目录
- 序列化
- 反序列化
- Mybatis中的实际使用
主要知识点:
- writeObject
- writeReplace
- readObject
- readResolve
序列化与反序列化的定义
序列化就是将对象转为字节码的过程,反序列化则是将字节码转换为对象的过程
序列化
JAVA序列化
java.io.ObjectOutputStream代表对象输出流,它的writeObject(Object obj)方法可对参数指定的obj对象进行序列化,把得到的字节序列写到一个目标输出流中。
java.io.ObjectInputStream代表对象输入流,它的readObject()方法从一个源输入流中读取字节序列,再把它们反序列化为一个对象,并将其返回。
只有实现了Serializable和Externalizable接口的类的对象才能被序列化。Externalizable接口继承自 Serializable接口,实现Externalizable接口的类完全由自身来控制序列化的行为,而仅实现Serializable接口的类可以 采用默认的序列化方式 。
通常对象序列化包括如下步骤:
1) 创建一个对象输出流,它可以包装一个其他类型的目标输出流,如文件输出流;
2) 通过对象输出流的writeObject()方法写对象。
对象反序列化的步骤如下:
1) 创建一个对象输入流,它可以包装一个其他类型的源输入流,如文件输入流;
2) 通过对象输入流的readObject()方法读取对象。
通过测试代码分析序列化执行过程,通过本文可以理解writeObject,writeReplace方法的执行顺序,以及序列化执行的具体过程。
public class Author implements Serializable {
protected int id;
protected String username;
protected String password;
protected String email;
protected String bio;
protected Section favouriteSection;
public Author() {
this(-1, null, null, null, null, null);
}
public Author(Integer id, String username, String password, String email, String bio, Section section) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.email = email;
this.bio = bio;
this.favouriteSection = section;
}
public Author(int id) {
this(id, null, null, null, null, null);
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public void setBio(String bio) {
this.bio = bio;
}
public void setFavouriteSection(Section favouriteSection) {
this.favouriteSection = favouriteSection;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public String getBio() {
return bio;
}
public Section getFavouriteSection() {
return favouriteSection;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("readObject");
in.defaultReadObject();
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException{
System.out.println("writeObject");
out.defaultWriteObject();
}
Object writeReplace() throws ObjectStreamException{
System.out.println("writeReplace");
Author replaced=new Author();
replaced.setId(123);
return replaced;
}
@Test
public void testSeria() throws Exception{
Author author=new Author();
author.setId(456);
Serializable result= deserialize(serialize((Serializable)author));
System.out.println(((Author)result).getId());
}
protected byte[] serialize(Serializable value) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(value);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
return bos.toByteArray();
}
protected Serializable deserialize(byte[] value) throws Exception {
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(value);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Serializable result = (Serializable) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return result;
}
上面的测试代码我们序列化的是ID是456的Author对象,但是反序列化后的对象确实123.
writeReplace
writeObject
readObject
123
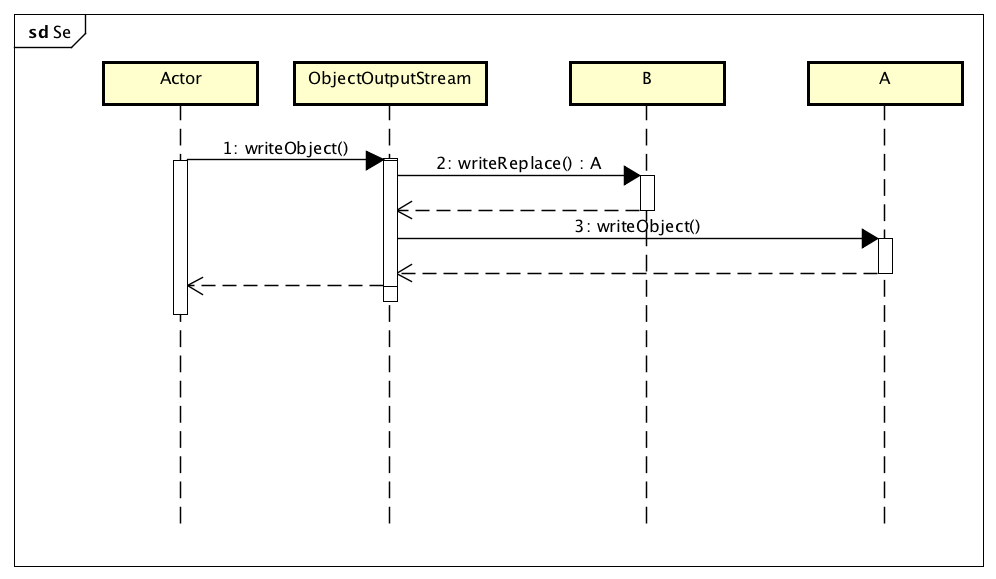
这样似乎和文章开头介绍的序列化只是不一样,这个是哪里除了问题呢?在上文说了通常的序列化是如上文所说处理的,但是在ObjectOuputStream中还有一个writeReplace方法,通过该方法可以替换掉原来需要序列化的对象,时序图如下所示:
通过测试代码可以发现,序列化过程如下:
相关源码如下:
在调用writeObject方法时会判断需要序列化对象是否存在writeReplace方法,如果存在则会调用该方法得到一个新的目标对象,并将其进行序列化
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (enableOverride) {
writeObjectOverride(obj);
return;
}
try {
writeObject0(obj, false);
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (depth == 0) {
