基础知识:设备坐标系统属性
其他知识:GDI映射模式
视口与窗口坐标转换公式:

以下代码都需要该代码支持:


1 //int wmId, wmEvent; 2 PAINTSTRUCT ps; 3 HDC hdc; 4 static int cxClient, cyClient; 5 static HPEN hPen,oldHPen; 6 static int cxChar, cxCpas, cyChar; 7 TEXTMETRIC tm; 8 9 switch (message) 10 { 11 //case WM_COMMAND: 12 // wmId = LOWORD(wParam); 13 // wmEvent = HIWORD(wParam); 14 // // 分析菜单选择: 15 // switch (wmId) 16 // { 17 // case IDM_ABOUT: 18 // DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_ABOUTBOX), hWnd, About); 19 // break; 20 // case IDM_EXIT: 21 // DestroyWindow(hWnd); 22 // break; 23 // default: 24 // return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam); 25 // } 26 // break; 27 case WM_CREATE: 28 hPen = CreatePen(PS_DASH, 0, RGB(255, 0, 0)); 29 hdc = GetDC(hWnd); 30 GetTextMetrics(hdc, &tm); 31 cxChar = tm.tmAveCharWidth; 32 cxCpas = (tm.tmPitchAndFamily & 1 ? 3 : 2)*cxChar / 2; 33 cyChar = tm.tmHeight + tm.tmExternalLeading; 34 ReleaseDC(hWnd, hdc); 35 case WM_SIZE: 36 cxClient = LOWORD(lParam); 37 cyClient = HIWORD(lParam); 38 return 0;
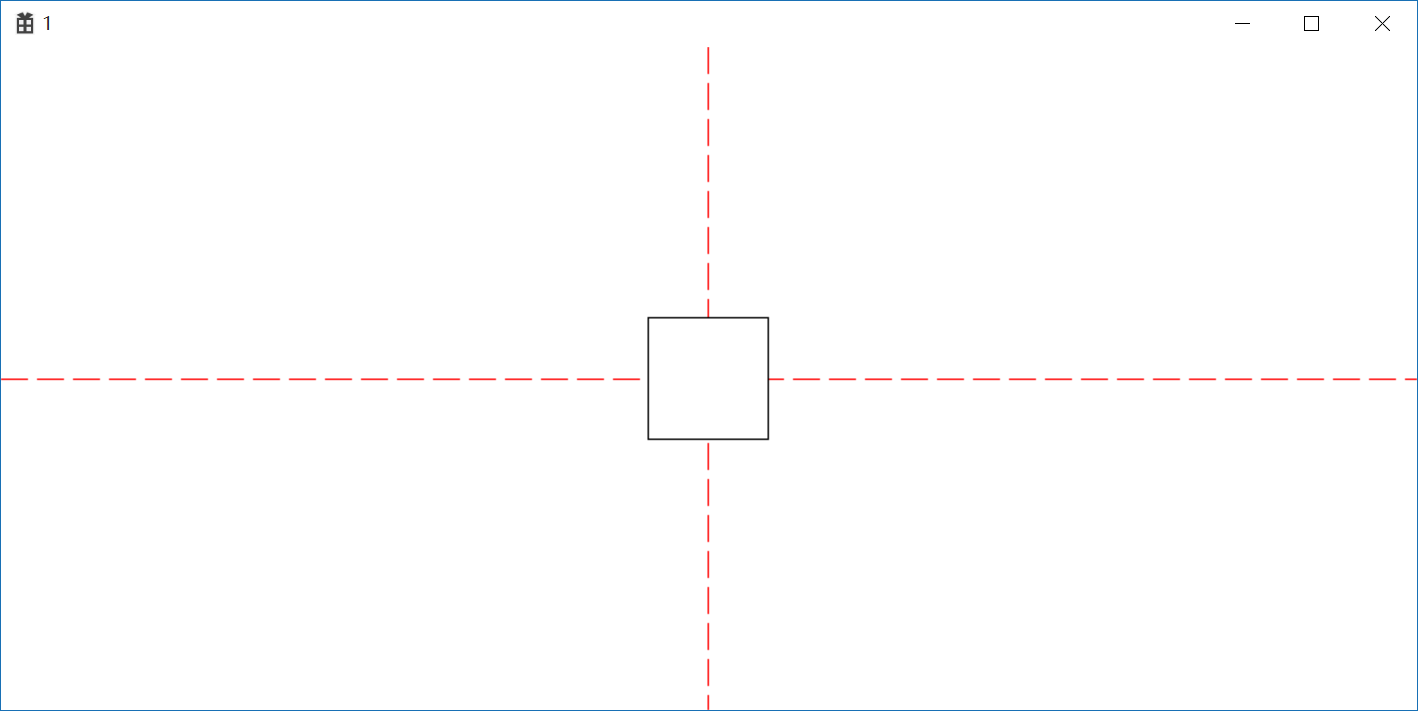
原点设置在窗口中间通过更改矩形坐标实现居中


1 //原点设置在窗口中间通过更改矩形坐标实现居中 2 oldHPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2,NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 SetViewportOrgEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient / 2, NULL); 9 Rectangle(hdc, -50, 50, 50, -50);
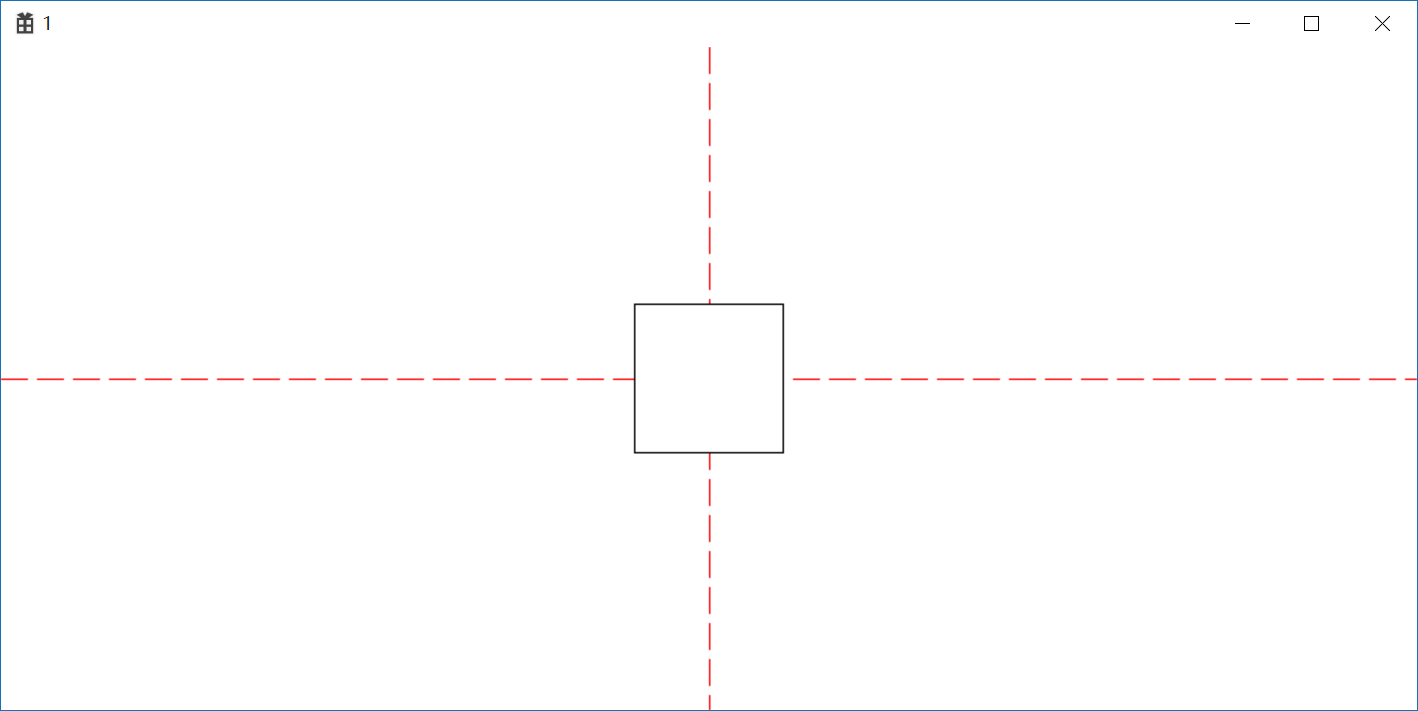
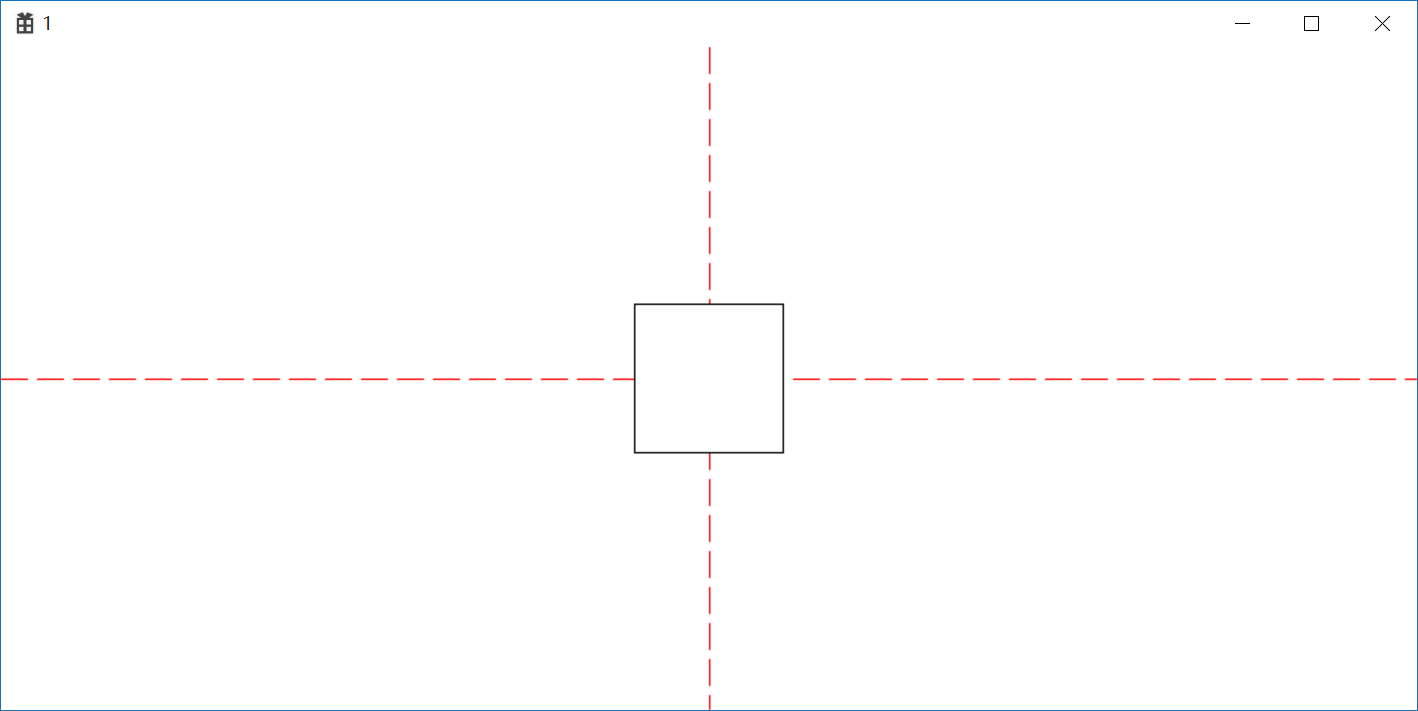
通过设置原点使矩形实现居中


1 //通过设置原点使矩形实现居中 2 oldHPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2,NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 SetViewportOrgEx(hdc, (cxClient / 2)-150, (cyClient / 2)-150, NULL); 9 Rectangle(hdc, 100, 100, 200, 200);
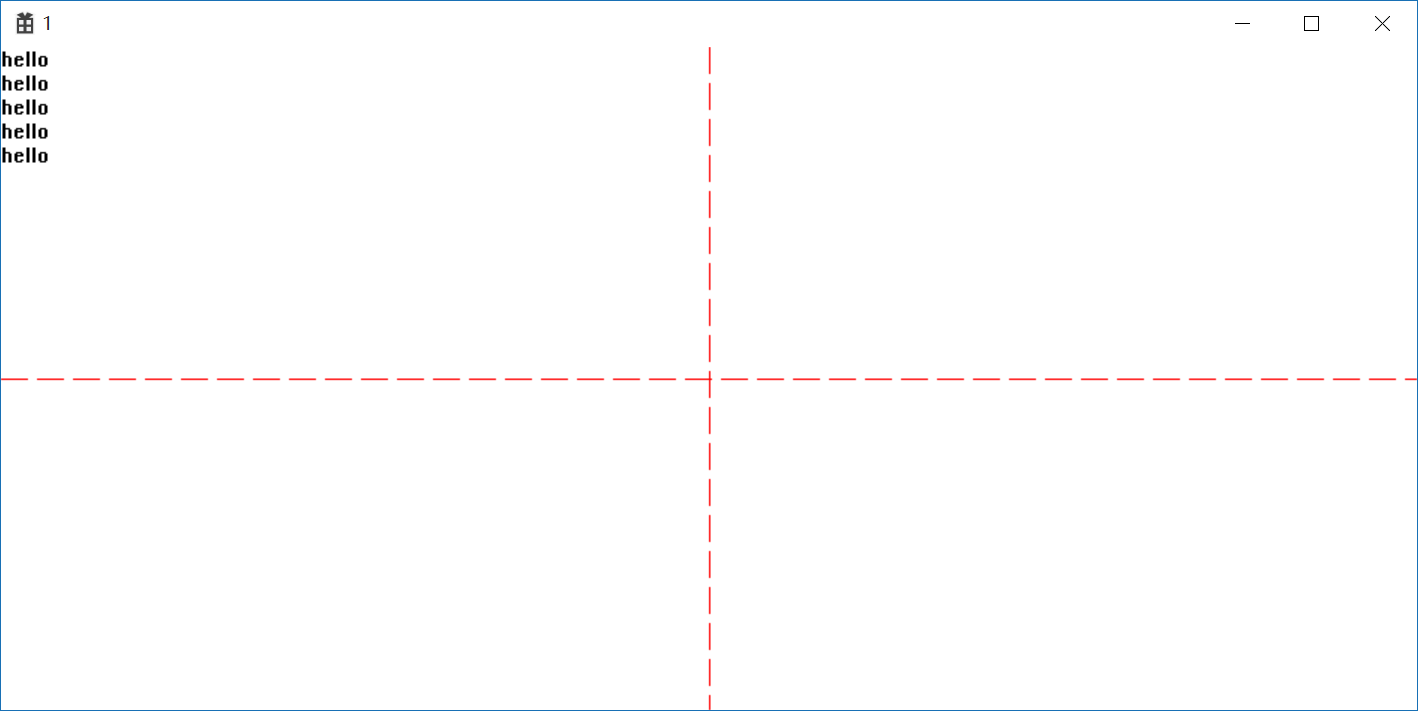
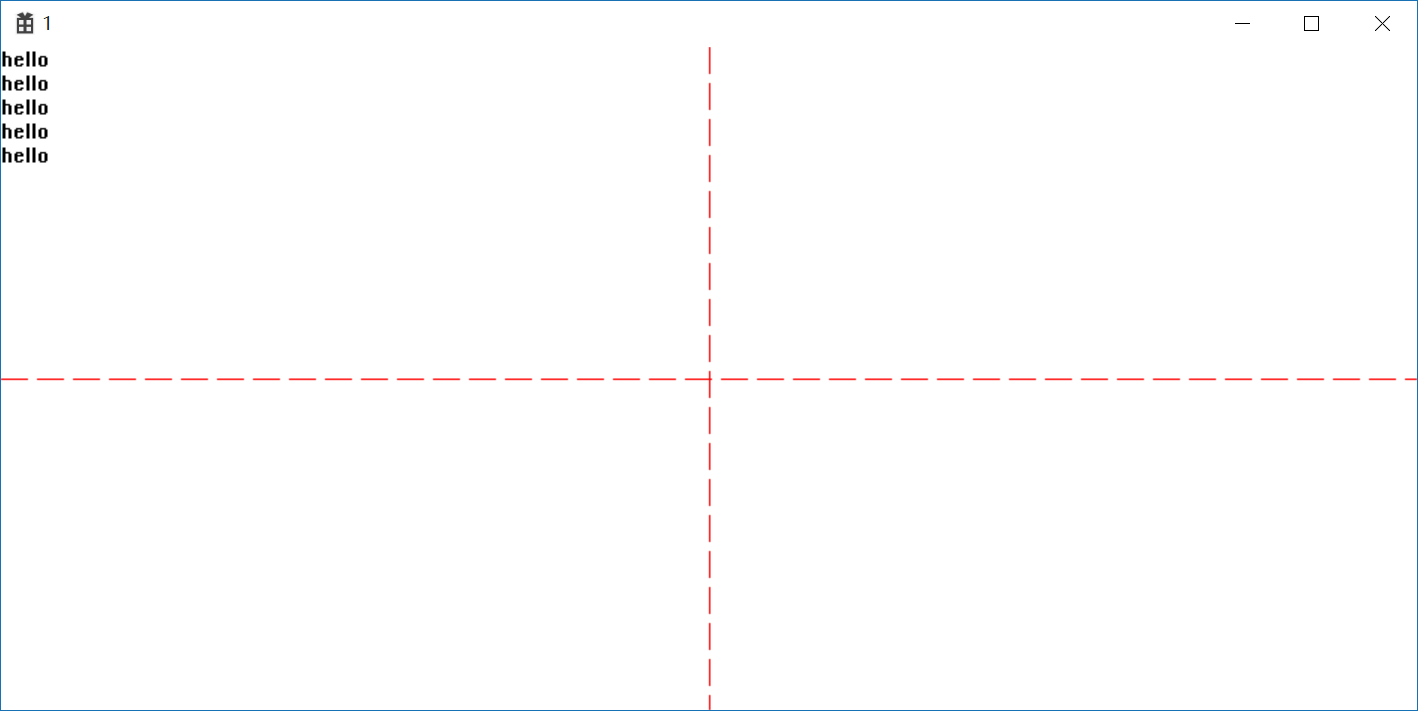
通过更改TextOut的y轴实现hello的垂直输出


