在使用Socket/TCP来传输文件,弄起来不仅会有些复杂,而且较经典的"粘包"问题有时候会让人火冒七丈。如果你不喜欢用Socket来传文件,不妨试试WCF,WCF的流模式传输还是相当强大和相当实用的。
因为开启流模式是基于绑定的,所以,它会影响到整个终结点的操作协定。如果你不记得或者说不喜欢背书,不想去记住哪些绑定支持流模式,可以通过以下方法:
因为开启流模式,主要是设置一个叫TransferMode的属性,所以,你看看哪些Binding的派生类有这个属性就可以了。
TransferMode其实是一个举枚,看看它的几个有效值:
Buffered:缓冲模式,说白了就是在内存中缓冲,一次调用就把整个消息读/写完,也就是我们最常用的方式,就是普通的操作协定的调用方式;
StreamedRequest:只是在请求的时候使用流,说简单一点就是在传入方法的参数使用流,如 int MyMethod(System.IO.Stream stream);
StreamedResponse:就是操作协定方法返回一个流,如 Stream MyMethod(string file_name);
一般而言,如果使用流作为传入参数,最好不要使用多个参数,如这样:
bool TransferFile(Stream stream, string name);
上面的方法就有了两个in参数了,最好别这样,为什么?有空的话,自己试试就知道了。那如果要传入更多的数据,怎么办?呵呵,还记得消息协定吗?
好的,下面我们来弄一个上传MP3文件的实例。实例主要的工作是从客户端上传一个文件到服务器。
老规矩,一般做这种应用程序,应该先做服务器端。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using System.IO;
namespace WCFServerTemplate1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 服务器基址
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:1378/services");
// 声明服务器主机
using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(MyService), baseAddress))
{
// 添加绑定和终结点
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IService), binding, "/test");
// 添加服务描述
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(new ServiceMetadataBehavior { HttpGetEnabled = true });
try
{
// 打开服务
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("服务已启动。");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream("rec.mp3", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
streamInput.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到rec.map3。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using System.IO;
namespace WCFServerTemplate1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 服务器基址
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:1378/services");
// 声明服务器主机
using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(MyService), baseAddress))
{
// 添加绑定和终结点
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IService), binding, "/test");
// 添加服务描述
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(new ServiceMetadataBehavior { HttpGetEnabled = true });
try
{
// 打开服务
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("服务已启动。");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream("rec.mp3", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
streamInput.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到rec.map3。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
}
从例子我们看到,操作方法是这样定义的:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
因为它的返回值是Bool类型,不是流,而只是传入的参数是流,因为在配置绑定时,应用使用StreamedRequest。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
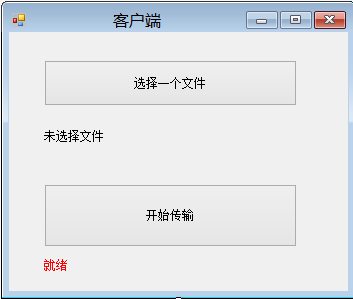
现在,我们做客户端,因为要选择文件上传,所以使用Windows Forms项目类型。
在窗口上拖两个按钮,一个用来选择文件,另一个用于启动文件上传,另外两个Label就是用来显示一些文本。
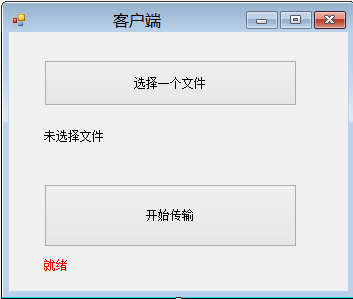
而窗体的实现代码部分如下:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
namespace wformClient
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnSelectFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog();
dlg.Filter = "MP3音频文件|*.mp3";
if (DialogResult.OK.Equals(dlg.ShowDialog()))
{
this.lbSelectedFilename.Text = dlg.FileName;
this.lbMessage.Text = "准备就绪。";
}
}
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
bool res = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (res == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
namespace wformClient
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnSelectFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog();
dlg.Filter = "MP3音频文件|*.mp3";
if (DialogResult.OK.Equals(dlg.ShowDialog()))
{
this.lbSelectedFilename.Text = dlg.FileName;
this.lbMessage.Text = "准备就绪。";
}
}
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
bool res = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (res == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
}
}
}
记住,千万别忘了引用服务!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
现在可以运行了。
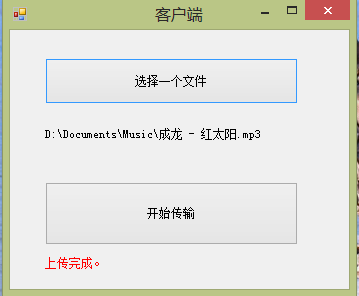

不知道大家注意到没有?在服务器端代码中,我们设置了绑定的MaxReceivedMessageSize为500M,这一般是在消息模式下,为了安全(防止恶意攻击)而设置的限制,那么,如果使用了流模式,这个值还用不用设置。想验证也很简单,把这行代码注释掉,再运行试试。
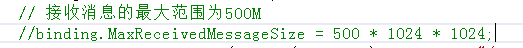
运行程序,结发现,是不成功的,你看看我下面的截图,只传了40多K,还远着呢。
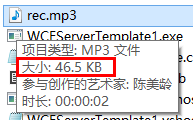
