As a system administrator or Linux power user, you may have probably come across or even on several occasions, used the versatile Linux Rsync tool, which enables users to expeditiously copy or synchronize files locally and remotely. It is as well a great tool popularly used for backup operations and mirroring.
Some of its eminent features and advantages include; it is exceptionally versatile in that, it can copy locally, to/from a remote shell or remote rsync, it is also remarkably flexible, allowing users to specify any number of files to copy.
Suggested Read: 10 Practical Examples of Rsync Command in Linux
Furthermore, it permits copying of links, devices, file or directory owner, groups and the permissions. It also supports usage without root privileges coupled with many more.
One imperative differential of rsync in comparison to other file-coying commands in Linux is its use of the remote-update protocol, to transfer only the difference between files or directory content.
Therefore, in this article, we shall examine how rsync can help us only sync new or changed files or directory content while making backups and beyond in Linux.
To start with, you need remember that the conventional and simplest form of using rsync is as follows:
# rsync options source destination
That said, let us dive into some examples to uncover how the concept above actually works.
Syncing Files Locally Using Rsync
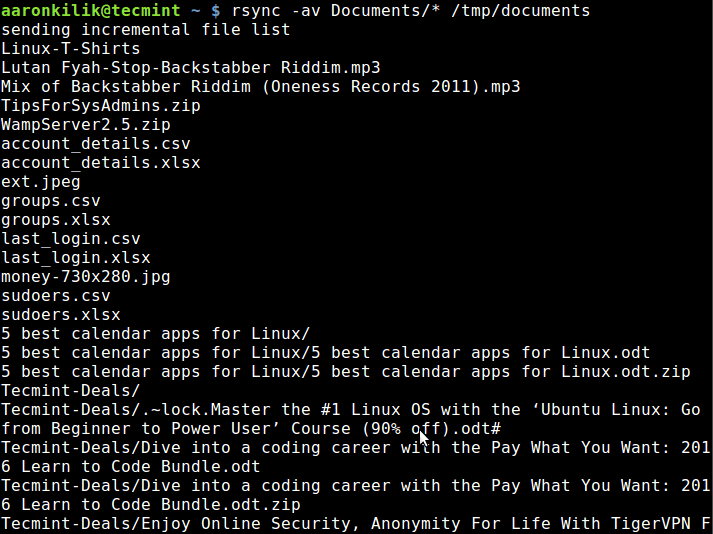
Using the command below, am able to copy files from my Documents directory to /tmp/documentsdirectory locally:
$ rsync -av Documents/* /tmp/documents
In the command above, the option:
-a– means archive mode-v– means verbose, showing details of ongoing operations
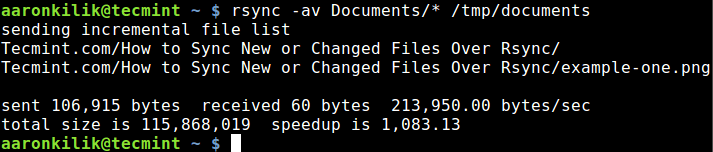
By default, rsync only copies new or changed files from a source to destination, when I add a new file into myDocuments directory, this is what happens after running the same command second time:
$ rsync -av Documents/* /tmp/documents
As you can observe and notice from the output of the command, only the new file is copied to the destination directory.
