In mathematics, the rearrangement inequality[1] states that
for every choice of real numbers
and every permutation
of x1, . . ., xn. If the numbers are different, meaning that
then the lower bound is attained only for the permutation which reverses the order, i.e. σ(i) = n − i + 1 for all i = 1, ..., n, and the upper bound is attained only for the identity, i.e. σ(i) = i for all i = 1, ..., n.
Note that the rearrangement inequality makes no assumptions on the signs of the real numbers.
Applications
Many famous inequalities can be proved by the rearrangement inequality, such as the arithmetic mean – geometric mean inequality, the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality, and Chebyshev's sum inequality.
Proof
The lower bound follows by applying the upper bound to
Therefore, it suffices to prove the upper bound. Since there are only finitely many permutations, there exists at least one for which
is maximal. In case there are several permutations with this property, let σ denote one with the highest number of fixed points.
We will now prove by contradiction, that σ has to be the identity (then we are done). Assume that σ is not the identity. Then there exists a j in {1, ..., n − 1} such that σ(j) ≠ j and σ(i) = i for all i in {1, ..., j − 1}. Hence σ(j) > j and there exists k in {j + 1, ..., n} with σ(k) = j. Now
Therefore,
Expanding this product and rearranging gives
hence the permutation
which arises from σ by exchanging the values σ(j) and σ(k), has at least one additional fixed point compared to σ, namely at j, and also attains the maximum. This contradicts the choice of σ.
If
then we have strict inequalities at (1), (2), and (3), hence the maximum can only be attained by the identity, any other permutation σ cannot be optimal.
 数学中的排列不等式及其应用
数学中的排列不等式及其应用




 排列不等式在数学中是一个基本的不等式,适用于任意实数的排列。本文详细阐述了该不等式的原理,并展示了其在算术平均与几何平均不等式、柯西-施瓦茨不等式以及切比雪夫求和不等式中的应用。通过证明过程,我们了解了如何利用排列不等式解决实际问题。
排列不等式在数学中是一个基本的不等式,适用于任意实数的排列。本文详细阐述了该不等式的原理,并展示了其在算术平均与几何平均不等式、柯西-施瓦茨不等式以及切比雪夫求和不等式中的应用。通过证明过程,我们了解了如何利用排列不等式解决实际问题。





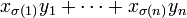
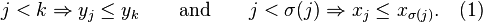



















 527
527

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