因此,MaxReceivedMessageSize还是要设置的,不然,它的默认值太小了,传不了大文件。
现在又希望上面的例子多一个功能,文件上传后,依然按客户端原文件命名,而不是rec.mp3,这就意味着操作方法要传两个参数,前面我提了一下,不要忘了消息协定,而这个我们可以通过消息协定来完成。
因此,服务器端代码要改一改了,首先,定义一个消息协定。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
[MessageContract]
public class TransferFileMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string File_Name; //文件名
[MessageBodyMember]
public Stream File_Stream; //文件流
}
[MessageContract]
public class TransferFileMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string File_Name; //文件名
[MessageBodyMember]
public Stream File_Stream; //文件流
}
接着操作方法也要改动。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
return false;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
return false;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
在测试服务器端运行成功后,要记得更新客户端的引用。
可是,遗憾的是,服务没有正常启动。为什么呢?想一想,如果光看错误消息,你可能不太明白。我给你20秒的时间想一想,为什么上面的代码不能正常运行。
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
好了,其实,问题就出在操作协定的定义上:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
我们前面说过,什么叫双工,有来有往,是吧?对啊,上面的方法是有传入参数,也有返回值,有来有去啊,是双工啊,为啥不行了呢?
哈哈,问题就在于我们使用了消息协定,在这种前提下,我们的方法就不能随便定义了,使用消息协定的方法,如果:
a、消息协定作为传入参数,则只能有一个参数,以下定义是错误的:
void Reconcile(BankingTransaction bt1, BankingTransaction bt2);
b、除非你返回值为void,如不是,那你必须返回一个消息协定,bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)我们这个定义明显不符合要求。
那如何解决呢?我们要再定义一个用于返回的消息协定。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
[MessageContract]
public class ResultMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string ErrorMessage;
[MessageBodyMember]
public bool IsSuccessed;
}
[MessageContract]
public class ResultMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string ErrorMessage;
[MessageBodyMember]
public bool IsSuccessed;
}
然后把上面的操作方法也改一下。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
public ResultMessage UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
ResultMessage rMsg = new ResultMessage();
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
rMsg.ErrorMessage = "传入的参数无效。";
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
return rMsg;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
rMsg.IsSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
rMsg.ErrorMessage = ex.Message;
}
return rMsg;
}
public ResultMessage UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
ResultMessage rMsg = new ResultMessage();
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
rMsg.ErrorMessage = "传入的参数无效。";
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
return rMsg;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
rMsg.IsSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
rMsg.ErrorMessage = ex.Message;
}
return rMsg;
}
现在你试试能不能正常运行?好了,客户端记得更新引用,而且,客户端的代码也要修改。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
var response = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(Path.GetFileName(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text), fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (response.IsSuccessed == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
else
this.lbMessage.Text="错误信息:" + response.ErrorMessage;
}
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
var response = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(Path.GetFileName(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text), fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (response.IsSuccessed == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
else
this.lbMessage.Text="错误信息:" + response.ErrorMessage;
}
现在再来测测吧。
在使用Socket/TCP来传输文件,弄起来不仅会有些复杂,而且较经典的"粘包"问题有时候会让人火冒七丈。如果你不喜欢用Socket来传文件,不妨试试WCF,WCF的流模式传输还是相当强大和相当实用的。
因为开启流模式是基于绑定的,所以,它会影响到整个终结点的操作协定。如果你不记得或者说不喜欢背书,不想去记住哪些绑定支持流模式,可以通过以下方法:
因为开启流模式,主要是设置一个叫TransferMode的属性,所以,你看看哪些Binding的派生类有这个属性就可以了。
TransferMode其实是一个举枚,看看它的几个有效值:
-
Buffered:缓冲模式,说白了就是在内存中缓冲,一次调用就把整个消息读/写完,也就是我们最常用的方式,就是普通的操作协定的调用方式;
-
StreamedRequest:只是在请求的时候使用流,说简单一点就是在传入方法的参数使用流,如 int MyMethod(System.IO.Stream stream);
-
StreamedResponse:就是操作协定方法返回一个流,如 Stream MyMethod(string file_name);
一般而言,如果使用流作为传入参数,最好不要使用多个参数,如这样:
bool TransferFile(Stream stream, string name);
上面的方法就有了两个in参数了,最好别这样,为什么?有空的话,自己试试就知道了。那如果要传入更多的数据,怎么办?呵呵,还记得消息协定吗?
