我这段时间因为字符串太差而被关了起来了(昨晚打cf不会处理字符串现场找大佬模板瞎搞,差点就凉了),所以决定好好补一下字符串的知识QAQ,暂时先学习kmp算法吧~
题目链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3375
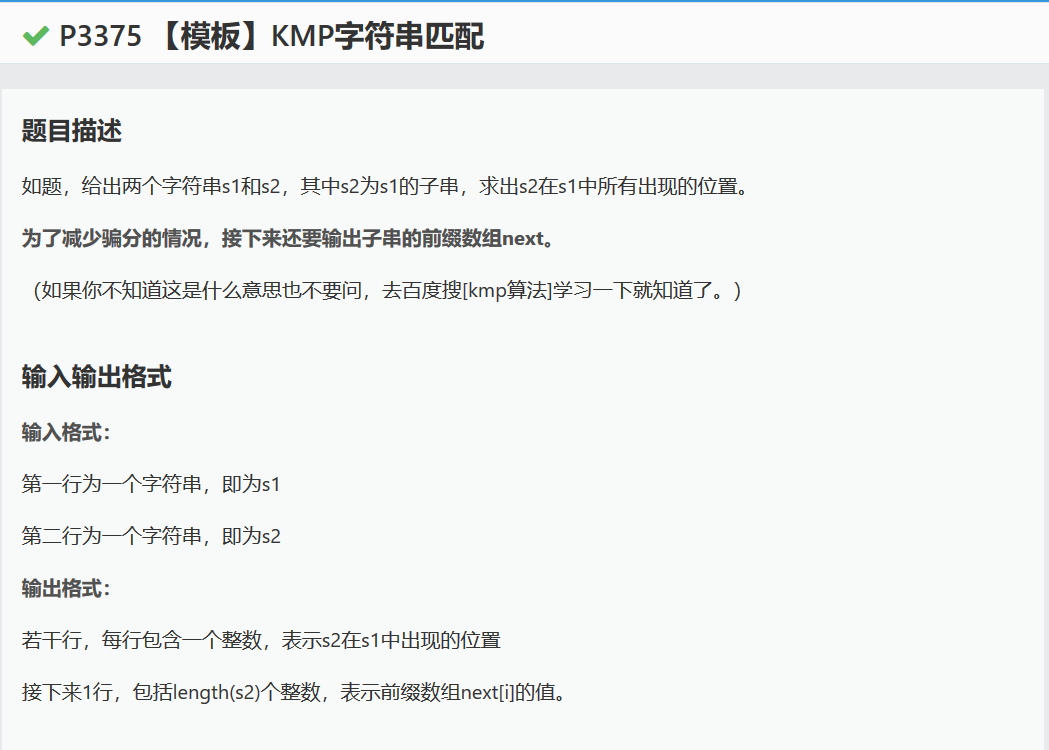
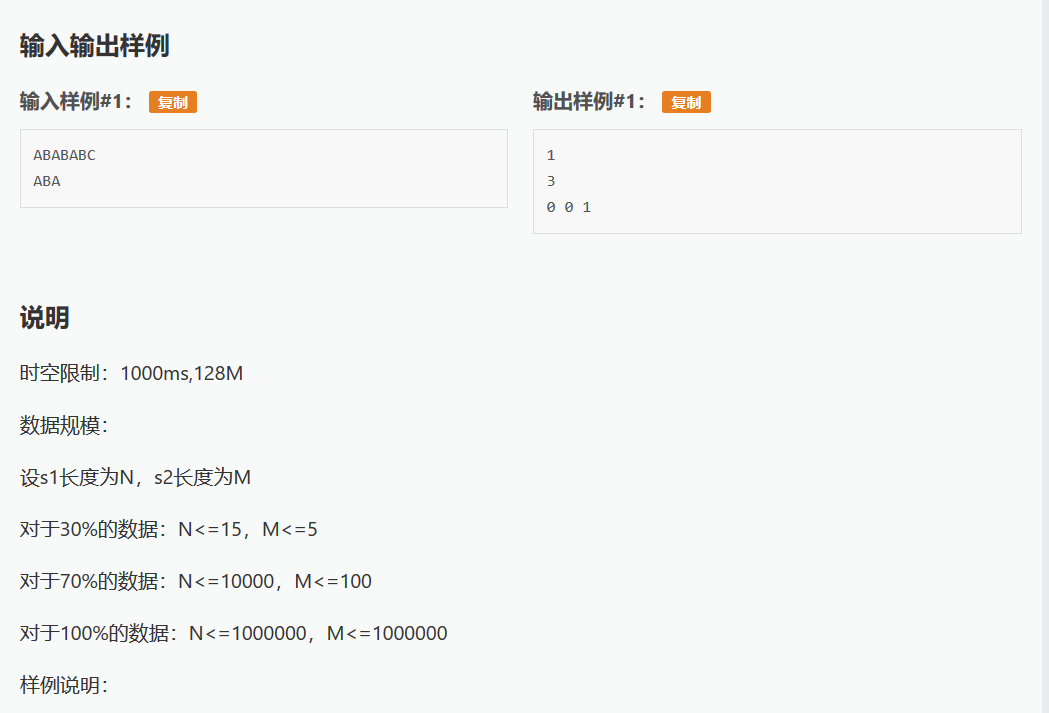
题目:
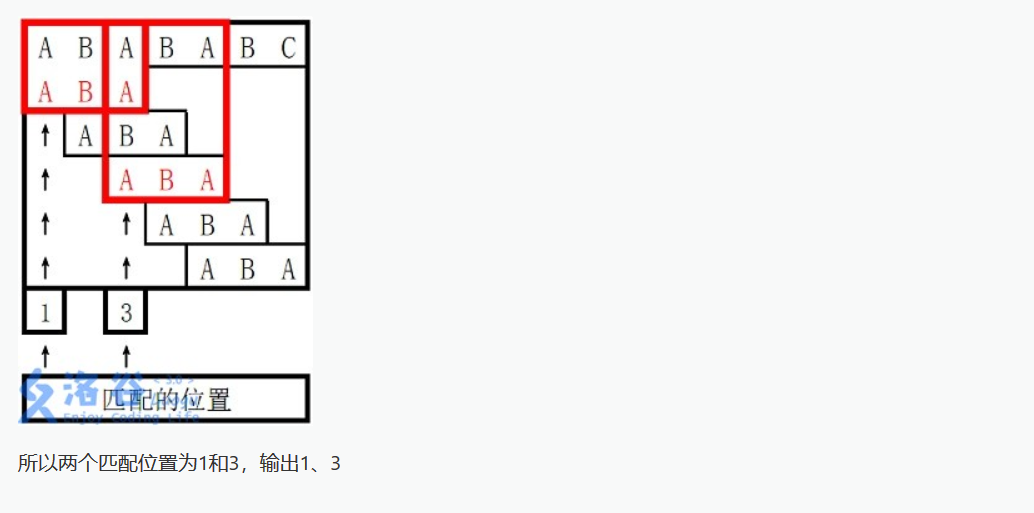
思路:本题是kmp模板题,不会kmp的看官可以看本题在洛谷的题解,题解区有大量的讲解,我顺便在这里推荐一篇大佬的文章,帮助大家理解kmp算法,http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/05/Knuth%E2%80%93Morris%E2%80%93Pratt_algorithm.html。
代码实现如下:
1 #include <set> 2 #include <map> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <stack> 5 #include <cmath> 6 #include <bitset> 7 #include <cstdio> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <cstdlib> 11 #include <cstring> 12 #include <iostream> 13 #include <algorithm> 14 using namespace std; 15 16 typedef long long ll; 17 typedef pair<ll, ll> pll; 18 typedef pair<ll, int> pli; 19 typedef pair<int, ll> pil;; 20 typedef pair<int, int> pii; 21 typedef unsigned long long ull; 22 23 #define lson i<<1 24 #define rson i<<1|1 25 #define bug printf("*********\n"); 26 #define FIN freopen("D://code//in.txt", "r", stdin); 27 #define debug(x) cout<<"["<<x<<"]" <<endl; 28 #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0); 