一、实验目的
- 理解和掌握 C++中函数的定义与使用方法
- 理解 C++中函数调用过程中值传递与引用传递的区别
- 灵活、综合运用 C++中分支结构、循环结构及 continue、break 等应用编程求解问题。
二、实验准备
实验前,请围绕以下内容预习/复习指定内容
- C++中函数的定义与使用方法
阅读、学习教材 3.1 节,学习/复习如下内容:- 函数定义的语法形式;函数形参和实参、返回值的作用;函数调用形式;函数参
数传递方式(值传递和引用传递) - 指定学习示例:第 3 章例 3-1,例 3-4,例 3-11,例 3-12
- 函数定义的语法形式;函数形参和实参、返回值的作用;函数调用形式;函数参
- C++中 if 语句、switch 语句、while 语句、do…while 语句的用法及其嵌套使用
- C++中 continue 语句、break 语句的用法
三、实验内容
- 验证性实验
- 运行教材 P68 例 3-4 源码,据此理解函数声明、函数定义、函数调用的方法,以
及形参、实参、返回值的作用,以及参数的值传递过程。 - 运行教材 P78 例 3-11 源码、P79 例 3-12 源码,观察二者运行结果的区别,结合
3.1.3 节的分析,理解并总结值传递和引用传递的区别
- 运行教材 P68 例 3-4 源码,据此理解函数声明、函数定义、函数调用的方法,以
- 编程实验
用 c++编程实现以下内容:- 习题 2-28(教材 P63)
- 习题 2-29(教材 P63)
- 习题 2-32(教材 P63)
- 习题 2-34(教材 P63)
四、实验结论
- 验证性实验部分
- 函数声明和函数定义各自的作用,二者的区别;
- 函数声明用于声明一个新的函数,可以将声明语句放在main函数之前,方便子函数之间的乱序调用,例如
int max(int a,int b); - 函数定义是指对函数内容的具现,例如
int max(int a,int b){return a>b?a:b;} - 两者区别在于函数声明只是告诉编译器有一个函数,并没有告知具体的参数调用,函数过程,返回值,而函数定义将函数声明不具备的元素完整的呈现给编译器。
- 函数声明用于声明一个新的函数,可以将声明语句放在main函数之前,方便子函数之间的乱序调用,例如
- 什么是形参?什么是实参?函数参数和返回值在函数中起到什么作用?
- 形参指出现在函数定义中,只能在函数内使用的参数。
- 实参指出现在主调用函数中,进入被调用函数后不能使用的参数,在被调用函数运算结束后,实参的值不会发生改变
- 函数参数是指调用时该函数必须传递的参数,在函数中利用其实现算法
- 函数返回值在函数中起到返回函数算法结果的作用
- 函数参数传递过程中,值传递和引用传递区别是什么?
- 值传递只传递参数的值,引用传递传递参数的地址
- 函数声明和函数定义各自的作用,二者的区别;
编程实验部分
2-28
- else-if
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ while(1){ char tmp; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit) Select One:"<<endl; cin>>tmp; if(tmp=='A'){cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl;continue;} else if(tmp=='D'){cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl;continue;} else if(tmp=='S'){cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl;continue;} else if(tmp=='Q'){break;} else continue; } return 0; }- switch-case
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ while(1){ char tmp; cout<<"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit) Select One:"<<endl; cin>>tmp; switch(tmp){ case 'A':cout<<"数据已经增加"<<endl;break; case 'D':cout<<"数据已经删除"<<endl;break; case 'S':cout<<"数据已经排序"<<endl;break; case 'Q':return 0; default:break; } } return 0; }Screenshot:
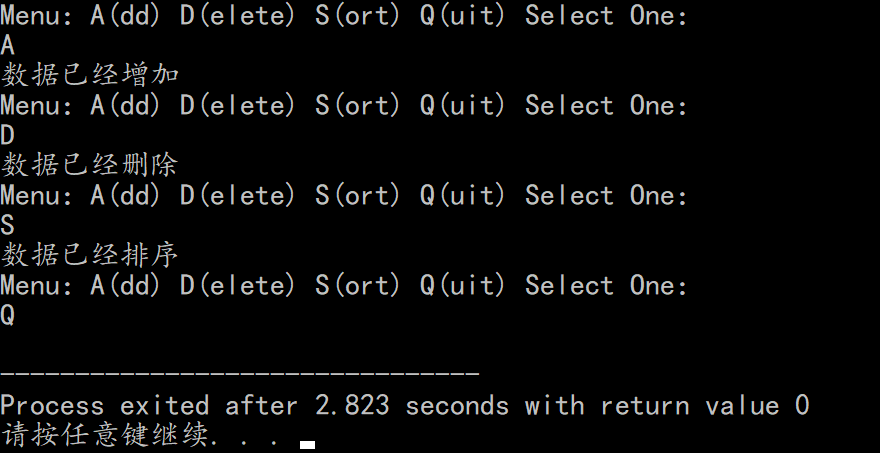 .