好的,下面我们来弄一个上传MP3文件的实例。实例主要的工作是从客户端上传一个文件到服务器。
老规矩,一般做这种应用程序,应该先做服务器端。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
using System;
-
using System.Collections.Generic;
-
using System.Linq;
-
using System.Text;
-
using System.Threading.Tasks;
-
-
using System.Runtime;
-
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
-
using System.ServiceModel;
-
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
-
-
using System.IO;
-
-
namespace WCFServerTemplate1
-
{
-
class Program
-
{
-
static void Main(string[] args)
-
{
-
// 服务器基址
-
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:1378/services");
-
// 声明服务器主机
-
using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(MyService), baseAddress))
-
{
-
// 添加绑定和终结点
-
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
-
// 启用流模式
-
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
-
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
-
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
-
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
-
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IService), binding, "/test");
-
// 添加服务描述
-
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(new ServiceMetadataBehavior { HttpGetEnabled = true });
-
try
-
{
-
// 打开服务
-
host.Open();
-
Console.WriteLine("服务已启动。");
-
}
-
catch (Exception ex)
-
{
-
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
-
}
-
Console.ReadKey();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
-
public interface IService
-
{
-
[OperationContract]
-
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput);
-
}
-
-
public class MyService : IService
-
{
-
-
public bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
-
{
-
bool isSuccessed = false;
-
try
-
{
-
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream("rec.mp3", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
-
{
-
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
-
streamInput.CopyTo(outputStream);
-
outputStream.Flush();
-
isSuccessed = true;
-
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到rec.map3。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
-
}
-
}
-
catch
-
{
-
isSuccessed = false;
-
}
-
return isSuccessed;
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Runtime;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Description;
using System.IO;
namespace WCFServerTemplate1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 服务器基址
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("http://localhost:1378/services");
// 声明服务器主机
using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(MyService), baseAddress))
{
// 添加绑定和终结点
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IService), binding, "/test");
// 添加服务描述
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(new ServiceMetadataBehavior { HttpGetEnabled = true });
try
{
// 打开服务
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("服务已启动。");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream("rec.mp3", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
streamInput.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到rec.map3。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
}
从例子我们看到,操作方法是这样定义的:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
bool UpLoadFile(System.IO.Stream streamInput)
因为它的返回值是Bool类型,不是流,而只是传入的参数是流,因为在配置绑定时,应用使用StreamedRequest。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
-
// 启用流模式
-
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
-
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
-
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
-
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
BasicHttpBinding binding = new BasicHttpBinding();
// 启用流模式
binding.TransferMode = TransferMode.StreamedRequest;
binding.MaxBufferSize = 1024;
// 接收消息的最大范围为500M
binding.MaxReceivedMessageSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024;
现在,我们做客户端,因为要选择文件上传,所以使用Windows Forms项目类型。
在窗口上拖两个按钮,一个用来选择文件,另一个用于启动文件上传,另外两个Label就是用来显示一些文本。
而窗体的实现代码部分如下:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
using System;
-
using System.Collections.Generic;
-
using System.ComponentModel;
-
using System.Data;
-
using System.Drawing;
-
using System.Linq;
-
using System.Text;
-
using System.Threading.Tasks;
-
using System.Windows.Forms;
