java线程在运行的声明周期会有6种不同的状态,在给定的一个时刻,线程只能处于其中的一个状态。

注意:java将操作系统中的运行和就绪两个状态合并称为运行状态。
阻塞状态是进入Synchronized关键字修饰的方法或代码块获取锁的状态。
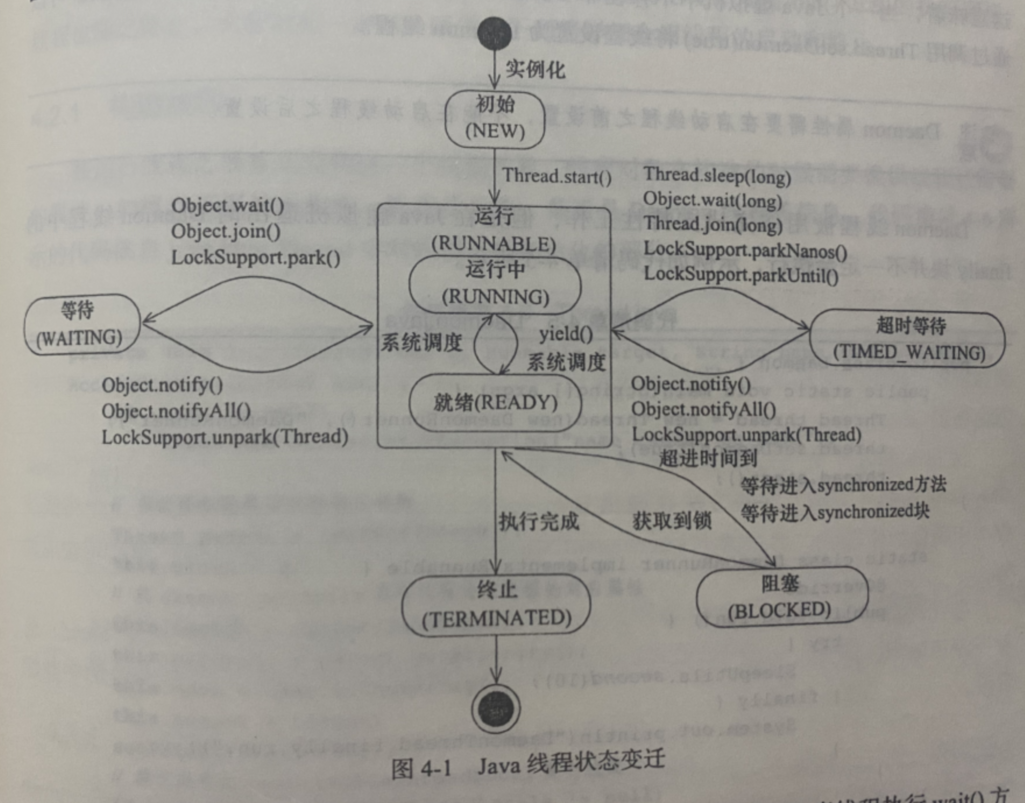
(1)线程创建后,调用start方法开始运行。
(2)线程执行wait方法,进入等待状态。
a.进入等待状态的线程需要依靠其他线程的通知才能返回运行状态
b.超时状态相当于在等待状态的基础上增加了超时限制,超时时间到达会自动返回运行状态。
(3)当线程调用同步方法时,在没有获取到锁的情况下,线程会进入阻塞状态
(4)线程在执行完Runnable的run方法后会进入到终止状态
测试代码:
public class 线程状态 {
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new TimeWaiting(),"TimeWaitingThread").start();
new Thread(new Waiting(),"WaitingThread").start();
//使用两个blocke线程,一个获取锁成功,另一个被阻塞
new Thread(new Blocked(),"BlockedThread-1").start();
new Thread(new Blocked(),"BlockedThread-2").start();
}
//该线程不断进行睡眠
static class TimeWaiting implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
SleepUtils.second(100);
}
}
}
//该线程在Waiting.class实例上等待
static class Waiting implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (Waiting.class){
try {
Waiting.class.wait();
/*
* Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the notify() method or
* the notifyAll() method for this object.
* In other words, this method behaves exactly as if it simply performs the call wait(0).
* The current thread must own this object's monitor.
* The thread releases ownership of this monitor and waits until another thread notifies threads waiting on this object's monitor to wake up either through a call to the notify method or the notifyAll method.
* The thread then waits until it can re-obtain ownership of the monitor and resumes execution.
* As in the one argument version, interrupts and spurious wakeups are possible,
* and this method should always be used in a loop:
synchronized (obj) {
while (<condition does not hold>)
obj.wait();
... // Perform action appropriate to condition
}
*/
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
//该线程在Blocked.class实例上加锁后,不会释放该锁。
static class Blocked implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run(){
synchronized (Blocked.class){
while(true){
SleepUtils.second(100);
}
}
}
}
}
class SleepUtils{
public static final void second(long seconds){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
- 72.























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








