在Python中集合set是基本数据类型的一种,它有可变集合(set)和不可变集合(frozenset)两种。创建集合set、集合set添加、集合删除、交集、并集、差集的操作都是非常实用的方法。
集合是可哈希的无序、可变类型,不能作为字典的键,但可以作为值使用。
一 创建集合
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
方法
1
:
set1
=
{
'a'
,
'b'
,
'c'
}
print
(
type
(set1))
# ---> <class 'set'>
方法
2
:
list1
=
[
'a'
,
'b'
,
'c'
,
'd'
]
str1
=
'python'
dict1
=
{
'name'
:
'sunwk'
,
'age'
:
1000
,}
tup1
=
(
'Google'
,
'Runoob'
,
1997
,
2000
)
print
(
'list1:'
,
set
(list1))
# --> list1: {'c', 'd', 'a', 'b'}
print
(
'str1:'
,
set
(str1))
# --> str1: {'o', 'y', 'h', 't', 'n', 'p'}
print
(
'dict1:'
,
set
(dict1))
# --> dict1: {'age', 'name'}
print
(
'tup1'
,
set
(tup1))
# --> tup1 {2000, 'Google', 1997, 'Runoob'}
实例
1
:
list1
=
[[
1
,
2
],
3
,
4
]
print
(
'list1:'
,
set
(list1))
# --> TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
'''
小结:
1、集合的创建使用set来创建或者直接使用{}括起来,和字典有些路类似,只不过结合没有键值对
2、可以把列表、字符串、字典、元组变成集合类型,总结起来就是可以把可迭代的数据类型变成结合。
3、int型是不可迭代类型,所以set(int)是不可以的。
4、set(dict)时,把字典中的键作为元素创建成结合
5、集合中每个元素必须都是不可变类型
'''
|
特殊应用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
list1
=
[
'a'
,
'b'
,
'c'
,
'a'
]
str1
=
'array'
print
(
'list1:'
,
set
(list1))
# --> list1: {'a', 'b', 'c'}
print
(
'str1:'
,
set
(str1))
# --> str1: {'a', 'r', 'y'}
'''
集合可以去除字符串、列表、字典、元组中重复的元素。
'''
|
二 集合增加元素
set.add()
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
d
=
{
1
,
2
,
'lvcm'
,
'zhangjm'
}
d.add(
"sunwk"
)
print
(
'd -->'
,d)
# d --> {'zhangjm', 'lvcm', 2, 'sunwk', 1}
|
set.update()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
f
=
{
1
,
2
,
'lvcm'
}
f.update(
'abc'
)
print
(f)
# {1, 2, 'a', 'lvcm', 'c', 'b'}
f.update([
12
,
'suwk'
])
print
(f)
# {'lvcm', 1, 2, 'suwk', 12}
|
小结:
- 使用add增加数据,会把添加的数据看成一个元素添加到原有集合中
- 使用update增加数据,会把添加的数据拆分成N个元素添加到原有集合中
三 集合删除元素
set.remove()
- 指定删除某个元素
- 无返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
g
=
{
'lvcm'
,
1
,
2
,
'suwk'
,
12
}
g.remove(
2
)
print
(g)
#{1, 12, 'suwk', 'lvcm'}
|
set.pop()
- 删除元素是随机的,无法指定删除元素
- 有返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
g
=
{
'lvcm'
,
1
,
2
,
'suwk'
,
12
}
a
=
g.pop()
print
(a)
print
(g)
|
set.clear
- 清空集合
- 无返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
g
=
{
'lvcm'
,
1
,
2
,
'suwk'
,
12
}
g.clear()
print
(g)
# set()
|
del
- 删除集合
- 无返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
g
=
{
'lvcm'
,
1
,
2
,
'suwk'
,
12
}
del
g
print
(g)
# NameError: name 'g' is not defined
|
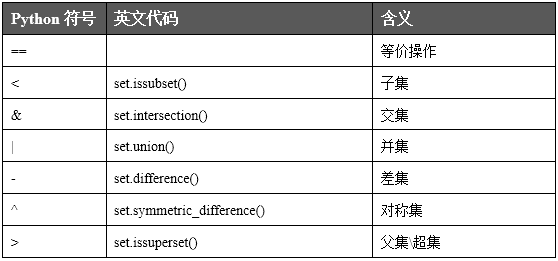
四 集合操作符
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
# 等价操作 (==)
print
(
set
(
'alex'
)
=
=
set
(
'alleexx'
))
# --> True
# 子集 set.issubset()(a<b)
print
(
set
(
'alex'
)<
set
(
'alexw'
))
# --> True
print
(
set
(
'alex'
)<
set
(
'alex'
))
# --> Flase
# 父集、超集 set.issuperset() (a>b)
e
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
f
=
{
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
print
(e.issuperset(f))
# --> True
# 交集 set.intersection() (a & b)
a
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
}
b
=
{
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
print
(a.intersection(b))
# --> {4, 5}
# 并集 set.union (c | d)
c
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
}
d
=
{
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
print
(c.union(d))
# --> {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
# 差集 set.difference() (e-f f-e)
e
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
}
f
=
{
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
print
(e.difference(f))
#(e-f) # --> {1, 2, 3} in e but not in f
print
(f.difference(e))
#(f-e) # --> {8, 6, 7} in f but not in e
#对称差集 set.symmetric_difference()(e^f)
e
=
{
1
,
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
}
f
=
{
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
,
8
}
print
(e.symmetric_difference(f))
# --> {1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8}
|







 博客介绍了Python中集合set的相关操作。集合有可变和不可变两种类型,是可哈希的无序、可变类型。详细讲解了集合的创建,增加元素的add()和update()方法,删除元素的remove()、pop()、clear和del操作,以及集合操作符等实用内容。
博客介绍了Python中集合set的相关操作。集合有可变和不可变两种类型,是可哈希的无序、可变类型。详细讲解了集合的创建,增加元素的add()和update()方法,删除元素的remove()、pop()、clear和del操作,以及集合操作符等实用内容。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








