面试过程中遇到的编程题整理,于此备录。分享,共勉。(持续更新中......欢迎补充)
(1)用户输入M, N值,从1至N开始顺序循环数数,每数到M输出该数值,直至全部输出。写出C程序。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 // 节点结构定义 5 typedef struct Link_Node 6 { 7 int data; 8 Link_Node* next; 9 }Node, *pNode; 10 11 // 创建循环链表 12 void CreateList(pNode& head, pNode& tail, int n) 13 { 14 if (n < 1) 15 { 16 head = NULL; 17 return; 18 } 19 20 head = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 21 head->data = 1; 22 head->next = NULL; 23 24 pNode p = head; 25 for (int i = 2; i < n+1; ++i) 26 { 27 p->next = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 28 p = p->next; 29 p->data = i; 30 p->next = NULL; 31 } 32 33 tail = p; 34 p->next = head; 35 } 36 37 // 打印循环链表 38 void Print(pNode& head) 39 { 40 pNode p = head; 41 while (p != NULL && p->next != head) 42 { 43 printf("%d ", p->data); 44 p = p->next; 45 } 46 if (p != NULL) 47 { 48 printf("%d\n", p->data); 49 } 50 } 51 52 // 用户输入M, N值,从1至N开始顺序循环数数,每数到M输出该数值。 53 // 直至全部输出 54 void LoopPrint(pNode& head, pNode& tail, int m) 55 { 56 pNode pPre = tail, pCur = head; 57 58 int nCount = m - 1; 59 while (pCur != NULL && pCur != pCur->next) 60 { 61 if (nCount > 0) 62 { 63 nCount--; 64 pPre = pCur; 65 pCur = pCur->next; 66 } 67 else 68 { 69 pPre->next = pCur->next; 70 printf("%d ", pCur->data); 71 free(pCur); 72 73 pCur = pPre->next; 74 nCount = m - 1; 75 } 76 } 77 78 if (pCur != NULL) 79 { 80 printf("%d ", pCur->data); 81 free(pCur); 82 83 head = tail = NULL; 84 } 85 86 printf("\n"); 87 } 88 89 void main() 90 { 91 pNode head = NULL, tail = NULL; 92 int m = 0, n = 0; 93 printf("请输入m,n的值:\n"); 94 scanf("%d", &m); 95 scanf("%d", &n); 96 // 创建循环链表 97 CreateList(head, tail, n); 98 // 打印链表 99 printf("打印链表数据信息如下:\n"); 100 Print(head); 101 printf("\n"); 102 // 循环输出 103 printf("循环数数,遇到M输出结果如下:\n"); 104 LoopPrint(head, tail, m); 105 system("pause"); 106 } 107 // run out: 108 /* 109 请输入m,n的值: 110 2 111 10 112 打印链表数据信息如下: 113 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 114 115 循环数数,遇到M输出结果如下: 116 2 4 6 8 10 3 7 1 9 5 117 请按任意键继续. . . 118 */
(2)从键盘输入10个学生的学号和成绩,按成绩从大到小建立一个有序链表,并输出。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct node 5 { 6 int xh; 7 int cj; 8 struct node *next; 9 }Node, *pNode; 10 11 void main() 12 { 13 pNode head = NULL, s, p, pre; 14 15 int i = 0; 16 while (i++ < 10) 17 { 18 s = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 19 s->next = NULL; 20 printf("第%d个学生(学号 成绩):", i); 21 scanf("%d%d", &s->xh, &s->cj); 22 if (head == NULL) 23 { 24 head = s; // 第一个学生 25 } 26 else 27 { 28 p = head; 29 pre = p; 30 while ((p != NULL) && (s->cj < p->cj)) 31 { 32 pre = p; 33 p = p->next; 34 } 35 if (p == head) 36 { 37 s->next = head; 38 head = s; 39 } 40 else if (p == NULL) 41 { 42 pre->next = s; 43 } 44 else 45 { 46 s->next = pre->next; 47 pre->next = s; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 printf("\n 输出结果: \n"); 53 p = head; 54 while (p != NULL) 55 { 56 printf("(%d)-->%d \n", p->xh, p->cj); 57 p = p->next; 58 } 59 60 system("pause"); 61 } 62 // run out: 63 /* 64 第1个学生(学号 成绩):1 69 65 第2个学生(学号 成绩):2 89 66 第3个学生(学号 成绩):3 59 67 第4个学生(学号 成绩):4 100 68 第5个学生(学号 成绩):5 68 69 第6个学生(学号 成绩):6 85 70 第7个学生(学号 成绩):7 82 71 第8个学生(学号 成绩):8 91 72 第9个学生(学号 成绩):9 72 73 第10个学生(学号 成绩):10 80 74 75 输出结果: 76 (4)-->100 77 (8)-->91 78 (2)-->89 79 (6)-->85 80 (7)-->82 81 (10)-->80 82 (9)-->72 83 (1)-->69 84 (5)-->68 85 (3)-->59 86 请按任意键继续. . . 87 */