Suggested Read: How to Sync Two Apache Web Servers/Websites Using Rsync
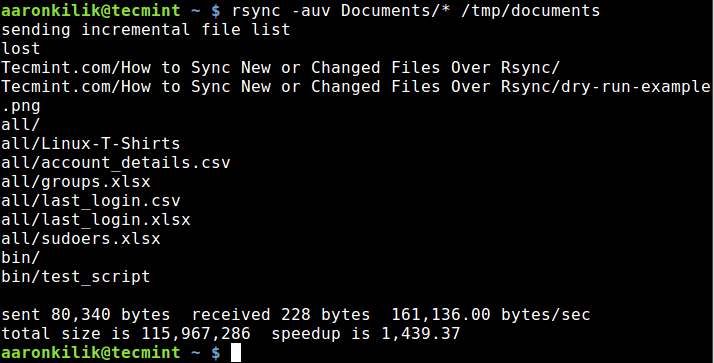
The --update or -u option allows rsync to skip files that are still new in the destination directory, and one important option, --dry-run or -n enables us to execute a test operation without making any changes. It shows us what files are to be copied.
$ rsync -aunv Documents/* /tmp/documents
After executing a test run, we can then do away with the -n and perform a real operation:
$ rsync -auv Documents/* /tmp/documents
Syncing Files From Local to Remote Linux
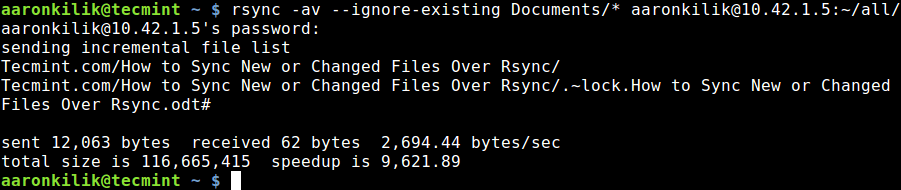
In the example below, I am copying files from my local machine to a remote sever with the IP address –10.42.1.5. So as to only sync new files on the local machine, that do not exist on the remote machine, we can include the --ignore-existing option:
$ rsync -av --ignore-existing Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/
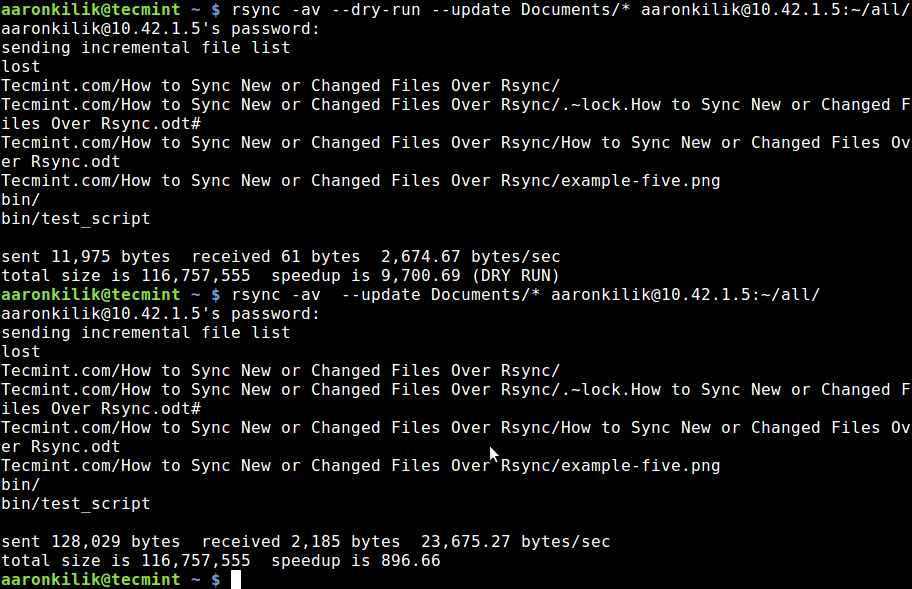
Subsequently, to sync only updated or modified files on the remote machine that have changed on the local machine, we can perform a dry run before copying files as below:
$ rsync -av --dry-run --update Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/ $ rsync -av --update Documents/* aaronkilik@10.42.1.5:~/all/
To update existing files and prevent creation of new files in the destination, we utilize the --existing option.
You can run through the rsync man page to discover additionally useful options for advanced usage, as I had mentioned earlier on, rsync is a very powerful and versatile Linux tool and many System Administrator and Linux power users know just how advantageous it is.
Most importantly, you can as well share your view on the examples we have covered here or even better still, offer us valuable tips on using this vital command line tool through the comment section below.




 本文介绍了如何使用Linux下的Rsync工具进行本地及远程文件同步。Rsync具备多种实用特性,如仅同步已更改文件、支持远程更新协议等,非常适合用于备份操作及镜像创建。
本文介绍了如何使用Linux下的Rsync工具进行本地及远程文件同步。Rsync具备多种实用特性,如仅同步已更改文件、支持远程更新协议等,非常适合用于备份操作及镜像创建。

















 1042
1042

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








