相交求交点:

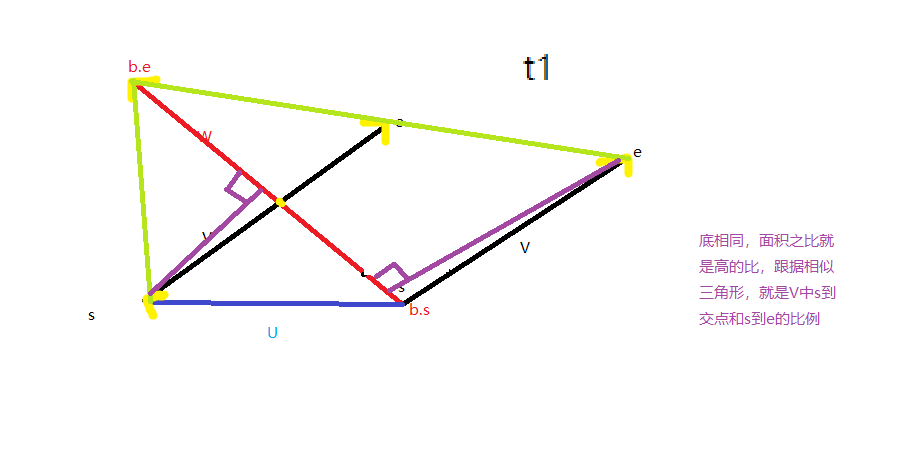
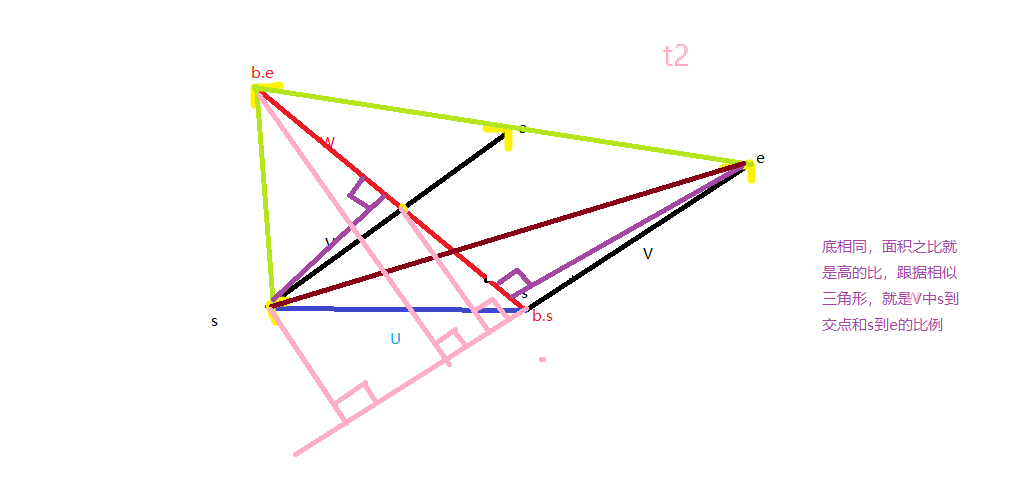
第二个公式容易记忆:(以第二个公式为模板)
Point res=b.s; t=((e-s)^(s-b.s))/((e-s)^(b.e-b.s)); res.x+=(e.x-s.x)*t; res.y+=(e.y-s.y)*t; return res;
例题:
poj 1269
intersecting lines
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int cmp(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<=1e-8)return 0;
if(x<0)return -1;
return 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x,y;
Point (){};
Point (double _x,double _y)
{
x=_x,y=_y;
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const{
return Point (x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
double operator *(const Point &b)const {
return (x*b.x+y*b.y);
}
double operator ^(const Point &b)const {
return (x*b.y-b.x*y);
}
};
struct Line
{
Point s,e;
Line(){};
Line(Point _s,Point _e)
{
s=_s,e=_e;
}
Point operator &(const Line &b)const{
Point res=b.s;
if(cmp((e-s)^(b.e-b.s))==0)
{
if(cmp((e-s)^(e-b.e))==0)
{
cout<<"LINE"<<endl;
return Point(0,0);
}
else
{
cout<<"NONE"<<endl;
return Point(0,0);
}
}
double t=((e-s)^(s-b.s))/((e-s)^(b.e-b.s));
res.x+=(b.e.x-b.s.x)*t;
res.y+=(b.e.y-b.s.y)*t;
return res;
}
};
int main ()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
Line line1,line2;
Point point ;
double x1,x2,x3,x4,y1,y2,y3,y4;
cout<<"INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT"<<endl;
while(n--)
{
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
line1=Line(Point(x1,y1),Point(x2,y2));
cin>>x3>>y3>>x4>>y4;
line2=Line(Point(x3,y3),Point(x4,y4));
point=line1&line2;
if(point.x!=0||point.y!=0)
printf("POINT %.2f %.2f\n",point.x,point.y);
}
cout<<"END OF OUTPUT"<<endl;
return 0;
}








 博客主要提及相交求交点,给出第二个易记忆公式,并以 poj 1269 intersecting lines 为例,还给出了转载链接。
博客主要提及相交求交点,给出第二个易记忆公式,并以 poj 1269 intersecting lines 为例,还给出了转载链接。
















 467
467

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