(3)利用无序数组元素构建一个有序单链表。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct node *next; 8 }Node, *pNode; 9 10 void main() 11 { 12 pNode head = NULL, s, p, pre; 13 // 构建有序链表 14 int nArray[10] = {23, 45, 12, 89, 65, 90, 32, 100, 7, 45}; 15 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) 16 { 17 s = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 18 s->data = nArray[i]; 19 s->next = NULL; 20 21 if (head == NULL) 22 { 23 head = s; 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 p = head; 28 pre = p; 29 while ((p != NULL) && (s->data < p->data)) 30 { 31 pre = p; 32 p = p->next; 33 } 34 35 if (p == head) 36 { 37 s->next = head; 38 head = s; 39 } 40 else if (p == NULL) 41 { 42 pre->next = s; 43 } 44 else 45 { 46 s->next = pre->next; 47 pre->next = s; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 printf("输出结果: \n"); 53 p = head; 54 while (p != NULL) 55 { 56 printf("%d \n", p->data); 57 p = p->next; 58 } 59 60 system("pause"); 61 } 62 // run out 63 /* 64 输出结果: 65 100 66 90 67 89 68 65 69 45 70 45 71 32 72 23 73 12 74 7 75 请按任意键继续. . . 76 */
(4)写一个函数找出一个整数数组中,第二大的数 (microsoft)
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const int MINNUMBER = -32767; 5 6 int find_sec_max(int data[], int count) 7 { 8 int maxnumber = data[0]; 9 int sec_max = MINNUMBER; 10 for (int i = 1; i < count; i++) 11 { 12 if (data[i] > maxnumber) 13 { 14 sec_max = maxnumber; 15 maxnumber = data[i]; 16 } 17 else 18 { 19 if (data[i] > sec_max) 20 sec_max = data[i]; 21 } 22 } 23 24 return sec_max; 25 } 26 27 void main() 28 { 29 int nArray[10] = {23, 1, 45, 1000, 990, 7, 89, 34, 45, 70}; 30 cout << find_sec_max(nArray, 10) << endl; 31 system("pause"); 32 } 33 // run out: 34 /* 35 990 36 请按任意键继续. . . 37 */
(5)求整型数组中的最小以及次小项。
参见随笔《面试题(1)-->【7】 》
(6)如何判断一个单链表是有环的?(注意不能用标志位,最多只能用两个额外指针)
程序代码如下:
1 // 方法1: 2 bool checkLoop(node * head) 3 { 4 if (NULL == head) 5 return false; 6 7 node *low = head; 8 node *fast = head->next; 9 while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) 10 { 11 low = low->next; 12 fast = fast->next->next; 13 if (low == fast) 14 return true; 15 } 16 17 return false; 18 } 19 20 // 方法2: 21 bool IsLoop(node *head) 22 { 23 if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next) 24 { 25 return false; 26 } 27 28 node *p1 = head; 29 node *p2 = head; 30 do 31 { 32 p1 = p1->next; 33 p2 = p2->next->next; 34 } while (p2 && p2->next && p1 != p2); 35 36 return (p1 == p2); 37 }
(7)字符串功能函数
参见随笔《字符串strcpy 》
参见随笔《字符串strlen 》
参见随笔《字符串strcat 》
参见随笔《字符串strcmp 》
参见随笔《字符串memcpy 》
(8)字符串函数集合
12、写一个函数把字符串A中的B字符子串用字符串C进行替换。
(9)c语言 文件读写代码
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 void main() 5 { 6 FILE *fp; 7 char ch, filename[10]; 8 scanf("%s", filename); 9 if ((fp = fopen(filename, "w")) == NULL) 10 { 11 printf("cann't open file\n"); 12 exit(0); 13 } 14 ch = getchar(); 15 while (ch != '#') 16 { 17 fputc(ch, fp); 18 putchar(ch); 19 ch = getchar(); 20 } 21 22 fclose(fp); 23 system("pause"); 24 }
