参考:libubox [4] - uloop runqueue ustream
libubox提供了流缓冲管理,定义在文件ustream.h,ustream.c和ustream-fd.c。
1. 数据结构
struct ustream_buf { struct ustream_buf *next; char *data; /** 指向上次操作buff开始地址 */ char *tail; /** 指向未使用buff开始地址 */ char *end; /** 指向buf结束地址 */ char head[]; /** 指向buf开始地址 */ }; struct ustream_buf_list { struct ustream_buf *head; /** 指向第1块ustream_buf */ struct ustream_buf *data_tail; /** 指向未使用的ustream_buf */ struct ustream_buf *tail; /** 指向最后的ustream_buf */ int (*alloc)(struct ustream *s, struct ustream_buf_list *l); int data_bytes; /** 已用存储空间大小 */ int min_buffers; /** 可存储最小的ustream_buf块个数 */ int max_buffers; /** 可存储最大的ustream_buf块个数 */ int buffer_len; /** 每块ustream_buf块存储空间大小 */ int buffers; /** ustream_buf块个数 */ }; struct ustream { struct ustream_buf_list r, w; struct uloop_timeout state_change; struct ustream *next; /* * notify_read: (optional) * called by the ustream core to notify that new data is available * for reading. * must not free the ustream from this callback */ void (*notify_read)(struct ustream *s, int bytes_new); /* * notify_write: (optional) * called by the ustream core to notify that some buffered data has * been written to the stream. * must not free the ustream from this callback */ void (*notify_write)(struct ustream *s, int bytes); /* * notify_state: (optional) * called by the ustream implementation to notify that the read * side of the stream is closed (eof is set) or there was a write * error (write_error is set). * will be called again after the write buffer has been emptied when * the read side has hit EOF. */ void (*notify_state)(struct ustream *s); /* * write: * must be defined by ustream implementation, accepts new write data. * 'more' is used to indicate that a subsequent call will provide more * data (useful for aggregating writes) * returns the number of bytes accepted, or -1 if no more writes can * be accepted (link error) */ int (*write)(struct ustream *s, const char *buf, int len, bool more); /* * free: (optional) * defined by ustream implementation, tears down the ustream and frees data */ void (*free)(struct ustream *s); /* * set_read_blocked: (optional) * defined by ustream implementation, called when the read_blocked flag * changes */ void (*set_read_blocked)(struct ustream *s); /* * poll: (optional) * defined by the upstream implementation, called to request polling for * available data. * returns true if data was fetched. */ bool (*poll)(struct ustream *s); /* * ustream user should set this if the input stream is expected * to contain string data. the core will keep all data 0-terminated. */ bool string_data; /** 此ustream是否为字符串,true-是;false-否 */ bool write_error; /** 写出错,true-是;false-否 */ bool eof, eof_write_done; enum read_blocked_reason read_blocked; }; struct ustream_fd { struct ustream stream; struct uloop_fd fd; };
