2018-2019-1 20165236 实验三 实时系统
一、任务一
学习使用Linux命令wc(1); 基于Linux Socket程序设计实现wc(1)服务器(端口号是你学号的后6位)和客户端; 客户端传一个文本文件给服务器; 服务器返加文本文件中的单词数。
1、实现mywc
wc命令的实现:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct message{
int lines;
int words;
int max_line_length;
int size;
int chars;
}info;
void error_print(char str[]){
printf("Error:%s",str);
}
void init(char filename[]){
struct stat get_message = {};
FILE *fp;
int ret_stat = stat(filename,&get_message);/*用stat函数读取filenmae文件的信息,并将结果写到get_message结构体中*/
if(ret_stat == -1){//stat函数不出错则进行信息输出
error_print(filename);
return ;
}
mode_t mode = get_message.st_mode; //接收文件信息,用于下面判断是不是目录
int length = 0;
if(S_ISDIR(mode)) //如果是目录,输出错误
printf("Error %s is dir\n0\t0\t0\t%s",filename,filename);
else{
info.size = get_message.st_size; //文件字节大小 wc -c
fp = fopen(filename,"r"); //以只读方式打开指定文件
char ch;
int flag = 0;
while((ch = fgetc(fp))!=EOF){ //一直读到文件尾
info.chars++; //字符数加1 wc -m
if(ch != '\n'){
length++; //记录当前行的长度 wc -L
}
if(ch == '\n'){
info.lines ++; //行数加1 wc -l
if(length>info.max_line_length)
info.max_line_length = length; //更新最大长度
length = 0;
}
if(ch == '\t' || ch == ' ' || ch == '\n'){
flag = 0; //计算单词数 wc -w
continue;
}
else{
if(flag == 0){
info.words++; //计算单词数 wc -w
flag = 1;
}
}
}
fclose(fp);
}
}
//计算键盘输入内容的相关信息,即参数中没有指定要打开的文件
void EmptyFile(){
char ch;
int flag = 0;
int length = 0;
while((ch = getchar())!=EOF){
info.chars++;
info.size += sizeof(ch); //字节累加
if(ch != '\n'){
length++;
}
if(ch == '\n'){
info.lines ++;
if(length>info.max_line_length)
info.max_line_length = length;
length = 0;
}
if(ch == '\t' || ch == ' ' || ch == '\n'){
flag = 0;
continue;
}
else{
if(flag == 0){
info.words++;
flag = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
if(argc == 2){
if(argv[1][0] != '-'){
init(argv[1]);
printf("%d %d %d %s\n",info.lines,info.words,info.size,argv[1]);
return 0;
}
else{ //未指定打开文件,类似 wc -lmwcL
EmptyFile();
}
}
else if(argc == 1){ //未指定打开文件和要输出的参数,(默认输出 -lwc)
EmptyFile();
printf("%d\t%d\t%d\n",info.lines,info.words,info.size);
return 0;
}
else if(argc == 3){
init(argv[2]);
}
int num;
while((num = getopt(argc,argv,"lwmcL"))!=-1){
switch(num){
case 'l':
printf("%d\t",info.lines);
break;
case 'w':
printf("%d\t",info.words);
break;
case 'm':
printf("%d\t",info.chars);
break;
case 'c':
printf("%d\t",info.size);
break;
case 'L':
printf("%d\t",info.max_line_length);
break;
}
}
if(argc != 2 && argv[1][0] != '-') //一定要判断,否则会越界
printf("%s\n",argv[2]);
return 0;
}
运行截图:
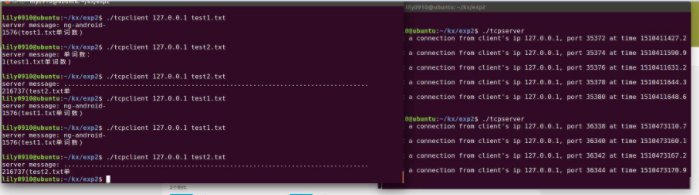
二、任务二
使用多线程实现wc服务器并使用同步互斥机制保证计数正确; 上方提交代码; 下方提交测试; 对比单线程版本的性能,并分析原因。
服务器客户端代码实现:
#include "csapp.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
static int byte_cnt; /* byte counter */
static sem_t mutex;
#define NTHREADS 4
#define SBUFSIZE 16
typedef struct {
int *buf; /* Buffer array */
int n; /* Maximum number of slots */
int front; /* buf[(front+1)%n] is first item */
int rear; /* buf[rear%n] is last item */
sem_t mutex; /* Protects accesses to buf */
sem_t slots; /* Counts available slots */
sem_t items; /* Counts available items */
} sbuf_t;
void echo_cnt(int connfd);
void *thread(void *vargp);
int wc(char *name)
{
char ch;
FILE *fp;
long count=0;
char s[21];
if ((fp=fopen(name,"r+"))==NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"不能打开文件\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while(fscanf(fp,"%s",s)!=EOF)
count++;
fclose(fp);
printf("File %s has %ld characters\n",name,count);
return 0;
}
sbuf_t sbuf; /* shared buffer of connected descriptors */
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i, listenfd, connfd, port, clientlen=sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
struct sockaddr_in clientaddr;
pthread_t tid;
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <port>\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
port = atoi(argv[1]);
sbuf_init(&sbuf, SBUFSIZE);
listenfd = Open_listenfd(port);
for (i = 0; i < NTHREADS; i++) /* Create worker threads */
Pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread, NULL);
while (1) {
connfd = Accept(listenfd, (SA *) &clientaddr, &clientlen);
sbuf_insert(&sbuf, connfd); /* Insert connfd in buffer */
}
}
static void init_echo_cnt(void)
{
Sem_init(&mutex, 0, 1);
byte_cnt = 0;
}
void echo_cnt(int connfd)
{
int n,x;