(10)memcpy内存拷贝函数
参见随笔《字符串memcpy 》
(11)判断大小端模式。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int CheckCpu() 5 { 6 union w 7 { 8 int a; 9 char b; 10 }c; 11 c.a = 1; 12 return (c.b == 1); 13 } 14 15 void main() 16 { 17 cout << CheckCpu() << endl; // 1 //说明是小端模式 18 system("pause"); 19 }
大小端模式分析:
嵌入式系统开发者应该对Little-endian和Big-endian模式非常了解。
采用Little-endian模式的CPU对操作数的存放方式是从低字节到高字节。而Big-endian模式对操作数的存放方式是从高字节到低字节。
例如,16bit宽的数0x1234在Little-endian模式CPU内存中的存放方式(假设从地址0x4000开始存放)为:
内存地址 存放内容
0x4000 0x34
0x4001 0x12
而在Big-endian模式CPU内存中的存放方式则为:
内存地址 存放内容
0x4000 0x12
0x4001 0x34
32bit宽的数0x12345678在Little-endian模式CPU内存中的存放方式(假设从地址0x4000开始存放)为:
内存地址 存放内容
0x4000 0x78
0x4001 0x56
0x4002 0x34
0x4003 0x12
而在Big-endian模式CPU内存中的存放方式则为:
内存地址 存放内容
0x4000 0x12
0x4001 0x34
0x4002 0x56
0x4003 0x78
联合体union的存放顺序是所有成员都从低地址开始存放,面试者的解答利用该特性,轻松地获得了CPU对内存采用Little-endian还是Big-endian模式读写。
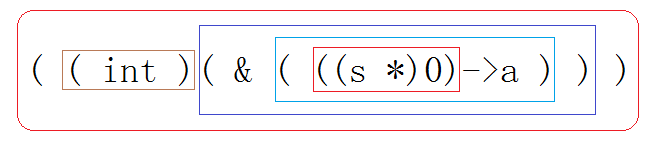
(12)写一个宏,求结构体中成员变量的偏移量。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstddef> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 #define offset(s, a) ((int)(&(((s *)0)->a))) 6 7 struct s 8 { 9 int a; 10 char d; 11 int b; 12 char c; 13 }; 14 15 void main() 16 { 17 cout << offset(s, a) << endl; // 0 18 cout << offset(s, b) << endl; // 8 19 cout << offset(s, c) << endl; // 12 20 cout << offset(s, d) << endl; // 4 21 system("pause"); 22 } 23 // run out: 24 /* 25 0 26 8 27 12 28 4 29 请按任意键继续. . . 30 */
解析图如下:
(13)用户输入两个整数,求最大公约数和最大公倍数。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 void main() 5 { 6 int max_divisor, min_multiple; 7 int n1, n2, m, n; 8 cout << "输入整数 n1 = "; 9 cin >> n1; 10 cout << "输入整数 n2 = "; 11 cin >> n2; 12 if (n1 < n2) 13 { 14 swap(n1, n2); 15 } 16 max_divisor = n1; 17 n = n2; 18 while (n != 0) 19 { 20 m = max_divisor % n; 21 max_divisor = n; 22 n = m; 23 } 24 min_multiple = n1 * n2 / max_divisor; 25 cout << "最大的公约数是: " << max_divisor << endl; 26 cout << "最小的公倍数是: " << min_multiple << endl; 27 system("pause"); 28 } 29 // run out: 30 /* 31 输入整数 n1 = 6 32 输入整数 n2 = 3 33 最大的公约数是: 3 34 最小的公倍数是: 6 35 请按任意键继续. . . 36 */
(14)单链表
1、创建有序单链表
2、向有序链表添加一个新节点
3、求链表的中间节点
4、逆置链表
5、判断是否有环
程序代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct node *next; 8 }Node, *pNode; 9 10 // 打印链表数据 11 void PrintList(pNode head) 12 { 13 if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next) 14 return; 15 16 pNode p = head->next; 17 while (p != NULL) 18 { 19 printf("%d \n", p->data); 20 p = p->next; 21 } 22 } 23 24 // 查找链表的中间节点 25 Node* FindMiddleNode(pNode head) 26 { 27 int i = 0, j = 0; 28 pNode current = NULL; 29 pNode middle = NULL; 30 current = middle = head->next; 31 while (current != NULL) 32 { 33 if (i/2 > j) 34 { 35 ++j; 36 middle = middle->next; 37 } 38 ++i; 39 current = current->next; 40 } 41 42 return middle; 43 } 44 45 void CreateList(pNode& head, int nValue) 46 { 47 pNode s, p, pre; 48 s = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 49 s->data = nValue; 50 s->next = NULL; 51 52 if (NULL == head) 53 { 54 head = s; 55 } 56 else 57 { 58 p = head; 59 pre = p; 60 while ((p != NULL) && (s->data < p->data)) 61 { 62 pre = p; 63 p = p->next; 64 } 65 66 if (p == head) 67 { 68 s->next = head; 69 head = s; 70 } 71 else if (NULL == p) 72 { 73 pre->next = s; 74 } 75 else 76 { 77 s->next = pre->next; 78 pre->next = s; 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 83 pNode Reverse(pNode head) 84 { 85 pNode p = NULL, q = NULL; 86 if (NULL == head || head->next == NULL) 87 { 88 return head; 89 } 90 91 p = head->next; 92 q = p->next; 93 p->next = NULL; 94 while (q != NULL) 95 { 96 p = q; 97 q = q->next; 98 p->next = head->next; 99 head->next = p; 100 } 101 102 return head; 103 } 104 105 // 逆置无头节点的单链表 106 /* 107 pNode Reverse(pNode firstNode) 108 { 109 pNode p = NULL, q = NULL; 110 if (NULL == firstNode || firstNode->next == NULL) 111 { 112 return firstNode; 113 } 114 115 p = firstNode; 116 q = p->next; 117 p->next = NULL; 118 while (q != NULL) 119 { 120 p = q; 121 q = q->next; 122 p->next = firstNode; 123 firstNode = p; 124 } 125 126 return firstNode; 127 } 128 */ 129 130 bool IsLoop(pNode headNode) 131 { 132 pNode p1 = headNode; 133 pNode p2 = headNode; 134 if (NULL == headNode || headNode->next == NULL) 135 { 136 return false; 137 } 138 do 139 { 140 p1 = p1->next; 141 p2 = p2->next->next; 142 } while(p2 && p2->next && p1 != p2); 143 144 return (p1 == p2); 145 } 146 147 // 有序链表插入节点 148 pNode Insert_node(pNode head, int nValue) 149 { 150 pNode item = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 151 item->data = nValue; 152 item->next = NULL; 153 154 if (NULL == head->next) 155 { 156 head->next = item; 157 return head; 158 } 159 160 Node *p = head->next; 161 Node *q = NULL; 162 while (p != NULL && (p->data > item->data)) 163 { 164 q = p; 165 p = p->next; 166 } 167 168 if (p == head->next) 169 { 170 item->next = p; 171 head->next = item; 172 return head; 173 } 174 175 q->next = item; 176 item->next = p; 177 return head; 178 } 179 180 void main() 181 { 182 // 构建有头节点的有序链表 183 pNode headNode = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 184 headNode->data = -1; 185 headNode->next = NULL; 186 187 int nArray[10] = {23, 45, 12, 89, 65, 90, 32, 100, 7, 45}; 188 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) 189 { 190 CreateList(headNode->next, nArray[i]); 191 } 192 193 printf("有序链表(由大到小)输出结果: \n"); 194 PrintList(headNode); 195 196 headNode = Insert_node(headNode, 110); // 最前面插入 197 headNode = Insert_node(headNode, 30); // 中间插入 198 headNode = Insert_node(headNode, 5); // 末尾插入 199 200 printf("有序链表(由大到小)输出结果: \n"); 201 PrintList(headNode); 202 203 pNode midNode = FindMiddleNode(headNode); 204 if (midNode != NULL) 205 { 206 printf("中间节点的数据值: %d \n", midNode->data); 207 } 208 209 pNode head = Reverse(headNode); 210 if (head != NULL) 211 { 212 printf("逆置后输出结果: \n"); 213 PrintList(head); 214 } 215 216 printf("是否有环? %d \n", IsLoop(headNode)); 217 system("pause"); 218 } 219 // run out 220 /* 221 有序链表(由大到小)输出结果: 222 100 223 90 224 89 225 65 226 45 227 45 228 32 229 23 230 12 231 7 232 有序链表(由大到小)输出结果: 233 110 234 100 235 90 236 89 237 65 238 45 239 45 240 32 241 30 242 23 243 12 244 7 245 5 246 中间节点的数据值: 45 247 逆置后输出结果: 248 5 249 7 250 12 251 23 252 30 253 32 254 45 255 45 256 65 257 89 258 90 259 100 260 110 261 是否有环? 0 262 请按任意键继续. . . 263 */
