一:继承条件下的构造方法调用
package test; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class TestInherits { @SuppressWarnings("unused") public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }

通过 super 调用基类构造方法(
通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
)后运行截图:
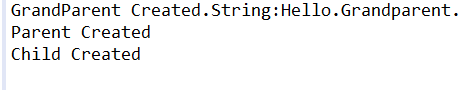
如果super()语句不在第一行,报错:Constructor call must be the first statement in a constructor。
二:方法覆盖
package test;
class Pa
{
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Parent Created");
}
}
class Ch extends Pa
{
public void display()
{
super.display();
System.out.println("Child Created");
}
}
public class Override {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Ch c = new Ch();
c.display();
}
}
在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
运行结果:

没有调用父类中被覆盖的方法
运行结果:

三:类型转换
package test; class Mammal{} class Dog extends Mammal {} class Cat extends Mammal{} public class TestCast { public static void main(String args[]) { Mammal m; Dog d=new Dog(); Cat c=new Cat(); m=d; //d=m; d=(Dog)m; //d=c; //c=(Cat)m; } }
结果:

结论:
子类对象可以直接赋给基类变量。
基类对象要赋给子类对象变量,必须执行类型转换,
其语法是: 子类对象变量=(子类名)基类对象名;
四:子类父类拥有同名的方法
package test; public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
运行结果:

结论:
当子类与父类拥有一样的方法,并且让一个父类变量引用一个子类对象时,到底调用哪个方法,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定,这就是说:对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的,它就调用父类型的方法。
 Java继承与多态详解
Java继承与多态详解







 本文深入探讨Java中的继承机制,包括构造方法调用规则、方法覆盖、类型转换及子类父类同名方法的调用原则。通过具体代码示例,解析super关键字的使用,方法覆盖时super的作用,以及不同类型转换的正确操作。
本文深入探讨Java中的继承机制,包括构造方法调用规则、方法覆盖、类型转换及子类父类同名方法的调用原则。通过具体代码示例,解析super关键字的使用,方法覆盖时super的作用,以及不同类型转换的正确操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