writeFatalException(ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
private void writeObject0(Object obj, boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
。。。。
for (;;) {
// REMIND: skip this check for strings/arrays?
Class<?> repCl;
desc = ObjectStreamClass.lookup(cl, true);
//如果存在writeReplace方法,调用需要序列化对象的writeReplace方法,如果返回对象不为null且writeReplace返回对象和原序列化对象类相同则退出循环
if (!desc.hasWriteReplaceMethod() ||
(obj = desc.invokeWriteReplace(obj)) == null ||
(repCl = obj.getClass()) == cl)
{
break;
}
cl = repCl;
}
。。。
// remaining cases
if (obj instanceof String) {
writeString((String) obj, unshared);
} else if (cl.isArray()) {
writeArray(obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Enum) {
writeEnum((Enum<?>) obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Serializable) { //如果实现了Serializable接口
writeOrdinaryObject(obj, desc, unshared);
} else {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
throw new NotSerializableException(
cl.getName() + "\n" + debugInfoStack.toString());
} else {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName());
}
}
} finally {
depth--;
bout.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
private void writeOrdinaryObject(Object obj,
ObjectStreamClass desc,
boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
。。。
try {
desc.checkSerialize();
bout.writeByte(TC_OBJECT);
writeClassDesc(desc, false);
handles.assign(unshared ? null : obj);
if (desc.isExternalizable() && !desc.isProxy()) {
writeExternalData((Externalizable) obj);
} else {//写序列化数据
writeSerialData(obj, desc);
}
} finally {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
private void writeSerialData(Object obj, ObjectStreamClass desc)
throws IOException{
。。。
try {
curContext = new SerialCallbackContext(obj, slotDesc);
bout.setBlockDataMode(true);
//调用序列化对象的writeObject方法
slotDesc.invokeWriteObject(obj, this);
bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
bout.writeByte(TC_ENDBLOCKDATA);
} finally {
curContext.setUsed();
curContext = oldContext;
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
debugInfoStack.pop();
}
}
}
}
反序列化
上面主要讲述了序列化的相关知识,那么反序列化呢?下面就介绍一下反序列化步骤。
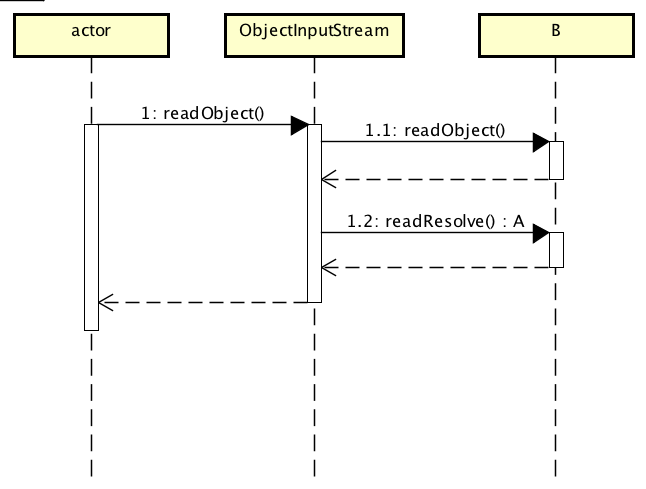
主要的几个方法如下:
-->readObject
|
\-->readObject0
|
\--->readOrdinaryObject
|
|--->invokeReadObject
| |
| \--->readObjectMethod.invoke
\------>invokeReadReslove
public final Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
if (enableOverride) {
return readObjectOverride();
}
// if nested read, passHandle contains handle of enclosing object
int outerHandle = passHandle;
try {
//调用readObject0方法完成反序列化
Object obj = readObject0(false);
handles.markDependency(outerHandle, passHandle);
ClassNotFoundException ex = handles.lookupException(passHandle);
if (ex != null) {
throw ex;
}
if (depth == 0) {
vlist.doCallbacks();
}
return obj;
} finally {
passHandle = outerHandle;
if (closed && depth == 0) {
clear();
}
}
}
private Object readObject0(boolean unshared) throws IOException {
。。。。
try {
switch (tc) {
case TC_NULL:
return readNull();
case TC_REFERENCE:
return readHandle(unshared);
case TC_CLASS:
return readClass(unshared);
case TC_CLASSDESC:
case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC:
return readClassDesc(unshared);
case TC_STRING:
case TC_LONGSTRING:
return checkResolve(readString(unshared));
