定义堆:堆是一棵完全二叉树,完全二叉树是指树的每一层节点都被填满,除了最后一层,最后一层
节点也要要求从最左边开始连续的排。
通常用一个数组存储堆:如下图所示
可见用数组存储堆就是按照层次遍历的顺序将堆中各个元素存入数组,下面计算堆中元素在数组中的指标位置。
假设堆中元素A位于堆的第 i 层 第 j 列,堆的根节点几位第 0 层,则可计算 A 在数组的位置(从1开始)为
t_p=\sum_{k=0}^{i-1}2^k+j = 2^i+j-1.
A的子女节点位于第 i+1 层第 2( j-1 )+(0,1) 列,因此数组指标
t_c=2^{i+1}+2( j-1 )+(0,1)
观察易知: t_c/2 = t_p+ (0,1/2);
t_c/2取整就位 t_p (父节点)
t_p*2 = t_L(左子女), t_p*2+1 = t_R(右子女)
最大堆定义:堆中任何一个节点的值不小于它的子女节点的值
堆排序的第一步是建堆。
首先给出算法的第一步一个节点沿路径下沉:
(1)对于任何选择的节点,比较其与左右子女节点的大小,选择最大的一个与父亲节点交换,在同样考虑
交换后的下沉节点,直到节点下沉到叶子节点或者节点不在下沉为止。
这一步使得被选节点沿着下沉路径处于合适的位置而不影响其他路径。
现在假设节点的左右子树均为最大堆,则左右子树的任何一条路径自上而下是递减的,当所选节点沿着适当
路径下沉到合适的位置时,容易知道新的以所选节点为根的子树成为最大堆。
(2)从树的最底部的第一个非叶子节点开始按照上述第一步将所有的节点下沉。
由于叶子节点都为最大堆,从而由归纳法知道,当根节点下沉后,整个堆就成为最大堆,建堆过程完成。
(3)每次从堆的根节点取出元素,将最后一个节点放入根部,进行一次下沉操作。
经过n次的这种操作完成整个排序,每次下沉需要logn的工作量,则总的算法复杂度是:O(nlogn).
堆排序算法的C++实现:
一、STL实现
利用C++的STL库向量来管理堆的存储,注意这里的模板类T默认具有比较大小的功能
vectorheap.h 文件
//此程序为实现堆排序算法,用到STL中的vector类
//注意当vectorheap被实例化成对象时并不是一个堆,必须在调用内部成员函数buildMaxHeap()后成为最大堆
//2011/3/24 肖成
#ifndef _VECTOR_HEAP
#define _VECTOR_HEAP
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class vectorheap
{
private:
//用向量存储堆中的元素
vector<T> vec;
public:
// 构造函数,这里与heapvec中不同的是首先不建堆,依据需要调用buildMaxHeap()函数建堆
vectorheap(vector<T> vec);
vectorheap(T*first, T*last);
//取子女节点下标
int getLeft(unsigned i);
int getRight(unsigned i);
//依据子堆建立新堆
void maxHeapIfy(int i);
//建堆
void buildMaxHeap();
//删除根节点
void deleteRoot();
//堆排序
vector<T> sortHeap();
//获取父节点下标
int getParent(int i);
//获取数据域
vector<T> getData();
};
template<class T>
vectorheap<T>::vectorheap(vector<T> vec)
{
this->vec=vec;
}
template<class T>
vectorheap<T>::vectorheap(T*first, T*last)
{
vec=vector<T>(first,last);
}
template<class T>
int vectorheap<T>::getLeft(unsigned i)
{
if(2*i>=vec.size())
return -1;
else
return 2*i;
}
template<class T>
int vectorheap<T>::getRight(unsigned i)
{
if(2*i+1>=vec.size())
return -1;
else
return 2*i+1;
}
template<class T>
void vectorheap<T>::maxHeapIfy(int i)
{
int left = getLeft(i);
if(left==-1)return;
int right = getRight(i);
int maxIndex;
if(right==-1)
maxIndex=left;
else
maxIndex=vec.at(left)>vec.at(right)?left:right;
if(vec.at(maxIndex)>vec.at(i))
{
T temp=vec.at(i);
vec[i]=vec.at(maxIndex);
vec[maxIndex]=temp;
maxHeapIfy(maxIndex);
}
}
template<class T>
void vectorheap<T>::buildMaxHeap()
{
for(int i=vec.size()/2;i>=0;i--)
maxHeapIfy(i);
}
template<class T>
void vectorheap<T>::deleteRoot()
{
vec[0]=vec[vec.size()-1];
vec.pop_back();
maxHeapIfy(0);
}
template<class T>
vector<T> vectorheap<T>::sortHeap()
{
buildMaxHeap();
vector<T> result;
while(vec.size()!=0)
{
result.push_back(vec.front());
deleteRoot();
}
return result;
}
template<class T>
int vectorheap<T>::getParent(int i)
{
if(i!=0)
return i/2;
else
return -1;
}
template<class T>