(15)字符串长度函数strlen
参见随笔《字符串(strlen) 》
(16)排序集
1、冒泡排序
2、选择排序
3、插入排序
4、快速排序
5、希尔排序
6、堆排序
7、归并排序
8、桶排序
9、基数排序
(17)写一个函数返回1 + 2 + 3 +…+ n的值(假定结果不会超过长整型变量的范围)
程度代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int Sum(int n) 5 { 6 return ((long)1 + n) * n / 2; 7 } 8 9 void main() 10 { 11 printf("%d\n", Sum(10)); // 55 12 system("pause"); 13 }
(18)合并有序链表,并且合并后仍然为有序链表
程序代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct node *next; 8 }Node, *pNode; 9 10 // 创建链表 11 void CreateList(pNode& head, int nValue) 12 { 13 pNode s, p, pre; 14 s = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); 15 s->data = nValue; 16 s->next = NULL; 17 18 if (NULL == head) 19 { 20 head = s; 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 p = head; 25 pre = p; 26 while ((p != NULL) && (s->data > p->data)) 27 { 28 pre = p; 29 p = p->next; 30 } 31 32 if (p == head) 33 { 34 s->next = head; 35 head = s; 36 } 37 else if (NULL == p) 38 { 39 pre->next = s; 40 } 41 else 42 { 43 s->next = pre->next; 44 pre->next = s; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 49 // 合并有序链表 50 pNode Merge(pNode head1, pNode head2) 51 { 52 if (NULL == head1) 53 return head2; 54 if (NULL == head2) 55 return head1; 56 57 pNode head = NULL; 58 pNode p1 = NULL; 59 pNode p2 = NULL; 60 if (head1->data < head2->data) 61 { 62 head = head1; 63 p1 = head1->next; 64 p2 = head2; 65 } 66 else 67 { 68 head = head2; 69 p2 = head2->next; 70 p1 = head1; 71 } 72 pNode pcurrent = head; 73 while (p1 != NULL && p2 != NULL) 74 { 75 if (p1->data <= p2->data ) 76 { 77 pcurrent->next = p1; 78 pcurrent = p1; 79 p1 = p1->next; 80 } 81 else 82 { 83 pcurrent->next = p2; 84 pcurrent = p2; 85 p2 = p2->next; 86 } 87 } 88 89 if (p1 != NULL) 90 pcurrent->next = p1; 91 92 if (p2 != NULL) 93 pcurrent->next = p2; 94 95 return head; 96 } 97 98 // 递归合并有序链表 99 pNode MergeRecursive(pNode head1, pNode head2) 100 { 101 if (NULL == head1) 102 return head2; 103 104 if (NULL == head2) 105 return head1; 106 107 pNode head = NULL ; 108 if (head1->data < head2->data ) 109 { 110 head = head1 ; 111 head->next = MergeRecursive(head1->next, head2); 112 } 113 else 114 { 115 head = head2; 116 head->next = MergeRecursive(head1, head2->next); 117 } 118 119 return head ; 120 } 121 // 打印无头结点的链表数据 122 void PrintListHead(pNode head) 123 { 124 if (NULL == head) 125 return; 126 127 pNode p = head; 128 while (p != NULL) 129 { 130 printf("%d ", p->data); 131 p = p->next; 132 } 133 printf("\n"); 134 } 135 136 // 构建有序链表 137 void create(pNode& headNode) 138 { 139 for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) 140 { 141 CreateList(headNode, rand() % 200); 142 } 143 144 PrintListHead(headNode); 145 printf("\n"); 146 } 147 148 void main() 149 { 150 // 构建有序链表1 151 pNode headNode1 = NULL, headNode2 = NULL; 152 pNode headNode3 = NULL, headNode4 = NULL; 153 154 printf("打印有序链表1:\n"); 155 create(headNode1); 156 157 printf("打印有序链表2:\n"); 158 create(headNode2); 159 160 printf("打印有序链表3:\n"); 161 create(headNode3); 162 163 printf("打印有序链表4:\n"); 164 create(headNode4); 165 166 pNode newHead1 = Merge(headNode1, headNode2); 167 pNode newHead2 = MergeRecursive(headNode3, headNode4); 168 printf("打印合并有序链表(1、2):\n"); 169 PrintListHead(newHead1); 170 printf("打印合并有序链表(3、4):\n"); 171 PrintListHead(newHead2); 172 173 system("pause"); 174 } 175 // run out: 176 /* 177 打印有序链表1: 178 41 64 67 78 100 124 134 158 162 169 179 180 打印有序链表2: 181 27 27 36 81 91 105 142 145 161 195 182 183 打印有序链表3: 184 4 21 92 95 102 116 118 153 182 191 185 186 打印有序链表4: 187 35 47 67 69 94 99 112 126 138 171 188 189 打印合并有序链表(1、2): 190 27 27 36 41 64 67 78 81 91 100 105 124 134 142 145 158 161 162 169 195 191 打印合并有序链表(3、4): 192 4 21 35 47 67 69 92 94 95 99 102 112 116 118 126 138 153 171 182 191 193 请按任意键继续. . . 194 */
(19)assert宏的实现
程序代码如下:
1 void _assert(const char *p, const char *f, int n) 2 { 3 cout << p << endl; 4 cout << f << endl; 5 cout << n << endl; 6 } 7 #define assert(e)\ 8 ((e) ? (void)0 : _assert(#e, __FILE__, __LINE__))
(20)实现全排列函数。
程序代码如下:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 template<class Type> 5 void Perm(Type list[], int k, int m) 6 { 7 static int nCount = 0; 8 if (k == m) 9 { 10 cout << ++nCount << ": "; 11 for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) 12 cout << list[i]; 13 14 cout << endl; 15 } 16 else 17 { 18 for (int i = k; i <= m; i++) 19 { 20 Swap(list[k], list[i]); 21 Perm(list, k + 1, m); 22 Swap(list[k], list[i]); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 27 template <class Type> 28 inline void Swap(Type &a, Type &b) 29 { 30 Type temp = a; a = b; b = temp; 31 } 32 33 void main() 34 { 35 int ar[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; 36 Perm(ar, 1, 4); 37 38 system("pause"); 39 } 40 // run out: 41 /* 42 1: 12345 43 2: 12354 44 3: 12435 45 4: 12453 46 5: 12543 47 6: 12534 48 7: 13245 49 8: 13254 50 9: 13425 51 10: 13452 52 11: 13542 53 12: 13524 54 13: 14325 55 14: 14352 56 15: 14235 57 16: 14253 58 17: 14523 59 18: 14532 60 19: 15342 61 20: 15324 62 21: 15432 63 22: 15423 64 23: 15243 65 24: 15234 66 请按任意键继续. . . 67 */
(21)将一个数值由N进制转换为M进制。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 //幂函数的小递归 不解释 8 int npow(int value, int pow) 9 { 10 int res = 0; 11 if (pow > 0) 12 { 13 res = value * npow(value, pow - 1); 14 return res; 15 } 16 else 17 return 1; 18 } 19 20 // N进制转换为M进制 21 char* ntom(int n, int m, char *data, char *res_str) 22 { 23 queue<int> iq; 24 stack<int> is; 25 26 int len = strlen(data); 27 //处理输入data中的字符 也就是10进制以上的进制中出现的ABCD… 28 while (len > 0) 29 { 30 if (data[len - 1] >= 'A' && data[len - 1] <= 'F') 31 data[len - 1] = 10 + (data[len - 1] - 'A') + '0'; 32 iq.push(data[len - 1] - '0'); 33 len--; 34 } 35 //将data转为10进制 并保存在val1中 val1是个中间值 36 int q_size = iq.size(); 37 int val1 = 0; 38 for (int ix = 0;ix < q_size; ix++) 39 { 40 val1 += iq.front() * npow(n, ix); 41 iq.pop(); 42 } 43 //将10进制数val1转为M进制 并依次压栈 44 int tmp2; 45 while (val1 > 0) 46 { 47 tmp2 = val1%m; 48 is.push(tmp2); 49 val1 = val1 / m; 50 } 51 52 int j = 0; 53 char res[20]; 54 //转换后的数如果存在ABCD…则处理 否则直接转为字符 并保存于res中 55 while (!is.empty()) 56 { 57 if (is.top() >= 10) 58 { 59 res[j] = 'A' + (is.top() - 10); 60 } 61 else 62 { 63 res[j] = is.top() + '0'; 64 } 65 j++; 66 is.pop(); 67 } 68 res[j] = '\0';//从不忘记为字符数组的最后以为加上结束符 