case TC_ARRAY:
return checkResolve(readArray(unshared));
case TC_ENUM:
return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared));
case TC_OBJECT://对象的反序列化
return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared));
case TC_EXCEPTION:
IOException ex = readFatalException();
throw new WriteAbortedException("writing aborted", ex);
case TC_BLOCKDATA:
case TC_BLOCKDATALONG:
if (oldMode) {
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
bin.peek(); // force header read
throw new OptionalDataException(
bin.currentBlockRemaining());
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected block data");
}
case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA:
if (oldMode) {
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected end of block data");
}
default:
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
String.format("invalid type code: %02X", tc));
}
} finally {
depth--;
bin.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
private Object readOrdinaryObject(boolean unshared) throws IOException{
if (bin.readByte() != TC_OBJECT) {
throw new InternalError();
}
ObjectStreamClass desc = readClassDesc(false);
desc.checkDeserialize();
Class<?> cl = desc.forClass();
if (cl == String.class || cl == Class.class
|| cl == ObjectStreamClass.class) {
throw new InvalidClassException("invalid class descriptor");
}
Object obj;
try {
obj = desc.isInstantiable() ? desc.newInstance() : null;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw (IOException) new InvalidClassException(
desc.forClass().getName(),
"unable to create instance").initCause(ex);
}
passHandle = handles.assign(unshared ? unsharedMarker : obj);
ClassNotFoundException resolveEx = desc.getResolveException();
if (resolveEx != null) {
handles.markException(passHandle, resolveEx);
}
//完成对象的反序列化
if (desc.isExternalizable()) {
readExternalData((Externalizable) obj, desc);
} else {
readSerialData(obj, desc);
}
handles.finish(passHandle);
//如果这个对象实现了readResolve方法则调用该方法
if (obj != null &&
handles.lookupException(passHandle) == null &&
desc.hasReadResolveMethod())
{
Object rep = desc.invokeReadResolve(obj);
if (unshared && rep.getClass().isArray()) {
rep = cloneArray(rep);
}
if (rep != obj) {
handles.setObject(passHandle, obj = rep);
}
}
return obj;
}
Mybatis中的实际使用
@Override
public Object invoke(Object enhanced, Method method, Method methodProxy, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
final String methodName = method.getName();
try {
synchronized (lazyLoader) {
//如果当前调用是writeReplace 则表示需要对象当前对象进行序列化,而当前对象是一个代理对象,直接对当前对象序列化显然是不合理的
//在上面的代码可以发现代理对对象都存在writeReplace方法,在序列化的时候会调用该方法,在对该方法进行增强处理返回原始对对象,如果需要延迟加载
//则返回了一个序列化状态保持对象
if (WRITE_REPLACE_METHOD.equals(methodName)) {
Object original;
//创建一个新的原始对象
if (constructorArgTypes.isEmpty()) {
original = objectFactory.create(type);
} else {
original = objectFactory.create(type, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
}
//复制属性
PropertyCopier.copyBeanProperties(type, enhanced, original);
//如果存在延迟加载对象则创建一个代理对象
if (lazyLoader.size() > 0) {
return new JavassistSerialStateHolder(original, lazyLoader.getProperties(), objectFactory, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs);
} else {//如果没有延迟加载对象
return original;
}
} else {// 如果不是writeReplace方法
//如果懒加载对象大于0且当前不是finalize方法