//通过更改TextOut的y轴实现hello的垂直输出 oldHPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hPen); MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2,NULL); LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); for(int t = 0,y; t < 5;++t) { y = cyChar*t; TextOut(hdc, 0, y, TEXT("hello"), 5); }
通过更改视口的原点实现hello的垂直输出


1 //通过更改视口的原点实现hello的垂直输出 2 oldHPen = (HPEN) SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2, NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 for(int t = 0, y; t < 5; ++t) 9 { 10 y = cyChar*t; 11 SetViewportOrgEx(hdc, 0, y, NULL); 12 TextOut(hdc, 0, 0, TEXT("hello"), 5); 13 }
通过更改视口原点的x轴实现hello的横排列输出


1 //通过更改视口原点的x轴实现hello的横排列输出 2 oldHPen = (HPEN) SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2, NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 for(int t = 0, x; t < 5; ++t) 9 { 10 x = 50*t; 11 SetViewportOrgEx(hdc, x, 0, NULL); 12 TextOut(hdc, 0, 0, TEXT("hello"), 5); 13 }
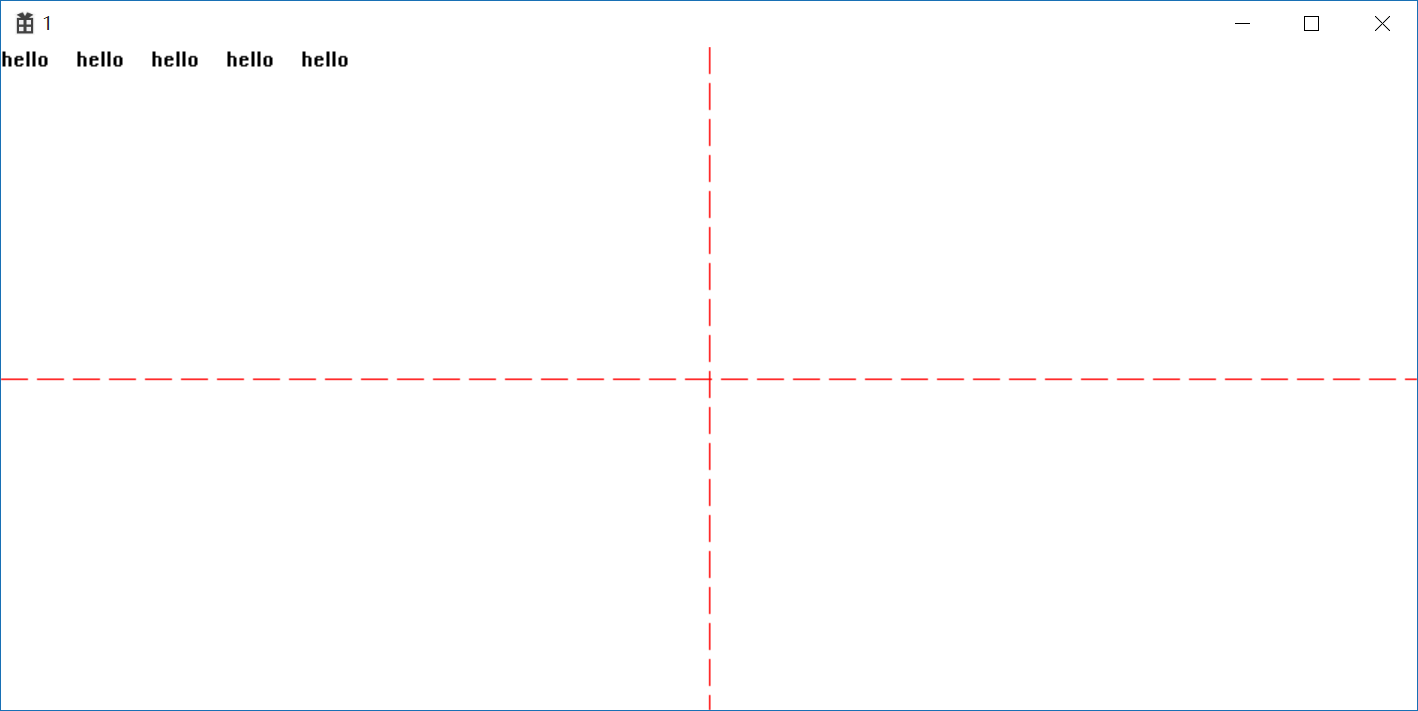
设置窗口原更改Rectanglex轴和y轴实现居中


1 //设置窗口原更改Rectanglex轴和y轴实现居中 2 oldHPen = (HPEN)SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2,NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 POINT apt; 9 apt.x = cxClient; 10 apt.y = cyClient; 11 DPtoLP(hdc, &apt, 1); 12 SetWindowOrgEx(hdc, -apt.x / 2, -apt.y / 2, NULL); 13 Rectangle(hdc, -50, 50, 50, -50);