-
using System.IO;
-
-
namespace wformClient
-
{
-
public partial class Form1 : Form
-
{
-
public Form1()
-
{
-
InitializeComponent();
-
}
-
-
private void btnSelectFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
-
{
-
OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog();
-
dlg.Filter = "MP3音频文件|*.mp3";
-
if (DialogResult.OK.Equals(dlg.ShowDialog()))
-
{
-
this.lbSelectedFilename.Text = dlg.FileName;
-
this.lbMessage.Text = "准备就绪。";
-
}
-
}
-
-
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
-
{
-
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
-
{
-
return;
-
}
-
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
-
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
-
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
-
bool res = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(fs);
-
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
-
if (res == true)
-
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
-
}
-
}
-
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.IO;
namespace wformClient
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void btnSelectFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog();
dlg.Filter = "MP3音频文件|*.mp3";
if (DialogResult.OK.Equals(dlg.ShowDialog()))
{
this.lbSelectedFilename.Text = dlg.FileName;
this.lbMessage.Text = "准备就绪。";
}
}
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
bool res = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (res == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
}
}
}
记住,千万别忘了引用服务!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
现在可以运行了。
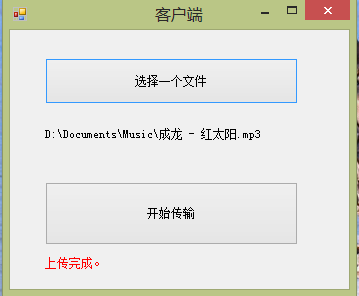

不知道大家注意到没有?在服务器端代码中,我们设置了绑定的MaxReceivedMessageSize为500M,这一般是在消息模式下,为了安全(防止恶意攻击)而设置的限制,那么,如果使用了流模式,这个值还用不用设置。想验证也很简单,把这行代码注释掉,再运行试试。
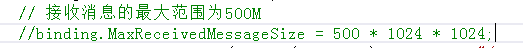
运行程序,结发现,是不成功的,你看看我下面的截图,只传了40多K,还远着呢。
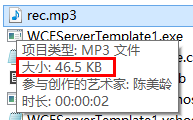
因此,MaxReceivedMessageSize还是要设置的,不然,它的默认值太小了,传不了大文件。
现在又希望上面的例子多一个功能,文件上传后,依然按客户端原文件命名,而不是rec.mp3,这就意味着操作方法要传两个参数,前面我提了一下,不要忘了消息协定,而这个我们可以通过消息协定来完成。
因此,服务器端代码要改一改了,首先,定义一个消息协定。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
[MessageContract]
-
public class TransferFileMessage
-
{
-
[MessageHeader]
-
public string File_Name; //文件名
-
[MessageBodyMember]
-
public Stream File_Stream; //文件流
-
}
[MessageContract]
public class TransferFileMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string File_Name; //文件名
[MessageBodyMember]
public Stream File_Stream; //文件流
}
接着操作方法也要改动。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
-
public interface IService
-
{
-
[OperationContract]
-
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
-
}
-
-
public class MyService : IService
-
{
-
-
public bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
-
{
-
bool isSuccessed = false;
-
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
-
{
-
return false;
-
}
-
try
-
{
-
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
-
{
-
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
-
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
-
outputStream.Flush();
-
isSuccessed = true;
-
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
-
}
-
}
-
catch
-
{
-
isSuccessed = false;
-
}
-
return isSuccessed;
-
}
-
}
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "MyNamespace")]
public interface IService
{
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
}
public class MyService : IService
{
public bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
bool isSuccessed = false;
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
return false;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
isSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。",DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch
{
isSuccessed = false;
}
return isSuccessed;
}
}
在测试服务器端运行成功后,要记得更新客户端的引用。
可是,遗憾的是,服务没有正常启动。为什么呢?想一想,如果光看错误消息,你可能不太明白。我给你20秒的时间想一想,为什么上面的代码不能正常运行。
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
好了,其实,问题就出在操作协定的定义上:
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
[OperationContract]
-
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
[OperationContract]
bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg);
我们前面说过,什么叫双工,有来有往,是吧?对啊,上面的方法是有传入参数,也有返回值,有来有去啊,是双工啊,为啥不行了呢?