vector<T> vectorheap<T>::getData()
{
return vec;
}
#endif二、自定义数组存储实现
自己管理数组大小比较麻烦,因此代码也会比较复杂
heapvec.h 文件
//此程序为实现堆排序算法,内部内存动态管理机制自己实现,类似于STL中的vector类
//注意当heapvec被实例化成非空对象即是一个堆
//2011/3/24 肖成
#ifndef _HEAP_DEFINE
#define _HEAP_DEFINE
#include <assert.h>
template<class T>
class heap
{
private:
T* data;
int realSize;
int size;
void setValue(int index, T value);
public:
//基本的构造函数
heap();
heap(T *, int);
heap(heap<T>& h);
//heap(int);
//返回堆的大小
int getSize();
//取出向量
//vector<int> getVector();
//返回堆的根节点值
T getRoot();
//删除根节点
void deleteRoot();
//清空
void clear();
//设置根值
void setRoot(T value);
//设置全部元素
void setData(T* vec, int size);
//截断
void cutSize(int size);
//取值(根据下标)
T getValue(int index);
//根据子女节点取父节点下标
int getParent(int soon);
//获取子节点下标
int getLeft(int parent);
int getRight(int parent);
//假设指标i的子树均是最大堆,调整使得以i为根的子树变成最大堆
void maxHeapIfy(int i);
//建立最大堆
void buildMaxHeap();
//堆排序
T* sortHeap();
//堆中加入元素
void insertValue(T value);
};
template<class T>
heap<T>::heap()
{
data = new T[5];
size=5;
realSize=0;
}
template<class T>
heap<T>::heap(T *dat, int size)
{
realSize=size;
this->size=(realSize/5+1)*5;
this->data = new T[size];
for(int i=0;i<realSize; i++)
*(this->data+i)=*(dat+i);
//立马建立最大堆
buildMaxHeap();
}
template<class T>
heap<T>::heap(heap<T>& hp)
{
this->size=hp.size;
this->realSize=hp.realSize;
this->data=new T[size];
for(int i=0;i<realSize; i++)
*(this->data+i)=*(hp.data+i);
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::clear()
{
if(realSize!=0)
{
size=5;
realSize=0;
delete []data;
data = new T[5];
}
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::cutSize(int size)
{
this->realSize=size;
this->size=(realSize/5+1)*5;
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::deleteRoot()
{
data[0]=data[realSize-1];
realSize = realSize-1;
this->size=(realSize/5+1)*5;
maxHeapIfy(0);
}
template<class T>
int heap<T>::getLeft(int i)
{
if(2*i>=realSize)
return -1;
else
return 2*i;
}
template<class T>
int heap<T>::getRight(int i)
{
if(2*i+1>=realSize)
return -1;
else
return 2*i+1;
}
template<class T>
int heap<T>::getParent(int i)
{
if(i!=0)
return i/2;
else
return -1;
}
template<class T>
T heap<T>::getRoot()
{
assert(realSize!=0);
return data[0];
}
template<class T>
int heap<T>::getSize()
{
return realSize;
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::insertValue(T value)
{
if(size<=realSize+1)
{
size=size+5;
realSize=realSize+1;
T *newData = new T[size];
for(int i=0;i<realSize-1;i++)
*(newData+i)=*(data+i);
newData[realSize-1]=value;
delete []data;
data=newData;
}
else
{
realSize=realSize+1;
data[realSize-1]=value;
}
int tempIndex=realSize-1;
for(int i=tempIndex/2; i>=0; i=i/2)
{
if(value>data[i])
{
data[tempIndex]=data[i];
data[i]=value;
tempIndex=i;
}
else