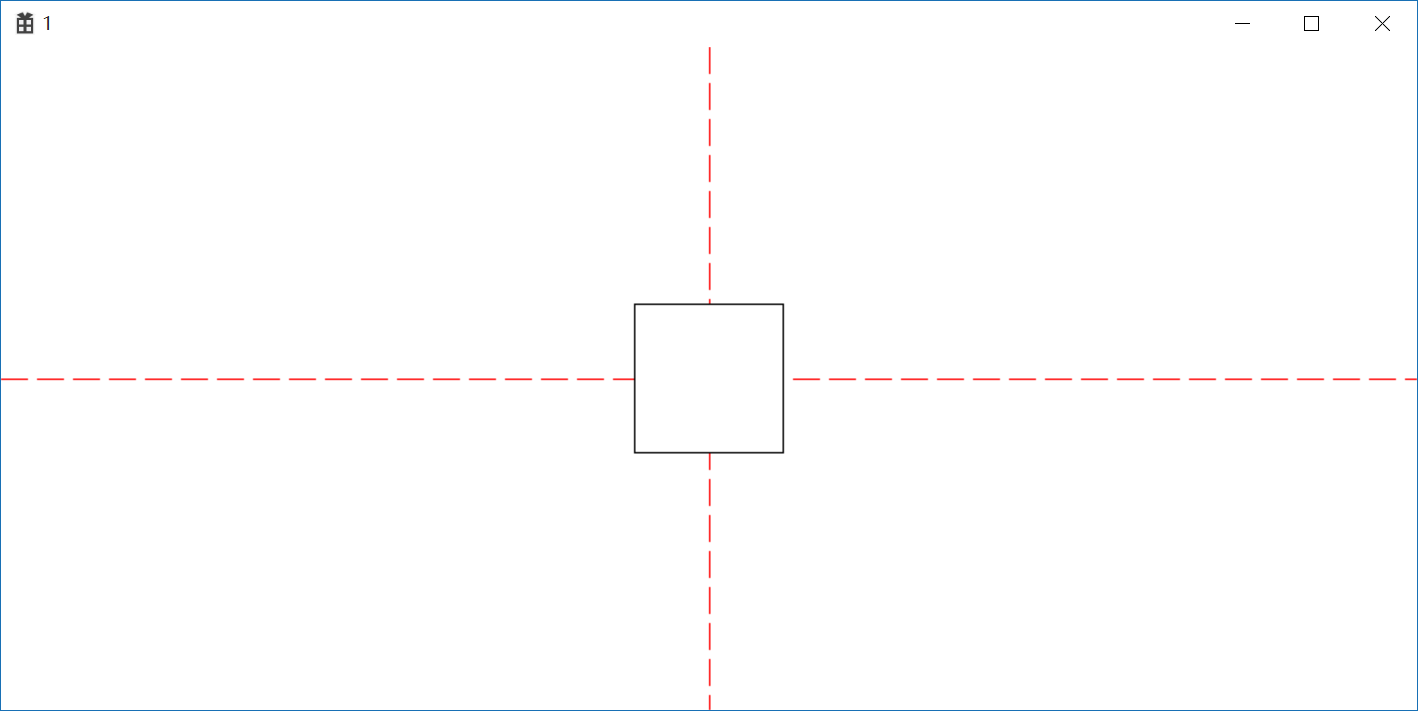
设置窗口原点实现Rectangle居中


1 //设置窗口原点实现Rectangle居中 2 oldHPen = (HPEN) SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 3 MoveToEx(hdc, cxClient / 2, 0, NULL); 4 LineTo(hdc, cxClient / 2, cyClient); 5 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, cyClient / 2, NULL); 6 LineTo(hdc, cxClient, cyClient / 2); 7 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 8 POINT apt; 9 apt.x = cxClient; 10 apt.y = cyClient; 11 DPtoLP(hdc, &apt, 1); 12 SetWindowOrgEx(hdc, -apt.x / 2+50, -apt.y / 2+50, NULL); 13 Rectangle(hdc, 0, 0, 100, 100);
