交换,使第begin位取到不同的可能字符,再遍历后面的字符
Permutation(array, str, begin+1);//遍历其后面的所有字符;
swap(str[i], str[begin]);//为了防止重复的情况,还需要将begin处的元素重新换回来
/*举例来说“abca”,为什么使用了两次swap函数
交换时是a与b交换,遍历;
交换时是a与c交换,遍历;(使用一次swap时,是b与c交换)
交换时是a与a不交换;
*/
}
}
};
12、输入一颗二叉树的跟节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)。
思路:和减去本节点数后,若为0则添加路径到res;否则递归下去,递归过程是减去下一个节点数,再判断是否位0
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> temp;
vector<vector <int> >res;
vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {
if(root==NULL) return res;
temp.push_back(root->val);
if(expectNumber-root->val==0 && root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
res.push_back(temp);
FindPath(root->left,expectNumber-root->val);
FindPath(root->right,expectNumber-root->val);
if(!temp.empty())
{
temp.pop_back(); //记住pop出来,否则重复
}
return res;
}
};
13、输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思路:从A根节点开始判断B是不是A的字子树,若是则返回一;否则A递归到左右节点,再判B是不是A的子树。
class Solution {
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* pRootA, TreeNode* pRootB) {
if (pRootB == NULL) return true;
if (pRootA == NULL) return false;
if (pRootB->val == pRootA->val) {
return isSubtree(pRootA->left, pRootB->left)
&& isSubtree(pRootA->right, pRootB->right);
}
else
return false;
}
public:
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRootA, TreeNode* pRootB)
{
if (pRootA == NULL || pRootB == NULL) return false;
return isSubtree(pRootA, pRootB) ||
HasSubtree(pRootA->left, pRootB) ||
HasSubtree(pRootA->right, pRootB);
}
};
14、输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
思路:
1:递归反转,从尾到头更新
2:遍历,从头到尾更新
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
//递归
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
//如果链表为空或者链表中只有一个元素
if(pHead==NULL||pHead->next==NULL) return pHead;
//先反转后面的链表,走到链表的末端结点
ListNode* pReverseNode=ReverseList(pHead->next);
//再将当前节点设置为后面节点的后续节点
pHead->next->next=pHead;
pHead->next=NULL;
return pReverseNode;
}
};
//从头到尾遍历反转,前后断开
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==NULL) return NULL;//注意程序鲁棒性
ListNode* pNode=pHead;//当前指针
ListNode* pReverseHead=NULL;//新链表的头指针
ListNode* pPrev=NULL;//当前指针的前一个结点
while(pNode!=NULL){//当前结点不为空时才执行
ListNode* pNext=pNode->next;//链断开之前一定要保存断开位置后边的结点
if(pNext==NULL)//当pNext为空时,说明当前结点为尾节点
pReverseHead=pNode;
pNode->next=pPrev;//指针反转
pPrev=pNode; //指针更新
pNode=pNext;
}
return pReverseHead;
}
};




 本文围绕Java数据结构与算法展开,介绍了树的层遍历、链表环入口查找、字符流首个唯一字符查找等多个经典问题的解题思路。如树层遍历用队列,链表环入口用快慢指针推导,还涉及排序、位操作、归并排序等算法的应用。
本文围绕Java数据结构与算法展开,介绍了树的层遍历、链表环入口查找、字符流首个唯一字符查找等多个经典问题的解题思路。如树层遍历用队列,链表环入口用快慢指针推导,还涉及排序、位操作、归并排序等算法的应用。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