哈哈,问题就在于我们使用了消息协定,在这种前提下,我们的方法就不能随便定义了,使用消息协定的方法,如果:
a、消息协定作为传入参数,则只能有一个参数,以下定义是错误的:
void Reconcile(BankingTransaction bt1, BankingTransaction bt2);
b、除非你返回值为void,如不是,那你必须返回一个消息协定,bool UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)我们这个定义明显不符合要求。
那如何解决呢?我们要再定义一个用于返回的消息协定。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
[MessageContract]
-
public class ResultMessage
-
{
-
[MessageHeader]
-
public string ErrorMessage;
-
[MessageBodyMember]
-
public bool IsSuccessed;
-
}
[MessageContract]
public class ResultMessage
{
[MessageHeader]
public string ErrorMessage;
[MessageBodyMember]
public bool IsSuccessed;
}
然后把上面的操作方法也改一下。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
public ResultMessage UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
-
{
-
ResultMessage rMsg = new ResultMessage();
-
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
-
{
-
rMsg.ErrorMessage = "传入的参数无效。";
-
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
-
return rMsg;
-
}
-
try
-
{
-
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
-
{
-
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
-
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
-
outputStream.Flush();
-
rMsg.IsSuccessed = true;
-
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
-
}
-
}
-
catch(Exception ex)
-
{
-
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
-
rMsg.ErrorMessage = ex.Message;
-
}
-
return rMsg;
-
}
public ResultMessage UpLoadFile(TransferFileMessage tMsg)
{
ResultMessage rMsg = new ResultMessage();
if (tMsg == null || tMsg.File_Stream == null)
{
rMsg.ErrorMessage = "传入的参数无效。";
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
return rMsg;
}
try
{
using (FileStream outputStream = new FileStream(tMsg.File_Name, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write))
{
// 我们不用对两个流对象进行读写,只要复制流就OK
tMsg.File_Stream.CopyTo(outputStream);
outputStream.Flush();
rMsg.IsSuccessed = true;
Console.WriteLine("在{0}接收到客户端发送的流,已保存到{1}。", DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString(), tMsg.File_Name);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
rMsg.IsSuccessed = false;
rMsg.ErrorMessage = ex.Message;
}
return rMsg;
}
现在你试试能不能正常运行?好了,客户端记得更新引用,而且,客户端的代码也要修改。
[csharp] view plain copy print?
-
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
-
{
-
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
-
{
-
return;
-
}
-
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
-
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
-
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
-
var response = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(Path.GetFileName(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text), fs);
-
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
-
if (response.IsSuccessed == true)
-
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
-
else
-
this.lbMessage.Text="错误信息:" + response.ErrorMessage;
-
}
private async void btnTransfer_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text))
{
return;
}
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
WS.ServiceClient cl = new WS.ServiceClient();
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = false;
var response = await cl.UpLoadFileAsync(Path.GetFileName(this.lbSelectedFilename.Text), fs);
this.btnTransfer.Enabled = true;
if (response.IsSuccessed == true)
this.lbMessage.Text = "上传完成。";
else
this.lbMessage.Text="错误信息:" + response.ErrorMessage;
}
现在再来测测吧。
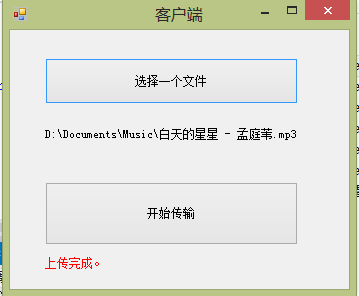
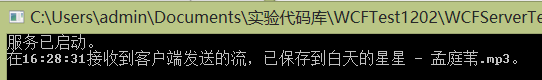
再看看服务器端。
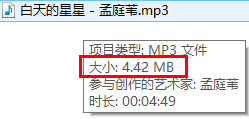
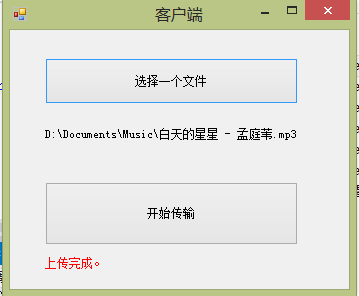
哈哈,现在就完美解决了。
再看看服务器端。
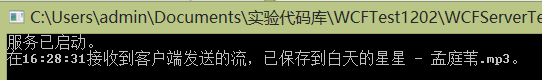
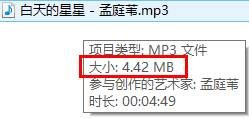
哈哈,现在就完美解决了。




 本文介绍如何使用WCF的流模式实现大文件的高效传输,包括服务端和客户端的具体实现过程,以及如何通过消息协定传递文件名。
本文介绍如何使用WCF的流模式实现大文件的高效传输,包括服务端和客户端的具体实现过程,以及如何通过消息协定传递文件名。
















 862
862

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