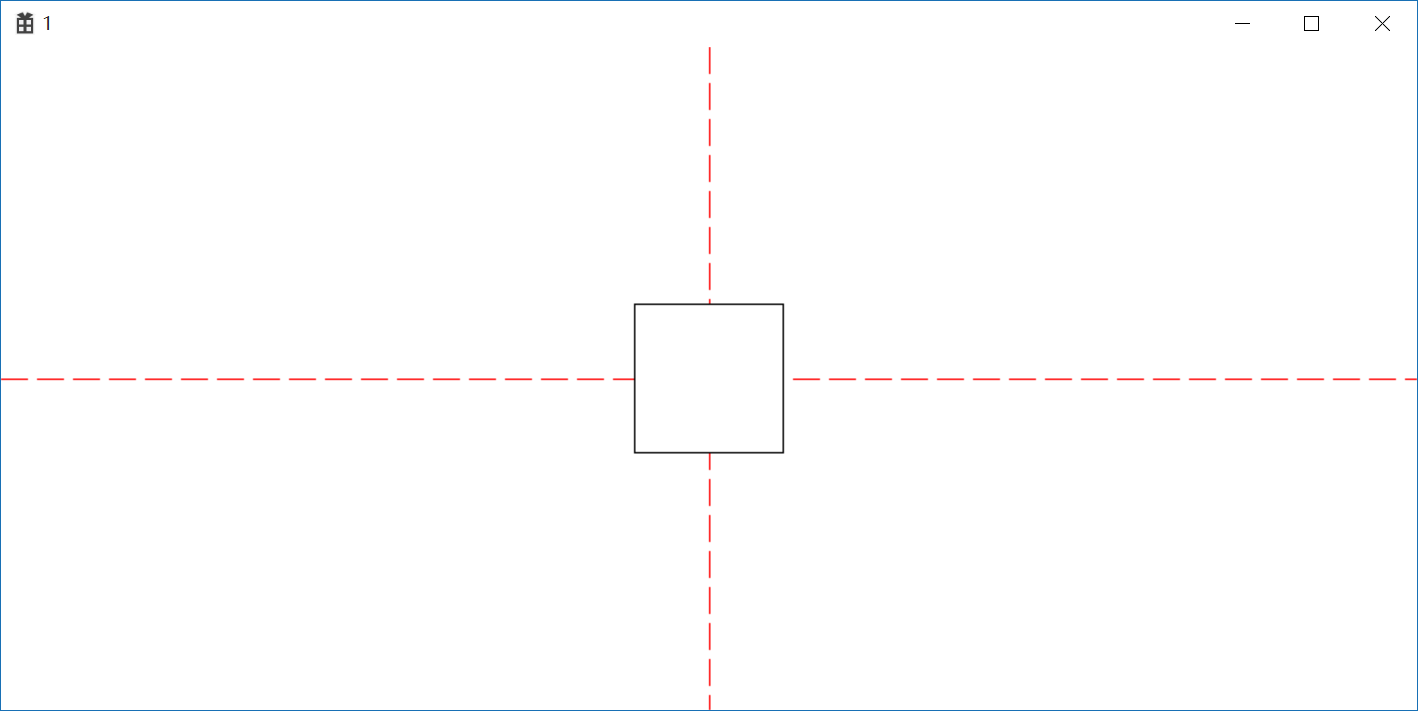
非MM_TEXT映射下的坐标转换更改Rectangle坐标轴


1 //非MM_TEXT映射下的坐标转换更改Rectangle坐标轴 2 SetMapMode(hdc, MM_LOMETRIC); 3 oldHPen = (HPEN) SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 4 POINT pt; 5 pt.x = cxClient; 6 pt.y = cyClient; 7 DPtoLP(hdc, &pt, 1); 8 MoveToEx(hdc, pt.x/2, 0, NULL); 9 LineTo(hdc, pt.x / 2, pt.y); 10 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, pt.y / 2, NULL); 11 LineTo(hdc, pt.x, pt.y / 2); 12 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 13 SetWindowOrgEx(hdc, -pt.x / 2, -pt.y / 2, NULL); 14 Rectangle(hdc, -50, 50, 50, -50);