2. 存储结构
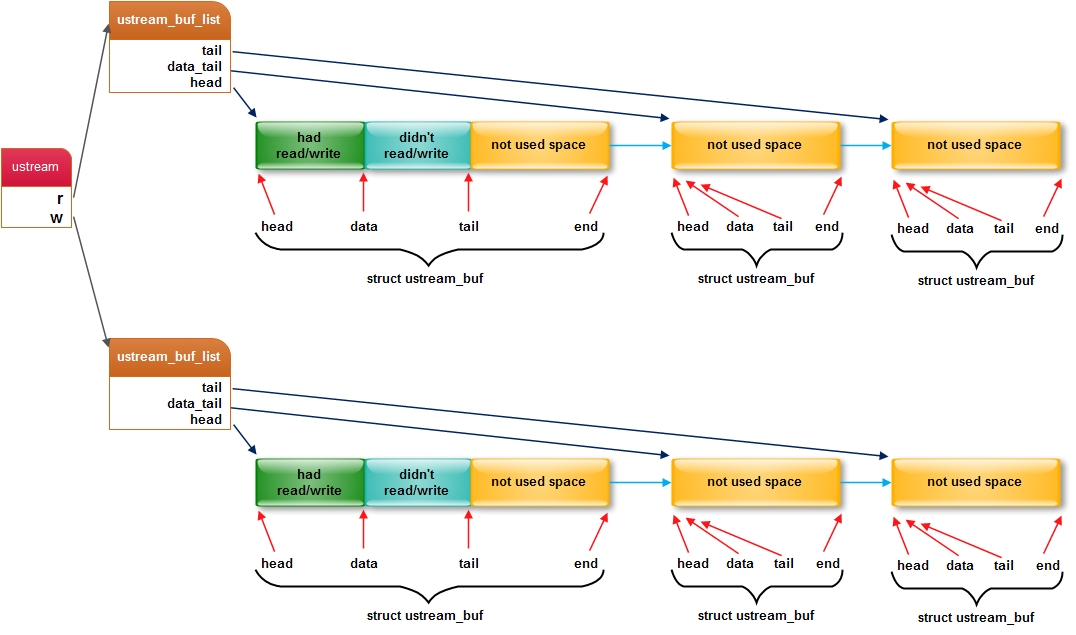
3. 函数
初始化/销毁
/** * ustream_fd_init: create a file descriptor ustream (uses uloop) */ void ustream_fd_init(struct ustream_fd *s, int fd) /** * ustream_init_defaults: fill default callbacks and options */ void ustream_init_defaults(struct ustream *s) /** * ustream_free: free all buffers and data associated with a ustream */ void ustream_free(struct ustream *s)
写入read buffer
/* * ustream_reserve: allocate rx buffer space * 分配len大小的read buffer可用内存空间,与ustream_fill_read()配合使用 * * len: int for how much space is needed (not guaranteed to be met) * maxlen: pointer to where the actual buffer size is going to be stored */ char *ustream_reserve(struct ustream *s, int len, int *maxlen) /** * ustream_fill_read: mark rx buffer space as filled * 设置被ustream_reseve()分配read buffer后写入的数据大小, * 回调notify_read()接口,表示有数据可读 */ void ustream_fill_read(struct ustream *s, int len)
读出read buffer,一般在notify_read()回调接口使用。
/* * ustream_get_read_buf: get a pointer to the next read buffer data * 获取新一次写入的内容,与ustream_consume()配置使用 */ char *ustream_get_read_buf(struct ustream *s, int *buflen) /** * ustream_consume: remove data from the head of the read buffer */ void ustream_consume(struct ustream *s, int len)
操作write buffer,尽最大能力调用write()回调用接口写入,如果超出能力将未写入的数据存储在write buffer中。
/* * ustream_write: add data to the write buffer */ int ustream_write(struct ustream *s, const char *buf, int len, bool more) int ustream_printf(struct ustream *s, const char *format, ...) int ustream_vprintf(struct ustream *s, const char *format, va_list arg)
把在write buffer 中的数据写入实际地方,调用write()回调接口和notify_write()回调接口。
一般在描述符的poll操作中调用,表示当描述符变为可写时立即把上一次写入的内容进行写入操作。
/* * ustream_write_pending: attempt to write more data from write buffers * returns true if all write buffers have been emptied. */ bool ustream_write_pending(struct ustream *s)




 本文介绍了libubox中的流缓冲管理实现,包括其数据结构、存储结构及关键函数。重点解析了ustream_buf和ustream_buf_list等数据结构,并详细说明了ustream的核心功能及其回调函数。
本文介绍了libubox中的流缓冲管理实现,包括其数据结构、存储结构及关键函数。重点解析了ustream_buf和ustream_buf_list等数据结构,并详细说明了ustream的核心功能及其回调函数。
















 1293
1293

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








