求助android studio 的可视化布局中文乱码-优快云论坛-youkuaiyun.com-中国最大的IT技术社区
http://bbs.youkuaiyun.com/topics/391887442
Android Studio各种类型乱码处理 - Helen_Chen的博客 - 博客频道 - youkuaiyun.com
http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/laurachen93/article/details/51475479
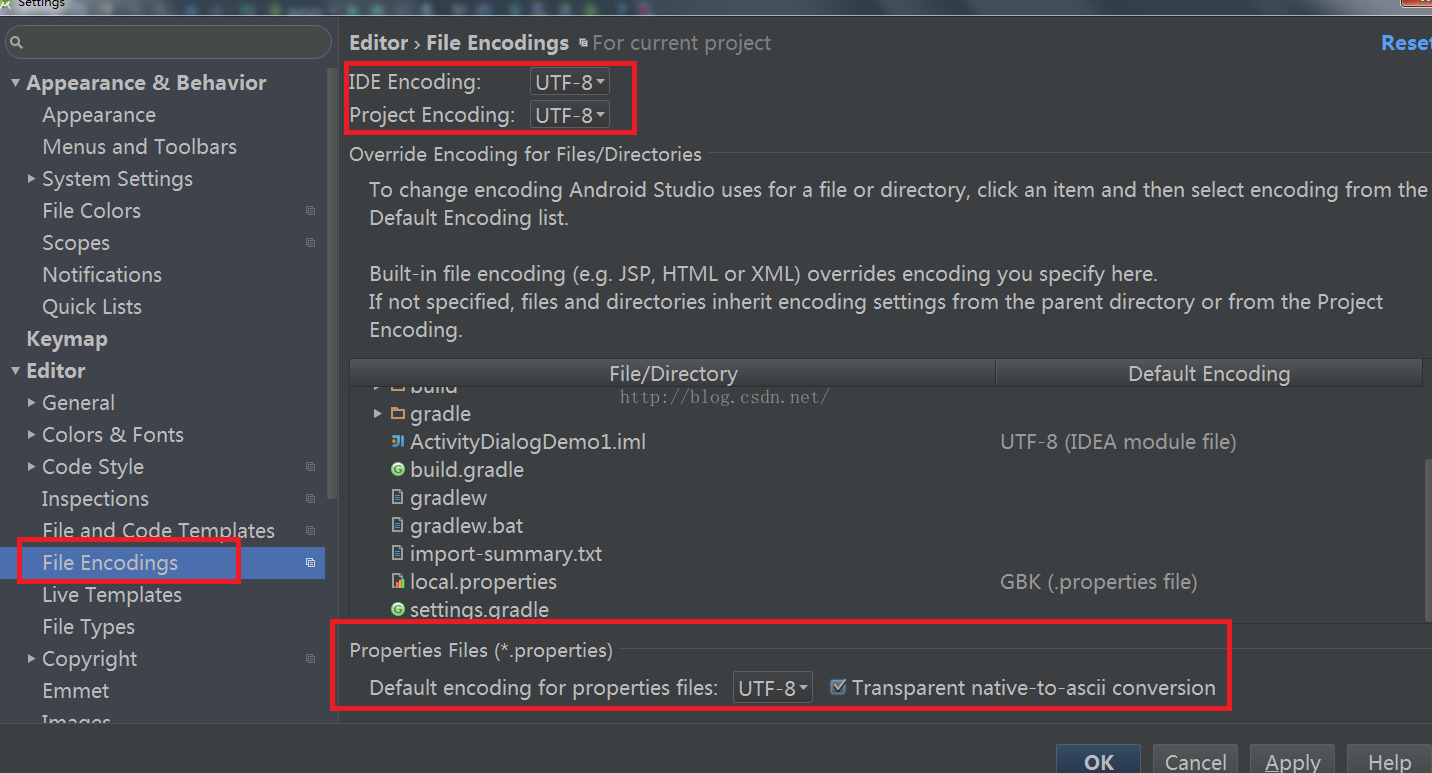
1.settings中修改文件编码为utf8;
2.xml布局文件,实时预览界面修改翻译为中文---右侧地球图标
---还是解决不了啊,不过最终编译显示OK,估计是AS2.4谷歌的bug,看来bug不少啊




















 551
551

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








