1719: [Usaco2006 Jan] Roping the Field 麦田巨画
Time Limit: 5 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MBSubmit: 80 Solved: 24
[ Submit][ Status][ Discuss]
Description
Farmer John is quite the nature artist: he often constructs large works of art on his farm. Today, FJ wants to construct a giant "field web". FJ's field is large convex polygon with fences along the boundary and fence posts at each of the N corners (1 <= N <= 150). To construct his field web, FJ wants to run as many ropes as possible in straight lines between pairs of non-adjacent fence posts such that no two ropes cross. There is one complication: FJ's field is not completely usable. Some evil aliens have created a total of G (0 <= G <= 100) grain circles in the field, all of radius R (1 <= R <= 100,000). FJ is afraid to upset the aliens, and therefore doesn't want the ropes to pass through, or even touch the very edge of a grain circle. Note that although the centers of all the circles are contained within the field, a wide radius may make it extend outside of the field, and both fences and fence posts may be within a grain circle. Given the locations of the fence posts and the centers of the circles, determine the maximum number of ropes that FJ can use to create his field web. FJ's fence posts and the circle centers all have integer coordinates X and Y each of which is in the range 0..1,000,000.
Input
* Line 1: Three space-separated integers: N, G, and R * Lines 2..N+1: Each line contains two space-separated integers that are the X,Y position of a fence post on the boundary of FJ's field. * Lines N+2..N+G+1: Each line contains two space-separated integers that are the X,Y position of a circle's center inside FJ's field.
Output
* Line 1: A single integer that is the largest number of ropes FJ can use for his artistic creation.
Sample Input
6 10
10 7
9 1
2 0
0 3
2 2
5 6
8 3
INPUT DETAILS:
A pentagonal field, in which all possible ropes are blocked by three
grain circles, except for the rope between fenceposts 2 and 4.
Sample Output
HINT
除了篱笆桩2和4之间可以连接绳索,其余均会经过怪圈
Source
大力预处理+区间dp
直接先预处理哪些绳索是和怪圈有交的
ok[l][r]表示l和r能否连绳索
这里有一个细节就是圆不在线段上方时
就要判断圆心和端点的距离否则时圆心和线段所在直线的距离
因为给出的是一个凸包
观察可得 如果选取了绳索(l,r)那么区间[l,r]里的点不能再向外连边了
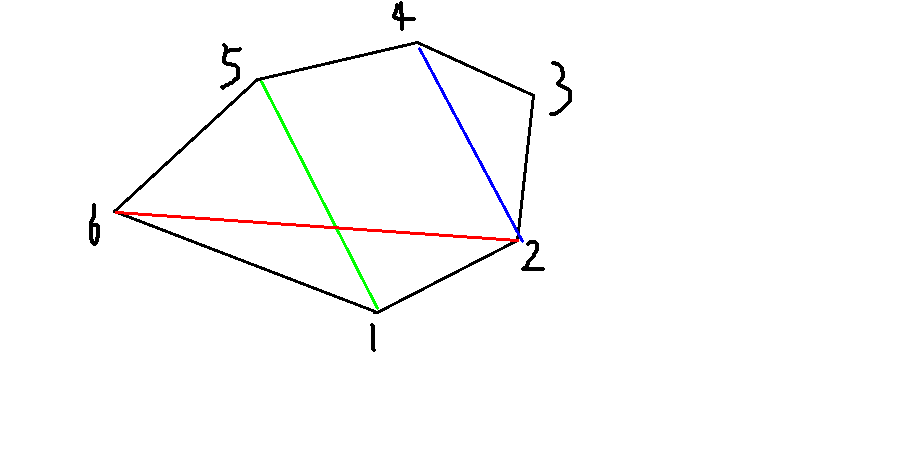
绿色的边表示已经连了 1和5
红色表示2和6不能连
蓝色表示2和4还可以连
所以可以区间dp
f[l][r]=max(f[l][m]+f[m][r])+ok[l][r]
代码:
#include<cmath> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #define Rep(i,x,y) for(int i=x;i<y;++i) #define For(i,x,y) for(int i=x;i<=y;++i) using namespace std; const int N = 1000; const double eps = 1e-10; int n,g,r; struct pts{ long long x,y; inline void rd(){ scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y); } pts operator - (pts b) { return (pts){x-b.x,y-b.y}; } long long operator ^ (pts b) { return x*b.y-y*b.x; } long long operator * (pts b) { return x*b.x+y*b.y; } }; struct line{ pts a,b; }; double DIS(const pts&a,const pts&b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } pts p[N],c[N]; int f[N][N]; bool vis[N][N]; bool ok[N][N]; bool cmp(pts a,pts b){ return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y); } bool CMP(pts a,pts b){ return ((a-p[1])^(b-p[1]))>0; } bool ck(line l,pts p){ pts ab=l.b-l.a; pts ba=l.a-l.b; if((ab*(p-l.a))<0) return DIS(p,l.a)<=r+eps; if((ba*(p-l.b))<0) return DIS(p,l.b)<=r+eps; long long K=(l.b-l.a)^(p-l.a); if(K<0) K=-K; return K/DIS(l.a,l.b)<=r+eps; } bool OK(line l){ For(i,1,g) if(ck(l,c[i])) return 0; return 1; } int dp(int l,int r){ if(l==r||vis[l][r]) return f[l][r]; vis[l][r]=1; Rep(m,l+1,r) f[l][r]=max(f[l][r],dp(l,m)+dp(m,r)); f[l][r]+=ok[l][r]; return f[l][r]; } int main(){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&g,&r); For(i,1,n) p[i].rd(); sort(p+1,p+n+1,cmp); sort(p+2,p+n+1,CMP); For(i,1,g) c[i].rd(); For(i,1,n){ For(j,i+2,n){ if(i==1&&j==n) continue; ok[i][j]=OK((line){p[i],p[j]}); } } printf("%d\n",dp(1,n)); return 0; }




 本文介绍了一个关于在限定条件下利用绳索进行艺术创作的问题,涉及计算几何与区间动态规划等算法。农民John要在麦田中创作绳索组成的艺术作品,但受到外星人制造的怪圈限制,需要计算最多能使用多少条绳索。
本文介绍了一个关于在限定条件下利用绳索进行艺术创作的问题,涉及计算几何与区间动态规划等算法。农民John要在麦田中创作绳索组成的艺术作品,但受到外星人制造的怪圈限制,需要计算最多能使用多少条绳索。
















 1331
1331

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