break;
}
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::setRoot(T value)
{
assert(realSize!=0);
assert(value>=data[0]);
data[0]=value;
}
template<class T>
T heap<T>::getValue(int index)
{
assert(index>=0 && index<realSize);
return data[index];
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::setValue(int index, T value)
{
//注意这个函数不保持最大堆性质,只在内部使用
assert(index>=0 && index<realSize);
data[index]=value;
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::maxHeapIfy(int i)
{
int left = getLeft(i);
if(left==-1)return;
int right = getRight(i);
int maxIndex;
if(right==-1)
maxIndex=left;
else
maxIndex=(getValue(left)>getValue(right)?left:right);
if(getValue(maxIndex)>getValue(i))
{
T value=getValue(i);
setValue(i,getValue(maxIndex));
setValue(maxIndex, value);
maxHeapIfy(maxIndex);
}
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::buildMaxHeap()
{
for(int i=realSize/2;i>=0;i--)
maxHeapIfy(i);
}
template<class T>
T* heap<T>::sortHeap()
{
heap<T> heapAnother(*this);
T *result = new T[heapAnother.realSize];
int i=0;
while(heapAnother.getSize()!=0)
{
result[i]=heapAnother.getRoot();
heapAnother.deleteRoot();
i++;
}
return result;
}
template<class T>
void heap<T>::setData(T* dat, int s)
{
realSize=s;
this->size=(realSize/5+1)*5;
this->data = new T[size];
for(int i=0;i<realSize; i++)
*(this->data+i)=*(dat+i);
buildMaxHeap();
}
#endif三、下面给出测试性例子
main.cpp 文件
// main.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include <iostream>
#include "heapvec.h"
#include "vectorheap.h"
using namespace std;
//定义向量的输出函数
template<class T>
void outPut(vector<T> vec)
{
for(unsigned i=0;i<vec.size();i++)
cout<<vec[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
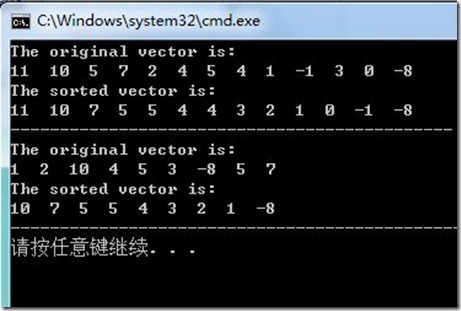
int main()
{
//等待排序数组
int a[]={1,2,10,4,5,3,-8,5,7};
int size=9;
//using the class heap in the file heapvec.h
//建堆后继续插入元素
heap<int> hp(a,9);
hp.insertValue(-1);
hp.insertValue(4);
hp.insertValue(0);
hp.insertValue(11);
//hp.cutSize(7);
//hp.setData(a,9);
cout<<"The original vector is: "<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<hp.getSize();i++)
{
cout<<hp.getValue(i)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"The sorted vector is: "<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<hp.getSize();i++)
cout<<*(hp.sortHeap()+i)<<" ";
cout<<endl;
cout<<"---------------------------------------------"<<endl;
//using STL vector class in the file vectorheap.h
vectorheap<int> vec(a,a+9);
cout<<"The original vector is: "<<endl;
outPut(vec.getData());
vector<int> result=vec.sortHeap();
cout<<"The sorted vector is: "<<endl;
outPut(result);
cout<<"----------------------------------------------"<<endl;
return 0;
}




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








