文件 FILE
读取文件:
open() 方法用于打开一个文件,并返回文件对象,在对文件进行处理过程都需要使用到这个函数,如果该文件无法被打开,会抛出 OSError。
注意:
使用 open() 方法一定要保证关闭文件对象,即调用 close() 方法。
open() 函数常用形式是接收两个参数:文件名(file)和模式(mode):open(file, mode='r')
完整语法格式:
open(file, mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True, opener=None)
- file: 必需,文件路径(相对或者绝对路径)。
- mode: 可选,文件打开模式
- buffering: 设置缓冲
- encoding: 一般使用utf8
- errors: 报错级别
- newline: 区分换行符
- closefd: 传入的file参数类型
- opener:
file的参数
相对路径:与当前运行的程序所在位置一致。
要么 将数据存储在程序文件所在的目录;要么将其存储在程序文件所在目录的下一个文件夹。中。
绝对路径:文件的准确位置。
windows系统使用反斜杠“\”。因为“\”是转移标记,所以在开头的单引号前加上r。
Linux和OS X中,使用斜杠“/”
mode的参数
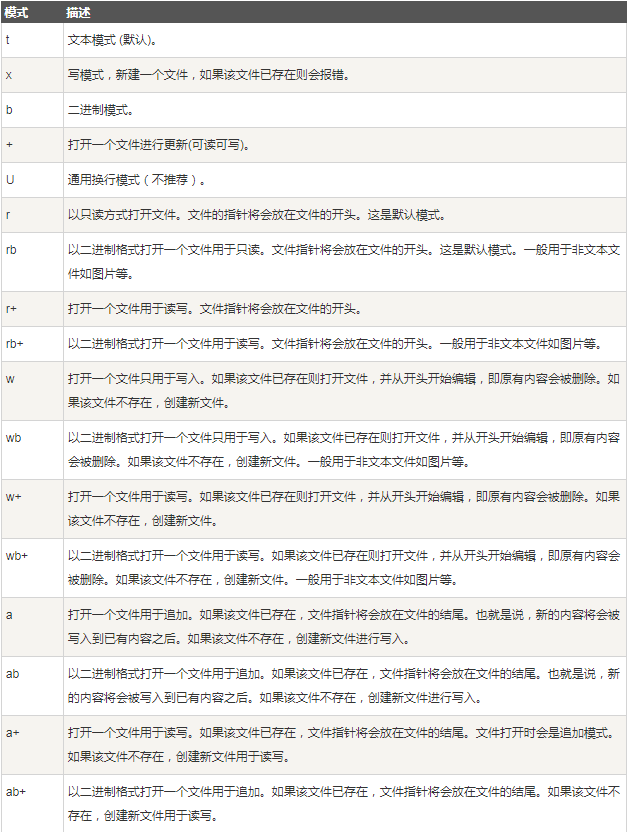
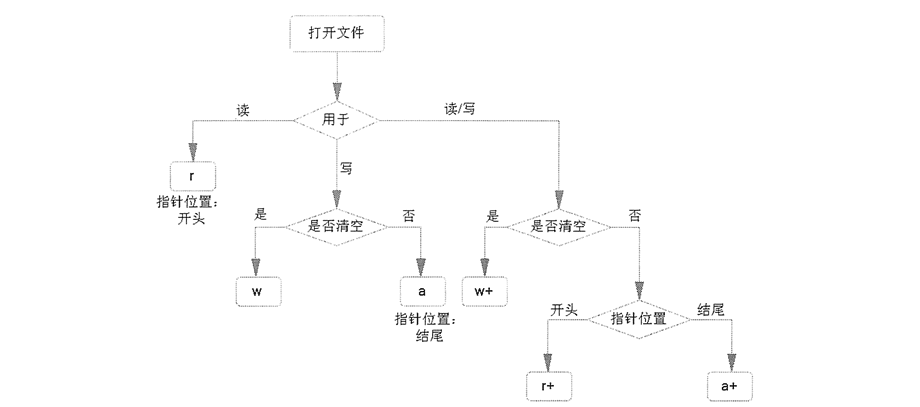
读取整个文件与逐行读取。
读取整个文件
with open('py.txt') as file_object: contents = file_object.read() print(file_object) #out;<_io.TextIOWrapper name='py.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp936'> print(contents)
逐行读取文件
with open('py.txt') as file_object: for line in file_object: print(line.rstrip())
将文件中的各行存储到列表中
with open('py.txt') as file_object: lines =file_object.readlines() print(lines)
此时如果遍历列表,则相当于逐行读取文件。
使用读取的文件
在使用关键字with时,open()返回的文件的对象只在with代码块内可用。
如果想在代码块外使用,可以将各行存储在一个列表中,在操作列表。
写入文件
如果需要换行,需要增加换行符。
with open('pyw.txt','w') as file_w: file_w.write('hello world') file_w.write('hello python') with open('pyw.txt','r') as file_r: c = file_r.read() print(c) #out:hello worldhello python
with open('pyw.txt','w') as file_w: file_w.write('hello world\n') file_w.write('hello python\n') with open('pyw.txt','r') as file_r: c = file_r.read() print(c) #out:hello world # hello python
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








