如何查看viewstate
鼠标右键页面,然后view page source
源码中搜索viewstate,会找到一个隐藏的字段。
<input type="hidden" name="__VIEWSTATE" id="__VIEWSTATE" value="/wEPaA8FDzhkNmJlYWE3ODdlY2ZhMxgFBRpjdGwwMCRjcGhNYWluJHVjUHJvZmlsZSRJZA8FATVkBSBjdGwwMCRjcGhNYWluJHVjUHJvZmlsZSRMYXN0TmFtZQ8FA+WNomQFG2N0bDAwJGNwaE1haW4kdWNQcm9maWxlJEFnZQ8FAjMyZAUhY3RsMDAkY3BoTWFpbiR1Y1Byb2ZpbGUkRmlyc3ROYW1lDwUG5L+K5rabZAUdY3RsMDAkY3BoTWFpbiR1Y1Byb2ZpbGUkTW9uZXkPBQwwLjAwMDAwMjU1MjBkq9Xg7eCkuRMKxXAWft9MqgH5A1AKB7Ai3JQcgVlh+OI=" />
还有可能搜到一个叫__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR的字段,不过这个不是viewstate
<input type="hidden" name="__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR" id="__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR" value="8EB90039" />
F12,然后在elements菜单中进行搜索
解密
通过这个页面,可以进行解密http://viewstatedecoder.azurewebsites.net/
需要注意是有可能只能部分解密
32 byte(s) left over, perhaps an HMACSHA256 signature?
浅谈ViewState
一、ViewState概述
① ViewState是基于webform的
② 在web窗体控件属性处设置runat = "server",这个控件会被附加一个隐藏的属性_ViewState,_ViewState存放了所有控件在ViewState中的状态值。
③ 页面会在输出时,自动添加下面的隐藏域:
value处的值只是base64编码并不是加密。
④ ViewState是一个名称/值的对象集合。
⑤ 当请求某个页面时,ASP.NET会把所有控件的状态序列化成一个字符串,然后作为窗体的隐藏属性送到客户端,当客户端将页面回传时,ASP.NET分析回传的窗体属性,并赋给控件对应的值。(恢复现场)
⑥ ViewState不能存储所有的数据类型,仅支持:String、Integer、Boolean、Array、ArrayList、Hashtable
防止篡改
How to Make ViewState Secure in ASP.NET
Understanding ASP.NET View State
What Is View State And How It Works In ASP.NET
Background
State Management Techniques
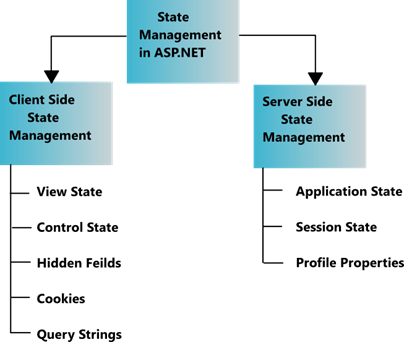

View State
//Declaration of a and b public string a, b; protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //TextBox1 and TextBox2 Value is Assigning on the variable a and b a = TextBox1.Text; b = TextBox2.Text; //after clicking on Button TextBox value Will be Cleared TextBox1.Text = TextBox2.Text = string.Empty; } protected void Button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //value of variable a and b is assingning on TextBox1 and Textbox2 TextBox1.Text = a; TextBox2.Text = b; }
Features Of View State
- Retains the value of the Control after post-back without using a session.
- Stores the value of Pages and Control Properties defined in the page.
- Creates a custom View State Provider that lets you store View State Information in a SQL Server Database or in another data store.
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //Value of Textbox1 and TectBox2 is assigin on the ViewState ViewState["name"] = TextBox1.Text; ViewState["password"] = TextBox2.Text; //after clicking on Button TextBox value Will be Cleared TextBox1.Text = TextBox2.Text = string.Empty; } protected void Button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //If ViewState Value is not Null then Value of View State is Assign to TextBox if (ViewState["name"] != null) { TextBox1.Text = ViewState["name"].ToString(); } if (ViewState["password"] != null) { TextBox2.Text = ViewState["password"].ToString(); } }
Data Objects That Can be Stored in View state
- String
- Boolean Value
- Array Object
- Array List Object
- Hash Table
- Custom type Converters
Advantages of View State
- Easy to Implement.
- No server resources are required: The View State is contained in a structure within the page load.
- Enhanced security features: It can be encoded and compressed or Unicode implementation.
Disadvantages of View State
- Security Risk: The Information of View State can be seen in the page output source directly. You can manually encrypt and decrypt the contents of a Hidden Field, but It requires extra coding. If security is a concern then consider using a Server-Based state Mechanism so that no sensitive information is sent to the client.
- Performance: Performance is not good if we use a large amount of data because View State is stored in the page itself and storing a large value can cause the page to be slow.
- Device limitation: Mobile Devices might not have the memory capacity to store a large amount of View State data.
- It can store values for the same page only.
When We Should Use View State
- When the data to be stored is small.
- Try to avoid secure data.




















 859
859

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








