window对象
window对象是BOM的核心,window对象指当前的浏览器窗口。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>window对象</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
alert("欢迎来到我的博客");
function open1(){
window.open('http://www.cnblogs.com/Harold-Hua/','_blank','width=600,height=400');
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="点击我,打开新窗口" onClick="open1()" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
计时器setInterval()
在执行时,从载入页面后每隔指定的时间执行代码。
语法:
setInterval(代码,交互时间);
参数说明:
1. 代码:要调用的函数或要执行的代码串。
2. 交互时间:周期性执行或调用表达式之间的时间间隔,以毫秒计(1s=1000ms)。
返回值:
一个可以传递给 clearInterval() 从而取消对"代码"的周期性执行的值。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>定时器</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
var attime;
function clock(){
var time=new Date();
attime= time.getHours() + ":" + time.getMinutes() + ":" + time.getSeconds();
document.getElementById("clock").value = attime;
}
setInterval(clock,100);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="text" id="clock" size="50" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
取消计时器clearInterval()
clearInterval() 方法可取消由 setInterval() 设置的交互时间。
语法:
clearInterval(id_of_setInterval)
参数说明:
id_of_setInterval:由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>计时器</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function clock(){
var time=new Date();
document.getElementById("clock").value = time;
}
var i = setInterval("clock()",100);
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="text" id="clock" size="50" />
<input type="button" value="Stop" onclick="clearInterval(i)" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
计时器setTimeout()
setTimeout()计时器,在载入后延迟指定时间后,去执行一次表达式,仅执行一次。
语法:
setTimeout(代码,延迟时间);
参数说明:
1. 要调用的函数或要执行的代码串。
2. 延时时间:在执行代码前需等待的时间,以毫秒为单位(1s=1000ms)。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>计时器</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var num=0;
function startCount() {
document.getElementById('count').value=num;
num=num+1;
setTimeout("startCount()",1000);
}
setTimeout("startCount()",1000)
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="text" id="count" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
取消计时器clearTimeout()
setTimeout()和clearTimeout()一起使用,停止计时器。
语法:
clearTimeout(id_of_setTimeout)
参数说明:
id_of_setTimeout:由 setTimeout() 返回的 ID 值。该值标识要取消的延迟执行代码块。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>计时器</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var num=0;
var i;
function startCount(){
document.getElementById('count').value=num;
num=num+1;
i=setTimeout("startCount()",1000);
}
function stopCount(){
clearTimeout(i);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="text" id="count" />
<input type="button" value="Start" onclick="startCount()" />
<input type="button" value="Stop" onclick="stopCount()" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
History 对象
history对象记录了用户曾经浏览过的页面(URL),并可以实现浏览器前进与后退相似导航的功能。
注意:从窗口被打开的那一刻开始记录,每个浏览器窗口、每个标签页乃至每个框架,都有自己的history对象与特定的window对象关联。
语法:
window.history.[属性|方法]
注意:window可以省略。
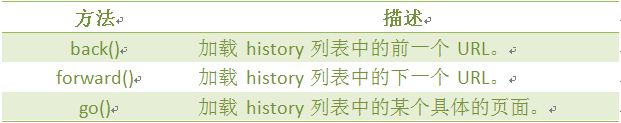
History 对象属性

History 对象方法
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>History对象</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
//浏览历史总长度
var HL = window.history.length ;
document.write(HL);
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>
返回前一个浏览的页面
back()方法,加载 history 列表中的前一个 URL。
语法:
window.history.back();
比如,返回前一个浏览的页面,代码如下:
window.history.back();
注意:等同于点击浏览器的倒退按钮。
back()相当于go(-1),代码如下:
window.history.go(-1);
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function GoBack() {
window.history.back();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
点击下面的锚点链接,添加历史列表项:
<br />
<a href="#target1">第一个锚点</a>
<a name="target1"></a>
<br />
<a href="#target2">第二个锚点</a>
<a name="target2"></a>
<br /><br />
使用下面按钮,实现返回前一个页面:
<form>
<input type="button" value="返回前一个页面" onclick="GoBack();" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
返回下一个浏览的页面
forward()方法,加载 history 列表中的下一个 URL。
如果倒退之后,再想回到倒退之前浏览的页面,则可以使用forward()方法,代码如下:
window.history.forward();
注意:等价点击前进按钮。
forward()相当于go(1),代码如下:
window.history.go(1);
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function GoForward() {
window.history.forward();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
点击下面的锚点链接,添加历史列表项:
<br />
<a href="#target1">第一个锚点</a>
<a name="target1"></a>
<br />
<a href="#target2">第二个锚点</a>
<a name="target2"></a>
<br /><br />
使用下面按钮,实现返回下一个页面:
<form>
<input type="button" value="返回下一个页面" onclick="GoForward()" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
返回浏览历史中的其他页面
go()方法,根据当前所处的页面,加载 history 列表中的某个具体的页面。
语法:
window.history.go(number);
参数:

