一、实验目的
1.熟悉体系结构的风格的概念
2.理解和应用管道过滤器型的风格。
3、理解解释器的原理
4、理解编译器模型
二、实验环境
硬件:
软件:Python或任何一种自己喜欢的语言
三、实验内容
1、实现“四则运算”的简易翻译器。
结果要求:
1)实现加减乘除四则运算,允许同时又多个操作数,如:2+3*5-6 结果是11
2)被操作数为整数,整数可以有多位
3)处理空格
4)输入错误显示错误提示,并返回命令状态“CALC”
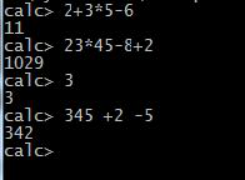
图1 实验结果示例
加强练习:
1、有能力的同学,可以尝试实现赋值语句,例如x=2+3*5-6,返回x=11。(注意:要实现解释器的功能,而不是只是显示)
2、尝试实现自增和自减符号,例如x++
2、采用管道-过滤器(Pipes and Filters)风格实现解释器
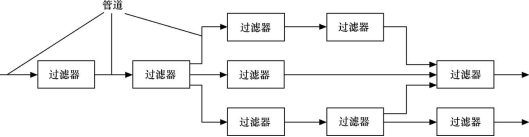
图2 管道-过滤器风格
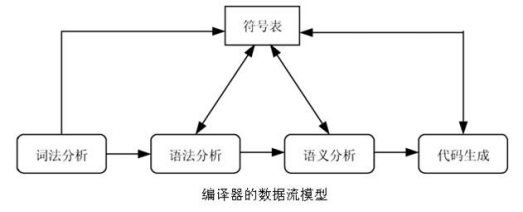
图 3 编译器模型示意图
本实验,实现的是词法分析和语法分析两个部分。
四、实验步骤:
源代码:
#include<stack>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
char str[1007];
stack<int> num;
stack<int> op;
int l;
bool isSpace(char k){
if(k==' ') return 1;
return 0;
}
bool isNum(char k){
if(k<='9' && k>='0') return true;
return false;
}
bool isOpEmpty(){
if(op.empty()) return 1;
if(op.top()==1) return 1;
return 0;
}
int getInt(int &x){
int t = str[x] - 48;
while(x+1<l && isNum(str[x+1])){
x++;
t = t * 10 + str[x] - 48;
}
return t;
}
void c1(int p){
int b = num.top();
num.pop();
int a = num.top();
num.pop();
if(p==2) num.push(a+b);
if(p==3) num.push(a-b);
if(p==4) num.push(a*b);
if(p==5) num.push(a/b);
}
int getOp(char k){
if(k=='(') return 1;
if(k=='+') return 2;
if(k=='-') return 3;
if(k=='*') return 4;
if(k=='/') return 5;
if(k==')') return 6;
return 0;
}
int isOp(char k){
if(getOp(k)) return 1;
return 0;
}
int calc(int &ans){
ans = 0;
l = strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
if(isSpace(str[i]))
continue;
if(isNum(str[i])){
num.push(getInt(i));
} else if(isOp(str[i])){
if(isOpEmpty()){
op.push(getOp(str[i]));
} else{
int p = getOp(str[i]);
int tp = op.top();
if(p==1)
op.push(1);
if(p==2 || p==3){
if(num.size()<2) return 1;
c1(tp);
op.pop();
op.push(p);
}
if(p==4 || p==5){
if(tp==4 || tp==5){
if(num.size()<2) return 1;
c1(tp);
op.pop();
}
op.push(p);
}
if(p==6){
while(tp!=1){
if(num.size()<2) return 1;
c1(tp);
op.pop();
tp = op.top();
}
op.pop();
}
}
} else{
return 1;
}
}
while(!op.empty()){
int tp = op.top();
op.pop();
if(num.size()<2) return 1;
c1(tp);
}
ans = num.top();
return 0;
}
void init()
{
while(!num.empty()) num.pop();
while(!op.empty()) op.pop();
}
int main()
{
int ans,val;
while(1){
init();
cout<<"calc>";
cin.getline(str,1000);
val = calc(ans);
if(val==0) cout<<ans<<endl;
else cout<<"Error!"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行效果:
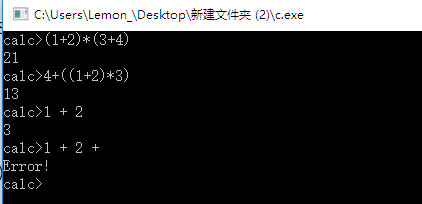























 3902
3902

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