方便进行下面的strcpy 69 strcpy(res_str, res); 70 71 return res_str; 72 } 73 74 void main() 75 { 76 int n, m; 77 char data[20]; 78 char res_str[20]; 79 cout << "请输入M、N的值(N进制转换为M进制): " << endl; 80 cin >> n >> m; 81 cout << "请输入转换的数值: " << endl; 82 cin >> data; 83 cout << "把数值" << data << "由" << n << "进制" << "转换为" << m << "进制的结果为:"; 84 cout << ntom(n, m, data, res_str) << endl; 85 86 system("pause"); 87 } 88 89 // run out: 90 /* 91 请输入M、N的值(N进制转换为M进制): 92 10 16 93 请输入转换的数值: 94 100 95 把数值100由10进制转换为16进制的结果为:64 96 请按任意键继续. . . 97 */
(22)写一个函数求整型数组中的次大数。
程序代码如下:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 // 写一个函数找出一个整数数组中第二大的数(次大数) 5 int Max2(int ar[], int n) 6 { 7 int Max1 = ar[0] > ar[1] ? ar[0] : ar[1]; 8 int Max2 = ar[0] > ar[1] ? ar[1] : ar[0]; 9 for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) 10 { 11 if (ar[i] > Max2) 12 { 13 Max2 = ar[i]; 14 } 15 if (ar[i] > Max1) 16 { 17 Max2 = Max1; 18 Max1 = ar[i]; 19 } 20 } 21 22 return Max2; 23 } 24 25 void main() 26 { 27 int ar[8] = {1, 25, 89, 47, 101, 8888, 9999, 66}; 28 cout << Max2(ar, 8) << endl; // 888 29 system("pause"); 30 }
(23)写程序实现由键盘输入内容,并将内容保存到一个文本文件中。
程序代码如下:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 ofstream fout("test.txt");// 定义输出文件流并打开文件得2分 8 if (!fout) 9 { 10 cerr << "文件没有打开!" << endl; 11 exit(1); 12 } 13 int x; 14 cin >> x; 15 while (x != -1) 16 { 17 fout << x << ' '; 18 cin >> x; 19 } // 能够从键盘向文件正确输出数据得6分 20 21 fout.close();// 关闭输出文件流得1分 22 }
(24)写一个函数从字符串N中查找子串字符串M第一次出现的位置。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 // 在字符串n中查找第一次出现子串m的索引值 5 int StrStr(const char *src, const char *sub) 6 { 7 const char *bp; 8 const char *sp; 9 int nIndex = -1; 10 if ((NULL == src)||(NULL == sub)) 11 { 12 return nIndex; 13 } 14 15 while (*src) 16 { 17 bp = src; 18 sp = sub; 19 do 20 { 21 if (!*sp) 22 { 23 return nIndex; 24 } 25 } while (*bp++ == *sp++); 26 27 ++src; 28 ++nIndex; 29 } 30 31 return -1; 32 } 33 34 void main() 35 { 36 char *pStr = "abcdefghijklmn"; 37 char *pDes = "ghi"; 38 char *pSec = "sec"; 39 cout << StrStr(pStr, pDes) << endl; // 5 40 cout << StrStr(pStr, pSec) << endl; // -1 41 cout << StrStr(pStr, NULL) << endl; // -1 42 cout << StrStr(NULL, pSec) << endl; // -1 43 system("pause"); 44 } 45 // run out: 46 /* 47 5 48 -1 49 -1 50 -1 51 请按任意键继续. . . 52 */
(25)有N个大小不等的自然数(1--N),请将它们由小到大排序。
要求程序算法:时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1)。
算法:N个不等的自然数1~N,排序完成后必然为1~N。
所以可以一次遍历,遇到a[i] != i的就把a[i] 和 a[a[i]]交换。
函数实现以及测试代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 void sort(int a[], int n) 5 { 6 int i; 7 int t; /*临时变量:空间复杂度O(1)*/ 8 9 for (i = 1; i < n + 1; ++i) /*时间复杂度O(n)*/ 10 { 11 while (a[i] != i) 12 { 13 t = a[a[i]]; 14 a[a[i]] = a[i]; // 排好一个元素 15 a[i] = t; 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 20 void print(int a[], int n) 21 { 22 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 23 { 24 cout << a[i] << " "; 25 } 26 } 27 28 void main() 29 { 30 int nArray[10] = {3, 5, 7, 9, 1, 4, 8, 0, 2, 6}; 31 sort(nArray, 9); 32 print(nArray, 10); 33 system("pause"); 34 } 35 36 // run out: 37 // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 请按任意键继续. . .