29 30 const double eps = 1e-8; 31 const int mod = 10007; 32 const int maxn = 1e6 + 7; 33 const double pi = acos(-1); 34 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 35 const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; 36 37 int lens1, lens2; 38 string s1, s2; 39 int nex[maxn]; 40 41 void get_next() { 42 nex[0] = -1; 43 for(int i = 0, k = -1; i < lens2; ) { 44 if(k == -1 || s2[i] == s2[k]) { 45 ++k;++i; 46 nex[i] = k; 47 } else k = nex[k]; 48 } 49 } 50 51 void kmp() { 52 get_next(); 53 int i = 0, j = 0; 54 while(i < lens1 && j < lens2) { 55 if(j == -1 || s1[i] == s2[j]) { 56 i++,j++; 57 if(j == lens2) { 58 printf("%d\n", i - j + 1); 59 j = nex[j]; 60 } 61 } else j = nex[j]; 62 } 63 } 64 65 int main() { 66 //FIN; 67 cin >>s1 >>s2; 68 lens1 = s1.size(), lens2 = s2.size(); 69 kmp(); 70 for(int i = 1; i <= lens2; i++) { 71 printf("%d%c", nex[i], i == lens2 ? '\n' : ' '); 72 } 73 return 0; 74 }




 本文详细介绍了KMP算法的基本原理及其应用,并通过一道洛谷平台的编程题进行实战演练,帮助读者掌握KMP算法的核心思想及其实现细节。
本文详细介绍了KMP算法的基本原理及其应用,并通过一道洛谷平台的编程题进行实战演练,帮助读者掌握KMP算法的核心思想及其实现细节。
















 977
977

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