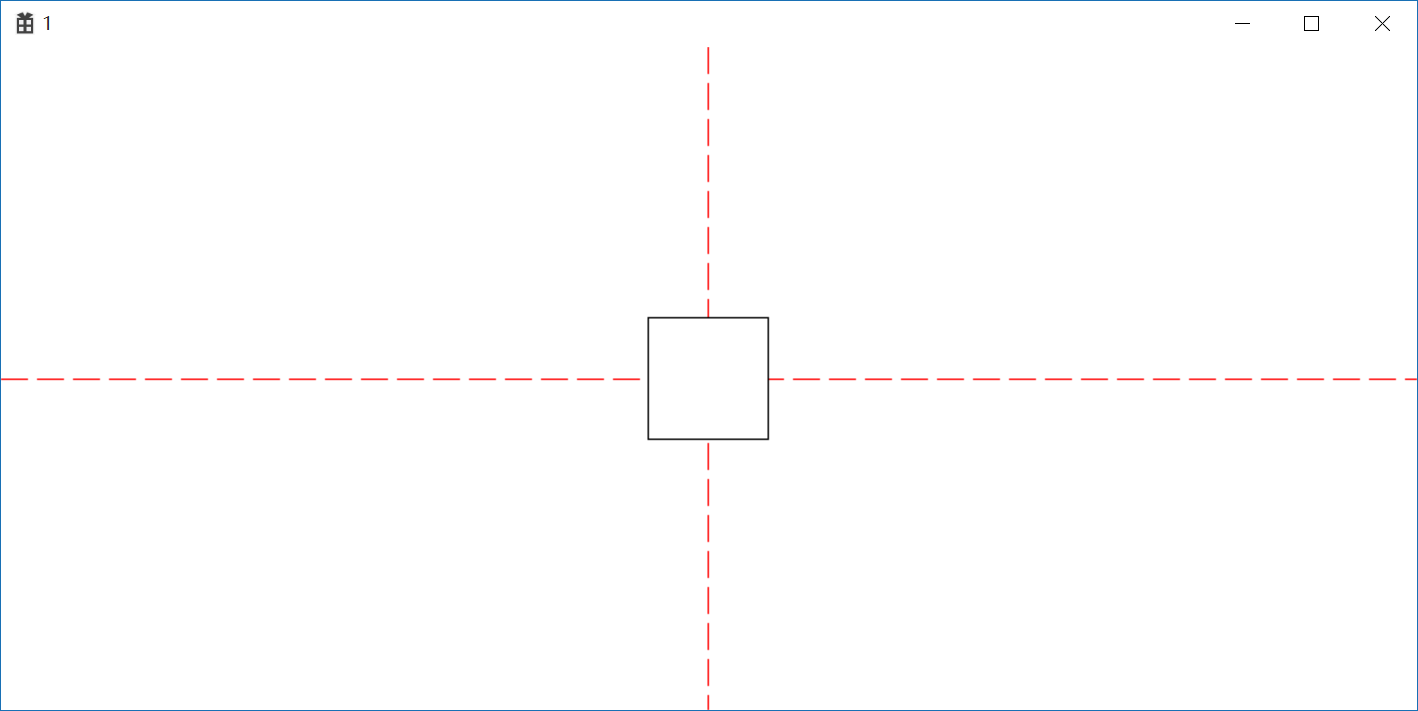
非MM_TEXT映射下的坐标转换更改原点实现Rectangle居中


1 //非MM_TEXT映射下的坐标转换更改原点实现Rectangle居中 2 SetMapMode(hdc, MM_LOMETRIC); 3 oldHPen = (HPEN) SelectObject(hdc, hPen); 4 POINT pt; 5 pt.x = cxClient; 6 pt.y = cyClient; 7 DPtoLP(hdc, &pt, 1); 8 MoveToEx(hdc, pt.x/2, 0, NULL); 9 LineTo(hdc, pt.x / 2, pt.y); 10 MoveToEx(hdc, 0, pt.y / 2, NULL); 11 LineTo(hdc, pt.x, pt.y / 2); 12 SelectObject(hdc, oldHPen); 13 SetWindowOrgEx(hdc, -pt.x / 2+50, -pt.y / 2+50, NULL); 14 Rectangle(hdc, 0,0, 100, 100);
等待更新……























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