浏览器中,返回当前页面之前浏览过的第二个历史页面,代码如下:
window.history.go(-2);
注意:和在浏览器中单击两次后退按钮操作一样。
同理,返回当前页面之后浏览过的第三个历史页面,代码如下:
window.history.go(3);
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function GoBack() {
window.history.go(-1);
}
function GoForward() {
window.history.go(1);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
点击下面的锚点链接,添加历史列表项:
<br />
<a href="#target1">第一个锚点</a>
<a name="target1"></a>
<br />
<a href="#target2">第二个锚点</a>
<a name="target2"></a>
<br /><br />
使用下面按钮,实现返回前或下一个页面:
<form>
<input type="button" value="返回前一个页面" onclick="GoBack();" />
<input type="button" value="返回下一个页面" onclick="GoForward();" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
Location对象
location用于获取或设置窗体的URL,并且可以用于解析URL。
语法:
location.[属性|方法]
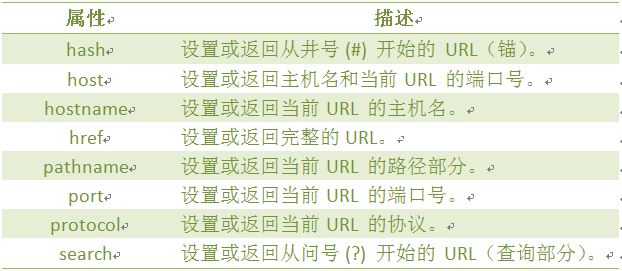
location对象属性图示:

location 对象属性:
location 对象方法:

<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>location</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write(location.href);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Navigator对象
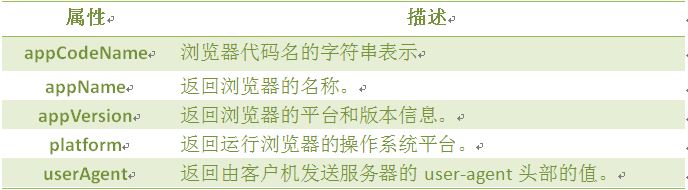
Navigator 对象包含有关浏览器的信息,通常用于检测浏览器与操作系统的版本。
对象属性:
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>无标题文档</title>
</head>
<script type="text/javascript">
var browser = navigator.appName;
var v_version = navigator.appVersion;
var p_platform = navigator.platform;
var u_userAgent = navigator.userAgent
document.write("Browser name:" + browser + "<br />");
document.write("Browser version:" + v_version + "<br />")
document.write("Browser platform:" + p_platform + "<br />");
document.write("Browser userAgent:" + u_userAgent + "<br />");
</script>
<body>
</body>
</html>
userAgent
返回用户代理头的字符串表示(就是包括浏览器版本信息等的字符串)
语法
navigator.userAgent
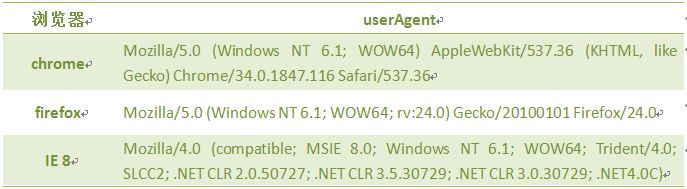
几种浏览的user_agent.,像360的兼容模式用的是IE、极速模式用的是chrom的内核。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>navigator</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function validB(){
var u_agent = navigator.userAgent;
var B_name="不是想用的主流浏览器!";
if(u_agent.indexOf("Firefox")>-1){
B_name="Firefox";
}else if(u_agent.indexOf("Chrome")>-1){
B_name="Chrome";
}else if(u_agent.indexOf("MSIE")>-1&&u_agent.indexOf("Trident")>-1){
B_name="IE(8-10)";
}
document.write("浏览器:"+B_name+"<br>");
document.write("u_agent:"+u_agent+"<br>");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type="button" value="查看浏览器" onclick="validB()" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
screen对象
screen对象用于获取用户的屏幕信息。
语法:
window.screen.属性
对象属性:
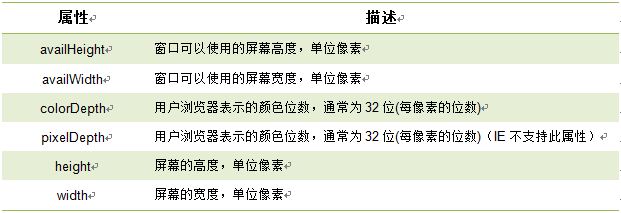
屏幕分辨率的高和宽
window.screen 对象包含有关用户屏幕的信息。
1. screen.height 返回屏幕分辨率的高
2. screen.width 返回屏幕分辨率的宽
注意:
1.单位以像素计。
2. window.screen 对象在编写时可以不使用 window 这个前缀。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>屏幕分辨率的高和宽</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write( "屏幕宽度:" + screen.width + "px<br />");
document.write( "屏幕高度:" + screen.height + "px<br />");
</script>
</body>
</html>
屏幕可用高和宽度
1. screen.availWidth 属性返回访问者屏幕的宽度,以像素计,减去界面特性,比如任务栏。
2. screen.availHeight 属性返回访问者屏幕的高度,以像素计,减去界面特性,比如任务栏。
注意:
不同系统的任务栏默认高度不一样,及任务栏的位置可在屏幕上下左右任何位置,所以有可能可用宽度和高度不一样。
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>屏幕分辨率的高和宽</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("可用宽度:" + screen.availWidth + "px<br />" );
document.write("可用高度:" + screen.availHeight + "px<br />" );
</script>
</body>
</html>




















 936
936

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








