C……没啥好说的……感觉……找一行或一列中有多少个连续的k个‘.’(虽然因为一个i,j写反了搞了好久才改出来orz)
(k==1的时候要特判一下,或者直接ans/2也可以的样子)
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn=1e5; int n,m,k,ans=0; char mz[2005][2005]; int main() { cin>>n>>m>>k; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cin>>mz[i][j]; if(k==1) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) if(mz[i][j]=='.') ans++; } else if(k>m&&k>n) ans=0; else { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { int cnt=0; for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { if(mz[i][j]=='.') { cnt++; if(cnt>=k) ans++; } else cnt=0; } } for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int cnt=0; for(int j=0;j<n;j++) { if(mz[j][i]=='.') { cnt++; if(cnt>=k) ans++; } else cnt=0; } } } cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
DP+拓扑排序
It is obvious that we can use dynamic programming algorithm to solve this stupid problem.
We can make an array f[i][j] to respect when you are at the point i, then how many letters j you can get. Note that i is ranging from 1 to n and j is from 1 to 26.
Then, you can do this dynamic programming algorithm by topological sorting. Specifically, you can use deg[i] to show how many edges that end at point i. First put all points i which satisfy deg[i] = 0 into a queue. When the queue is not empty, do the following steps repeatedly.
- Take one point from the front of the queue. We say it is i.
- Iterate all edges which begin at the point i. We say the endpoint of the edge is k. Then we update f[k][·] using f[i][·]. Finally we make deg[k] minus by 1. If deg[k] = 0, then we add the point k into the queue.
- Make a variable cnt plus by 1.
When there is no cycle in the graph, the queue will be empty with cnt = n. Then the answer is the maximum number among f[i][j]. If there are cycles in the graph, then cnt cannot be n. Thus the answer can be arbitrarily large. In that situation, we should output -1.
Time complexity: 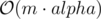 , where alpha is the size of the alphabet (i.e. alpha = 26).
, where alpha is the size of the alphabet (i.e. alpha = 26).
Memory complexity: 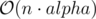 .
.
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn=3e5+5; int n,m,cnt=0; int dp[maxn][26],deg[maxn],head[maxn]; string a; queue<int>q; struct edge{ int to,nxt; }e[maxn<<1]; void add(int u,int v) { e[cnt].to=v; e[cnt].nxt=head[u]; head[u]=cnt++; } void topo() { queue<int>q; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(!deg[i]) { q.push(i); dp[i][a[i-1]-'a']++; } } int crt=0; while(!q.empty()) { int u = q.front();q.pop(); crt++; for(int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].nxt) { int v=e[i].to; deg[v]--; if(!deg[v]) q.push(v); for(int j=0;j<26;j++) dp[v][j]=max(dp[v][j],dp[u][j]+(a[v-1]-'a'==j)); } } if(crt<n) cout<<"-1"<<endl; else{ int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=0;j<26;j++) ans=max(ans,dp[i][j]); cout<<ans<<endl; } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin>>n>>m>>a; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(dp,0,sizeof(0)); for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int u,v; cin>>u>>v; add(u,v); deg[v]++; } topo(); return 0; }







 本文介绍了一个简单的算法问题,即在一个矩阵中计数连续的字符,并使用动态规划与拓扑排序解决了一个涉及字符串和图的问题。
本文介绍了一个简单的算法问题,即在一个矩阵中计数连续的字符,并使用动态规划与拓扑排序解决了一个涉及字符串和图的问题。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








