question:
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
my solution
class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { int [] result = new int[2] ; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) { if(nums[i]+nums[j] == target){ result[0]=i; result[1]=j; //System.out.println("elem1:"+i+";elem2:"+j); } } } return result; } }
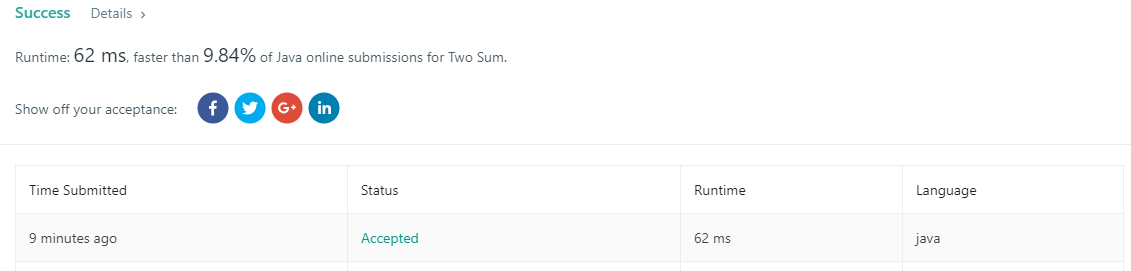
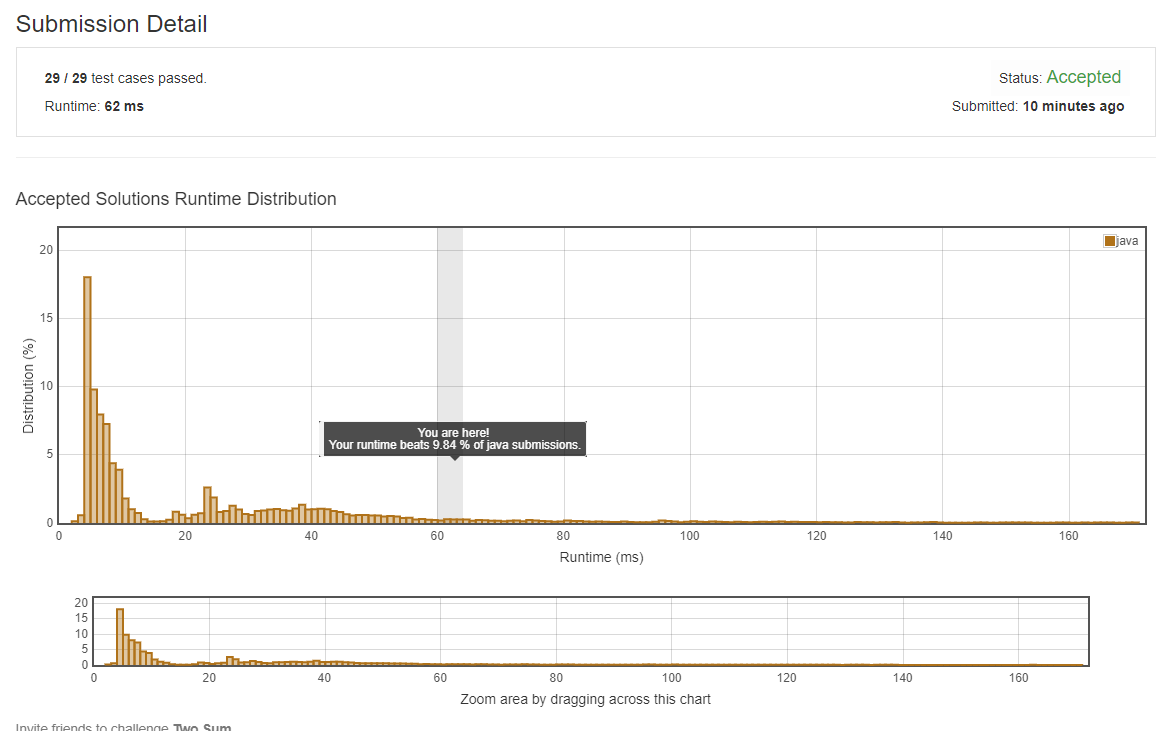
7ms的comminter code
class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { int m = 0; Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for (int i=0; i < nums.length; i++){ map.put(nums[i], i); } for(int j=0; j<nums.length; j++){ m = target - nums[j]; if (map.containsKey(m)&&(map.get(m)!=j)) return new int[] {j, map.get(m)}; } throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution"); } }
5ms的comminter code
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums == null) return new int[0];
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
int complement = target - nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(complement)){
return new int[]{i,map.get(complement)};
}
else map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
4ms的comminter code
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int len=nums.length;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put(nums[0], 0);
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i])){
int[] returnArray={map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
return returnArray;
} else{
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
}
int[] returnArray={0,0};
return returnArray;
}
}
3ms的comminter code
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] res = new int[]{-1, -1};
if (nums == null || nums.length < 2) return res;
int n = nums.length;
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = nums[i] * n + (nums[i] < 0 ? -i : i);
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[left] / n + nums[right] / n;
if (sum == target) {
res[0] = nums[left] < 0 ? -nums[left] % n : nums[left] % n;
res[1] = nums[right] < 0 ? -nums[right] % n : nums[right] % n;
return res;
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
2ms的comminter code
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int max = 2048;
int[] indexes = new int[max];
int bitMode = --max;
int first = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
int difference = target - nums[i];
if (difference == first) {
return new int[]{0, i};
}
int index = indexes[difference&bitMode];
if(index != 0) {
return new int[]{index, i};
}
indexes[nums[i]&bitMode] = i;
}
return new int[0];
}
}




 本文探讨了在给定整数数组中寻找两个数使其和等于特定目标值的问题,提供了多种解决方案,包括双循环、使用哈希表以及优化的哈希表方法,展示了不同算法的时间复杂度和效率。
本文探讨了在给定整数数组中寻找两个数使其和等于特定目标值的问题,提供了多种解决方案,包括双循环、使用哈希表以及优化的哈希表方法,展示了不同算法的时间复杂度和效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








