Defect Prevention Solution
80% of our problems /defects are caused by 20% of our activities!<?xml:namespace prefix = o />
Conception
What is DP?
Defect Prevention, causing defects not to happen. Defect Prevention is the process of improving quality and productivity by preventing the injection of defects into a product. DP is that we spend our 20% energy to solve 80% problems! Originally it’s a most important section of RUP process, but it’s necessary for all software projects need high quality and efficient development.
What’s it bring for project?
Quality, efficient and effective
What’s a defect’s affection?
We know normally our developing process as following.
<?xml:namespace prefix = v />
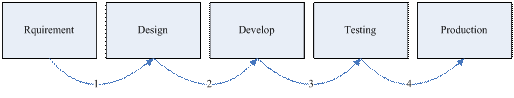
The bug in different step costs different effort. Etc, the requirement phase bug wastes design, develop, test and production; the develop phase bug waste testing and production.
What’s the difference between Defect and Fault?
Defect is the bug happens in development process before UAT (User Accept Testing and Production).
Fault is the bug feedback from Users, Customers and other roles after put into production environment.
What’s DP Function?
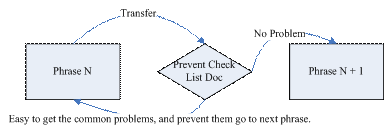
Get what’re commonest defects in whole project process in advance. And prevent them happens, no wasting effort happens. Then the efficiency has been improved, the project quality has been improved too.
Indeed, DP is helpful for various stages besides project development own, including personal life, studying and business and so on.
Why Hold DP?
Bugs are wasting project team time, including project managers, developers, testers and all participators. Bugs always cannot be avoided. But we can hold the action preventing/decreasing the repeated bugs. That’s why DP comes. It collects the history bugs data into common causes, and makes all members aware on these common causes to decrease the bugs repeatedly.
DP Objective
The quality objective of activities like defect prevention and phase kick-off meetings to ensure that the project can have more effective and efficient and high quality.
Defect prevention planning is undertaken both at the organization level and at the project level so as to plan the activities well in advance with a specific goal.
The purpose of this document is to provide guidelines for defect prevention planning, conducting, phase kick-off meetings and causal analysis meetings in various projects. However the company adopts RUP/Agile/XP development process.
So, after DP process, it increases each role’s awareness to caused defects.
DP Actions
1. Causal analysis meetings to identify the root cause (top common cause) of defects and suggest preventive actions;
2. The team to implement the preventive actions;
3. Kick-off meeting to increase awareness of quality issues specific to each development phrase;
4. Data collection and tracking of associated data. (Bugs records)
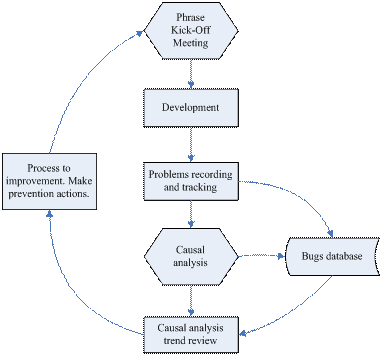
(Work Process I)
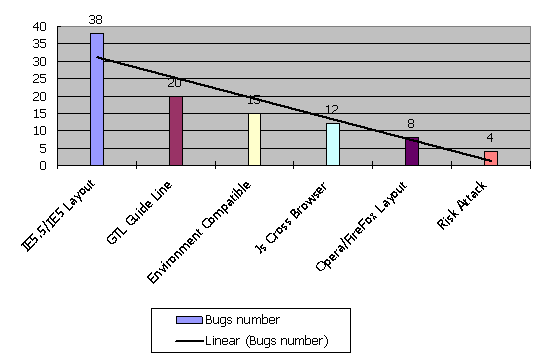
What’s Pareto chart mentioned in above diagram?
Take a virtual example. The following chart is Pareto chart. The bug number comes from statistics of last few weeks.
In last 4 weeks, there are 38 bugs on IE5.0/5.5, 20 bugs break the GTL Guide Line, 15 bugs is because of environment compatible…
So, from following Pareto chart, we can get IE5.0/5.5 is commonest issue in our last weeks.
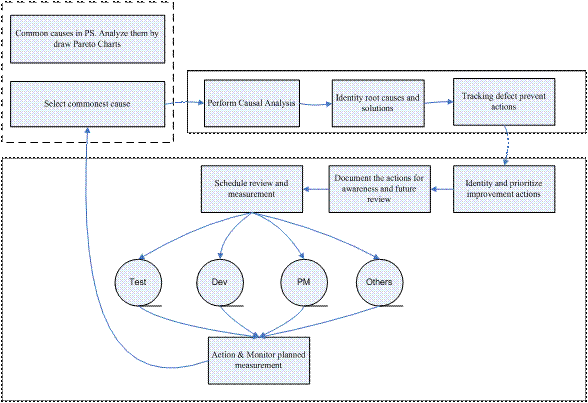
So, from the DP process, we got the common cause. And we do the analysis on it. The team member need to take consider: Why it’s the commonest problems? How to avoid it in next months? What’s objective of solving it in next weeks? How measure the actions? When we can improve to a new level?
After we finish the actions/solutions, put it into a document. And give it to every member for awareness. And testers need to analyze and track the bugs weekly and get the recent analysis, indeed, a 10 minutes review meeting for the whole team is preferred.
When the improvement phrase ends, the team holds a meeting reviews the improvement. If the result is fine, we take the action to the next/new common cause.
In this way, we improve our development one by one. That’s clear and definite.
How to get the common cause?
We use fishbone diagram, as following

Every sub pivot in this fishbone diagram represents an abstract bug cause. In this way, we can easily get the common cause: GTL Guide Line.
DP Effect
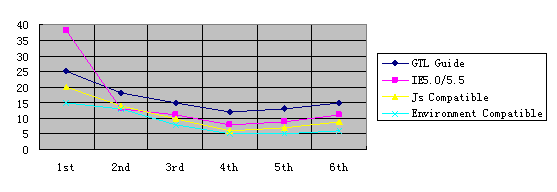
From my past experience, normally the correct actions will improve the development obviously. But after the actions and main focus, the bug will be back. But compared to the beginning case, it’s much better.
The following chart shows the achievement of DP. (It’s not true data. It just comes from my past experience on DP Coordinator position.)







 本文介绍了一种缺陷预防(DP)的方法论,旨在通过提前识别并预防软件开发过程中最常见的缺陷来提高项目质量和效率。DP重点关注减少重复出现的问题,通过根本原因分析、团队实施预防措施、阶段启动会议等方式提升整体质量。
本文介绍了一种缺陷预防(DP)的方法论,旨在通过提前识别并预防软件开发过程中最常见的缺陷来提高项目质量和效率。DP重点关注减少重复出现的问题,通过根本原因分析、团队实施预防措施、阶段启动会议等方式提升整体质量。
















 7013
7013

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