(26)建立单链表,把'a'--'z'26个字母插入到单链表中,并且倒叙,再打印数据。
程序实现以及测试程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 // 单连表的建立,把'a'--'z'26个字母插入到连表中,并且倒叙,还要打印! 5 typedef struct link_node 6 { 7 char data; 8 struct link_node *next; 9 }node, *pNode; 10 11 void print(pNode head) 12 { 13 if (NULL == head || (head->next == NULL)) 14 { 15 return; 16 } 17 pNode p = head->next; 18 while (p != NULL) 19 { 20 printf(" %c ", p->data); 21 p = p->next; 22 } 23 printf("\n"); 24 } 25 26 void main(void) 27 { 28 pNode p = NULL; 29 pNode q = NULL; 30 31 pNode head = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(node)); 32 head->data = ' '; 33 head->next = NULL; 34 35 pNode firstNode = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(node)); 36 firstNode->data = 'a'; 37 firstNode->next = NULL; 38 head->next = firstNode; 39 p = firstNode; 40 41 int longth = 'z' - 'b'; 42 int i = 0; 43 while (i <= longth ) 44 { 45 pNode tempNode = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(node)); 46 tempNode->data = 'b' + i; 47 tempNode->next = NULL; 48 q = tempNode; 49 50 head->next = tempNode; 51 tempNode->next = p; 52 p = q; 53 i++; 54 } 55 56 print(head); 57 58 system("pause"); 59 } 60 // run out: 61 /* 62 z y x w v u t s r q p o n m l k j i h g f e d c b a 63 请按任意键继续. . . 64 */
(27)用指针的方法,将字符串“ABCD1234efgh”前后对调显示。
程序实现以及测试程序如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <stdlib.h> 4 5 void main() 6 { 7 char str[] = "ABCD1234efgh"; 8 int length = strlen(str); 9 char * p1 = str; 10 char * p2 = str + length - 1; 11 while (p1 < p2) 12 { 13 char c = *p1; 14 *p1 = *p2; 15 *p2 = c; 16 ++p1; 17 --p2; 18 } 19 printf("str now is %s\n", str); 20 system("pause"); 21 } 22 // run out: 23 /* 24 str now is hgfe4321DCBA 25 请按任意键继续. . . 26 */
(28)《 字符串匹配KMP算法 》
(29)编写一个不定形参的函数(计算不计数的实参的平均数)
程序示例代码如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 #define _INTSIZEOF(n) ( (sizeof(n) + sizeof(int) - 1) & ~(sizeof(int) - 1) ) 5 // 4 + 4 - 1 = 7 // 4-1 = 3 6 // 0111 // ~0011 = 1100 7 // 0111 & 1100 = 0100 = 4 8 #define va_start(ap,v) ( ap = (va_list)&v + _INTSIZEOF(v) ) 9 // 指针 = (char*)&V(数值个数) + 4 10 #define va_arg(ap,t) ( *(t *)((ap += _INTSIZEOF(t)) - _INTSIZEOF(t)) ) 11 // (*(int *)((指针ap += INTSIZEOF(int)) - INTSIZEOF(int))) 12 // *(int *) ((ap = ap + INTSIZEOF(int)) - INTSIZEOF(int)) 13 // *(int *)(本段代码执行结果ap向前走4个字节,但是地址不变) 14 #define va_end(ap) ( ap = (va_list)0 ) 15 // ap = (char *)0 16 17 int average(int n_values, ...) 18 { 19 int sum = 0; 20 21 va_list var_arg; // char * 22 23 va_start(var_arg, n_values); 24 25 for (int i = 0 ; i < n_values; ++i) 26 { 27 sum += va_arg(var_arg, int); 28 } 29 30 va_end(var_arg); 31 return sum / n_values; 32 } 33 34 void main() 35 { 36 printf("%d \n", average(3, 10, 20, 30)); // 20 37 system("pause"); 38 }
(30)计算无符号长整型的二进制每四位的和。
程序代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int Count(unsigned long value) 5 { 6 int sum = 0; 7 while (value) 8 { 9 sum += value & 0x0f; 10 value >>= 4; 11 } 12 13 return sum; 14 } 15 16 void main() 17 { 18 cout << Count(2773) << endl; // 0000 1010 1101 0101 // 0 + 10 + 13 + 5 = 28 19 system("pause"); 20 }
(31)字符串类String的实现。请参见随笔《 字符串String 》
(32)
(33)
(34)
(35)
Good Good Study, Day Day Up.
顺序 选择 循环 总结







 本文精选了一系列经典的编程题目,涵盖链表操作、字符串处理、排序算法、数学问题等多个方面,并提供了详细的代码实现与解析,旨在帮助读者提升编程实战能力。
本文精选了一系列经典的编程题目,涵盖链表操作、字符串处理、排序算法、数学问题等多个方面,并提供了详细的代码实现与解析,旨在帮助读者提升编程实战能力。
















 397
397

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








