---恢复内容开始---
1.动手实验:继承条件下的构造方法调用
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
class Child extends Parent
{
public Child()
{
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class TestInherits
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Child c = new Child();
}
}
结果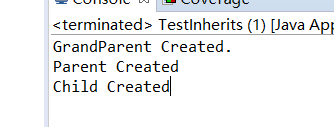
结论:是第一个语句
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2
为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
答:构造一个对象,先调用其构造方法,来初始化其成员函数和成员变量。子类拥有父的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化。
3.
参看ExplorationJDKSource.java示例 此示例中定义了一个类A,它没有任何成员: class A { }
package z;
public class ExplorationJDKSource {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
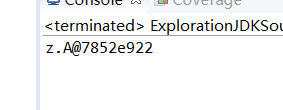
System.out.println(new A());
}
}
class A{}
使用javap –c命令反汇编ExplorationJDKSource.class 得:
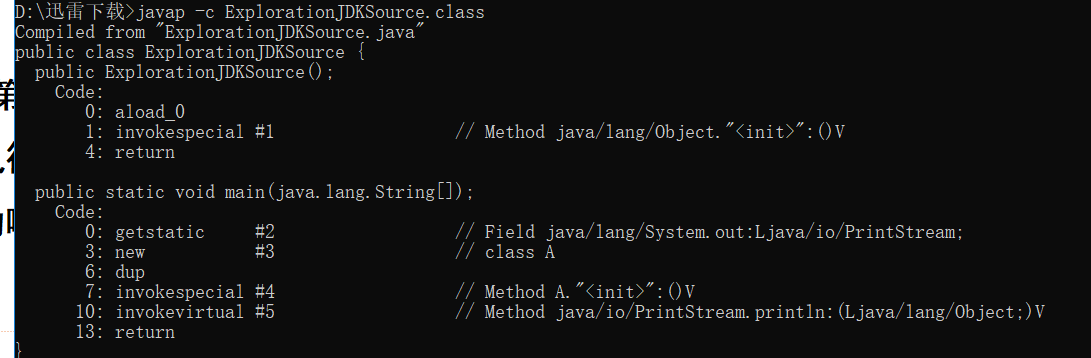
结论:
main方法实际是调用了String类的valueOf()方法而valueOf方法内部又调用Object.toString方法:public String toString(){return getClass().getName()+”@”+Integer.toHexString(hashCode());}
hashCode方法是本地方法,由JVM设计者实现:public native int hashCode()。
4.
请自行编写代码测试以下特性(动手动脑): 在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字
package z;
class person{
public person()
{
System.out.println("A");
}
}
class me extends person
{
public me()
{
super();
System.out.println("B");
}
}
class you extends person{
public you() {
super();
System.out.println("C");
}
}
public class test {
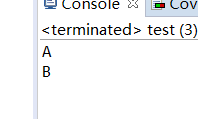
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
me me = new me();
}
}
(1)覆盖方法的允许访问范围不能小于原方法。
(2)覆盖方法所抛出的异常不能比原方法更多。
(3)声明为final方法不允许覆盖。 例如,Object的getClass()方法不能覆盖。
(4)不能覆盖静态方法。




















 178
178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








