Revolving DigitsDescription
One day Silence is interested in revolving the digits of a positive integer. In the revolving operation, he can put several last digits to the front of the integer. Of course, he can put all the digits to the front, so he will get the integer itself. For example, he can change 123 into 312, 231 and 123. Now he wanted to know how many different integers he can get that is less than the original integer, how many different integers he can get that is equal to the original integer and how many different integers he can get that is greater than the original integer. We will ensure that the original integer is positive and it has no leading zeros, but if we get an integer with some leading zeros by revolving the digits, we will regard the new integer as it has no leading zeros. For example, if the original integer is 104, we can get 410, 41 and 104.Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T (1<=T<=50) which means the number of test cases.
For each test cases, there is only one line that is the original integer N. we will ensure that N is an positive integer without leading zeros and N is less than 10^100000.Output
For each test case, please output a line which is "Case X: L E G", X means the number of the test case. And L means the number of integers is less than N that we can get by revolving digits. E means the number of integers is equal to N. G means the number of integers is greater than N.Sample Input
1 341Sample Output
Case 1: 1 1 1
【题意】
给定一个数字<=10^100000,一次将该数的第一位放到放到最后一位,求所有组成的不同的数比原数小的个数,相等的个数,大的个数。
【分析】
扩展KMP和KMP,KMP用来求循环节。
扩展KMP部分的代码(求next):
void exkmp()
{
nt[1]=2*l;int mx=0,id;
while(mx+1<=2*l&&s[mx+1]==s[mx+2]) mx++;
nt[2]=mx;id=2;
for(int i=3;i<=2*l;i++)
{
mx=id+nt[id]-1;
int now=nt[i-id+1];
if(i+now<=mx) nt[i]=now;
else
{
int j=mx-i+1;
if(j<0) j=0;
while(i+j<=2*l&&s[i+j]==s[1+j]) j++;
nt[i]=j;id=i;
}
}
}
KMP部分代码(求next):
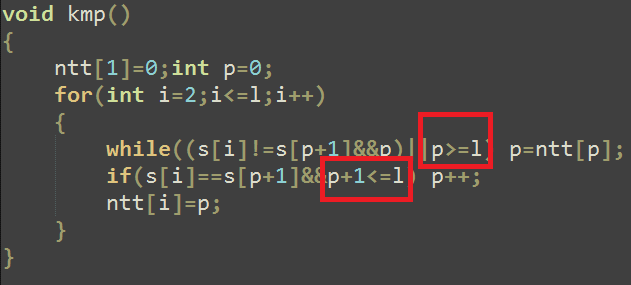
(注意红色部分)
啦啦啦啦
本题代码如下:


1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 #define Maxn 100010 8 9 char s[2*Maxn]; 10 int l; 11 12 int nt[2*Maxn]; 13 void exkmp() 14 { 15 nt[1]=2*l;int mx=0,id; 16 while(mx+1<=2*l&&s[mx+1]==s[mx+2]) mx++; 17 nt[2]=mx;id=2; 18 for(int i=3;i<=2*l;i++) 19 { 20 mx=id+nt[id]-1; 21 int now=nt[i-id+1]; 22 if(i+now<=mx) nt[i]=now; 23 else 24 { 25 int j=mx-i+1; 26 if(j<0) j=0; 27 while(i+j<=2*l&&s[i+j]==s[1+j]) j++; 28 nt[i]=j;id=i; 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 33 int ntt[Maxn*2]; 34 35 void kmp() 36 { 37 ntt[1]=0;int p=0; 38 for(int i=2;i<=l;i++) 39 { 40 while((s[i]!=s[p+1]&&p)||p>=l) p=ntt[p]; 41 if(s[i]==s[p+1]&&p+1<=l) p++; 42 ntt[i]=p; 43 } 44 } 45 46 int main() 47 { 48 int T,kase=0; 49 scanf("%d",&T); 50 while(T--) 51 { 52 scanf("%s",s+1); 53 l=strlen(s+1); 54 for(int i=1;i<=l;i++) s[i+l]=s[i]; 55 exkmp(); 56 int a1=0,a2=0,a3=0; 57 for(int i=1;i<=l;i++) 58 { 59 if(nt[i]>=l) a2++; 60 else if(s[i+nt[i]]<s[1+nt[i]]) a1++; 61 else a3++; 62 } 63 int x=1; 64 kmp(); 65 if(l%(l-ntt[l])==0) x=l/(l-ntt[l]); 66 printf("Case %d: ",++kase); 67 printf("%d %d %d\n",a1/x,a2/x,a3/x); 68 } 69 return 0; 70 }
2016-08-19 14:44:52




 本文介绍了一种通过循环排列数字来生成不同整数的算法,并分析了如何计算生成的整数中小于、等于和大于原数的数量。文章提供了详细的算法实现代码,包括扩展KMP算法用于求解循环节。
本文介绍了一种通过循环排列数字来生成不同整数的算法,并分析了如何计算生成的整数中小于、等于和大于原数的数量。文章提供了详细的算法实现代码,包括扩展KMP算法用于求解循环节。
















 709
709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