if (lazyLoader.size() > 0 && !FINALIZE_METHOD.equals(methodName)) {
//如果是积极的懒加载模式或者调用列触发加载全部方法则加载全部懒加载属性
if (aggressive || lazyLoadTriggerMethods.contains(methodName)) {
lazyLoader.loadAll();
} else if (PropertyNamer.isSetter(methodName)) {
//如果setter的属性是懒加载的则从懒加载映射表中删除
final String property = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(methodName);
lazyLoader.remove(property);
} else if (PropertyNamer.isGetter(methodName)) {
//如果getter的属性是懒加载的此时需要加载
final String property = PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(methodName);
if (lazyLoader.hasLoader(property)) {
lazyLoader.load(property);
}
}
}
}
}
return methodProxy.invoke(enhanced, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
@Override
public final void writeExternal(final ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
boolean firstRound = false;
final ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream os = stream.get();
if (os == null) {
os = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
firstRound = true;
stream.set(os);
}
//序列化userBean
os.writeObject(this.userBean);
//序列化未加载属性
os.writeObject(this.unloadedProperties);
//序列化对象工厂
os.writeObject(this.objectFactory);
//序列化构造参数类型
os.writeObject(this.constructorArgTypes);
//序列化构造参数
os.writeObject(this.constructorArgs);
final byte[] bytes = baos.toByteArray();
//完成序列化
out.writeObject(bytes);
if (firstRound) {
stream.remove();
}
}
@Override
public final void readExternal(final ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//反序列化
final Object data = in.readObject();
if (data.getClass().isArray()) {
this.userBeanBytes = (byte[]) data;
} else {
this.userBean = data;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected final Object readResolve() throws ObjectStreamException {
//如果userBean不为null且userBeanBytes长度为0则表示已经完成过 直接返回该对象
if (this.userBean != null && this.userBeanBytes.length == 0) {
return this.userBean;
}
/*第一次 */
try {
final ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(this.userBeanBytes));
//反序列化userBean
this.userBean = in.readObject();
//反序列化延迟加载属性
this.unloadedProperties = (Map<String, ResultLoaderMap.LoadPair>) in.readObject();
//反序列化对象工厂
this.objectFactory = (ObjectFactory) in.readObject();
//反序列化构造参数类型
this.constructorArgTypes = (Class<?>[]) in.readObject();
//反序列化构造参数
this.constructorArgs = (Object[]) in.readObject();
} catch (final IOException ex) {
throw (ObjectStreamException) new StreamCorruptedException().initCause(ex);
} catch (final ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw (ObjectStreamException) new InvalidClassException(ex.getLocalizedMessage()).initCause(ex);
}
final Map<String, ResultLoaderMap.LoadPair> arrayProps = new HashMap<String, ResultLoaderMap.LoadPair>(this.unloadedProperties);
final List<Class<?>> arrayTypes = Arrays.asList(this.constructorArgTypes);
final List<Object> arrayValues = Arrays.asList(this.constructorArgs);
//根据序列化是保存的数据创建一个反序列化代理对象
return this.createDeserializationProxy(userBean, arrayProps, objectFactory, arrayTypes, arrayValues);
}




 本文深入解析Java序列化机制,涵盖序列化与反序列化的流程、关键方法如writeObject与readObject的作用,及MyBatis框架如何确保序列化后的对象支持延迟加载。
本文深入解析Java序列化机制,涵盖序列化与反序列化的流程、关键方法如writeObject与readObject的作用,及MyBatis框架如何确保序列化后的对象支持延迟加载。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