.2-29
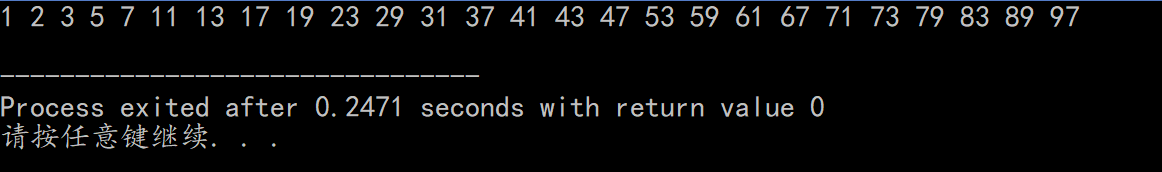
- 筛法求素数,对大于2的素数倍数设为合数,剩下的即是素数
- Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ bool num[101]={0}; for(int i=2;i<=100;++i){ if(!num[i])for(int j=i*2;j<=100;j+=i)num[j]=1; } for(int i=1;i<=100;++i)if(!num[i])cout<<i<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0; }Screenshot:
2-32
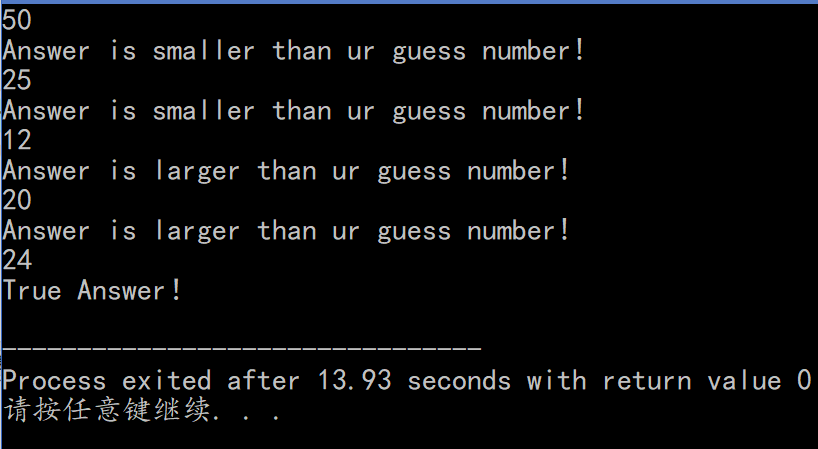
- while:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int n=rand()%100; int guess=101; while(guess!=n) { cin>>guess; if(guess<n)cout<<"Answer is larger than ur guess number!"<<endl; else if(guess>n)cout<<"Answer is smaller than ur guess number!"<<endl; } cout<<"True Answer!"<<endl; return 0; }- do-while:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int n=rand()%100; int guess=101; do{ cin>>guess; if(guess<n)cout<<"Answer is larger than ur guess number!"<<endl; else if(guess>n) cout<<"Answer is smaller than ur guess number!"<<endl; }while (guess!=n); cout<<"True Answer!"<<endl; return 0; }Screenshot:
2-34
- 使用DFS模拟拿球,use数组存放使用情况,每次种类为:
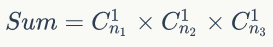 ,对每次模拟拿球结果累加,得到结果。
,对每次模拟拿球结果累加,得到结果。 - Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define rap(a,b) for(int a=0;a<b;++a) #define r() rand()%10 int color[5]; bool use[5]={0}; using namespace std; int dfs(int j,int t){ int tmp=0; if (t==3)return color[j];//第三次拿球直接返回个数 rap(i,5) if(!use[i]){ use[i]=1; tmp+=dfs(i,t+1); use[i]=0; } return tmp*color[j];//根据公式返回当前拿球状况下的个数 } int main(){ int sum=0; srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); rap(i,5)color[i]=r(); rap(i,5){ use[i]=1; sum+=dfs(i,1); use[i]=0; } cout<<sum<<endl; return 0; }- Screenshot:
- 填充1:
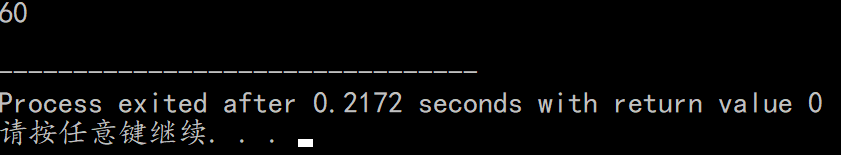
验证: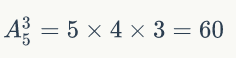
- 填充2
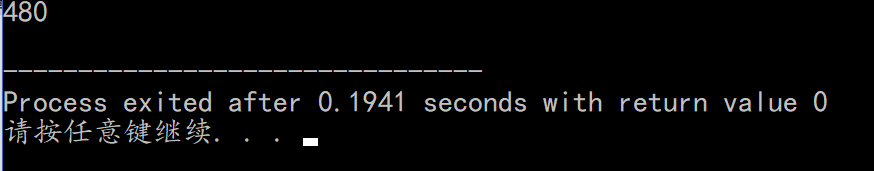
验证: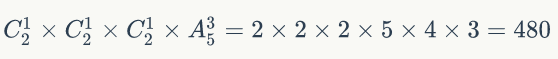
- 填充1:























 441
441

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