long int count;
char buf[MAXLINE];
char name[MAXLINE]
rio_t rio;
static pthread_once_t once = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
Pthread_once(&once, init_echo_cnt);
Rio_readinitb(&rio, connfd);
while((n = Rio_readlineb(&rio, buf, MAXLINE)) != 0) {
P(&mutex);
byte_cnt += n;
x = sizeof(buf);
buf[x] = 0;
count = wc(buf);
printf("thread %d received %d (%d total) bytes on fd %d\n",
(int) pthread_self(), n, byte_cnt, connfd);
name = buf;
V(&mutex);
sprint(buf,"%s:%ld characters".count);
Rio_writen(connfd, buf, n);
}
}
void sbuf_init(sbuf_t *sp, int n)
{
sp->buf = Calloc(n, sizeof(int));
sp->n = n; /* Buffer holds max of n items */
sp->front = sp->rear = 0; /* Empty buffer iff front == rear */
Sem_init(&sp->mutex, 0, 1); /* Binary semaphore for locking */
Sem_init(&sp->slots, 0, n); /* Initially, buf has n empty slots */
Sem_init(&sp->items, 0, 0); /* Initially, buf has zero data items */
}
/* $end sbuf_init */
/* Clean up buffer sp */
/* $begin sbuf_deinit */
void sbuf_deinit(sbuf_t *sp)
{
Free(sp->buf);
}
/* $end sbuf_deinit */
/* Insert item onto the rear of shared buffer sp */
/* $begin sbuf_insert */
void sbuf_insert(sbuf_t *sp, int item)
{
P(&sp->slots); /* Wait for available slot */
P(&sp->mutex); /* Lock the buffer */
sp->buf[(++sp->rear)%(sp->n)] = item; /* Insert the item */
V(&sp->mutex); /* Unlock the buffer */
V(&sp->items); /* Announce available item */
}
/* $end sbuf_insert */
/* Remove and return the first item from buffer sp */
/* $begin sbuf_remove */
int sbuf_remove(sbuf_t *sp)
{
int item;
P(&sp->items); /* Wait for available item */
P(&sp->mutex); /* Lock the buffer */
item = sp->buf[(++sp->front)%(sp->n)]; /* Remove the item */
V(&sp->mutex); /* Unlock the buffer */
V(&sp->slots); /* Announce available slot */
return item;
}
void *thread(void *vargp)
{
Pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while (1) {
int connfd = sbuf_remove(&sbuf); /* Remove connfd from buffer */
echo_cnt(connfd); /* Service client */
Close(connfd);
}
}
/* $end echoservertpremain */
/*
* echoclient.c - An echo client
*/
/*
* echoclient.c - An echo client
*/
/* $begin echoclientmain */
#include "csapp.h"
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int wc(char *name)
{
char ch;
FILE *fp;
long count=0;
char s[21];
if ((fp=fopen("test1.txt","r+"))==NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"不能打开文件%s\n",name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while(fscanf(fp,"%s",s)!=EOF)
count++;
fclose(fp);
printf("File %s has %ld characters\n",name,count);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int clientfd, port,n,count;
char *host, buf[MAXLINE];
rio_t rio;
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <host> <port>\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
host = argv[1];
port = atoi(argv[2]);
clientfd = Open_clientfd(host, port);
Rio_readinitb(&rio, clientfd);
while (Fgets(buf, MAXLINE, stdin) != NULL) {
if((num=recv(sockfd,buf,MAXDATASIZE,0))==-1)
{
printf("recv() error\n");
exit(1);
}
buf[num-1]='\0';
Rio_writen(clientfd, buf, strlen(buf));
Rio_readlineb(&rio, buf, MAXLINE);
Fputs(buf, stdout);
}
Close(clientfd);
exit(0);
}
/* $end echoclientmain */
/* $begin echoclientmain */
//#include "csapp.h"
/*int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int clientfd, port;
char *host, buf[MAXLINE];
char *name;
rio_t rio;
FILE *fp;
if (argc != 4) {
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <host> <port> <filename>\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
host = argv[1];
port = atoi(argv[2]);
name = argv[3];
clientfd = Open_clientfd(host, port);
Rio_readinitb(&rio, clientfd);
fp=fopen(name,"r+");
while (Fgets(buf, MAXLINE,fp) != NULL) {
Rio_writen(clientfd, buf, strlen(buf));
Rio_readlineb(&rio, buf, MAXLINE);
Fputs(buf, stdout);
}
Close(clientfd);
exit(0);
}
原因分析:
单线程稳定且易于实现,线程本身由于创建和切换的开销,采用多线程会降低速度,对于频繁的IO操作程序,多线程可以有效的并发。
三、实验体会
本次实验由于代码量太多因此我在其他同学的帮助下完成的,但我仍然搞懂了其中的一些核心代码,
充分理解了该实验中的多进程和多线程,不得不说在实验过程中还是非常有趣的。




 本文详细介绍了如何在Linux环境下使用多线程实现wc命令的服务器端和客户端程序,通过Socket编程进行文件传输,统计文本文件中的单词数。探讨了多线程在提高I/O密集型任务效率方面的优势。
本文详细介绍了如何在Linux环境下使用多线程实现wc命令的服务器端和客户端程序,通过Socket编程进行文件传输,统计文本文件中的单词数。探讨了多线程在提高I/O密集型任务效率方面的优势。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








