参考于 :
大话设计模式
马士兵设计模式视频

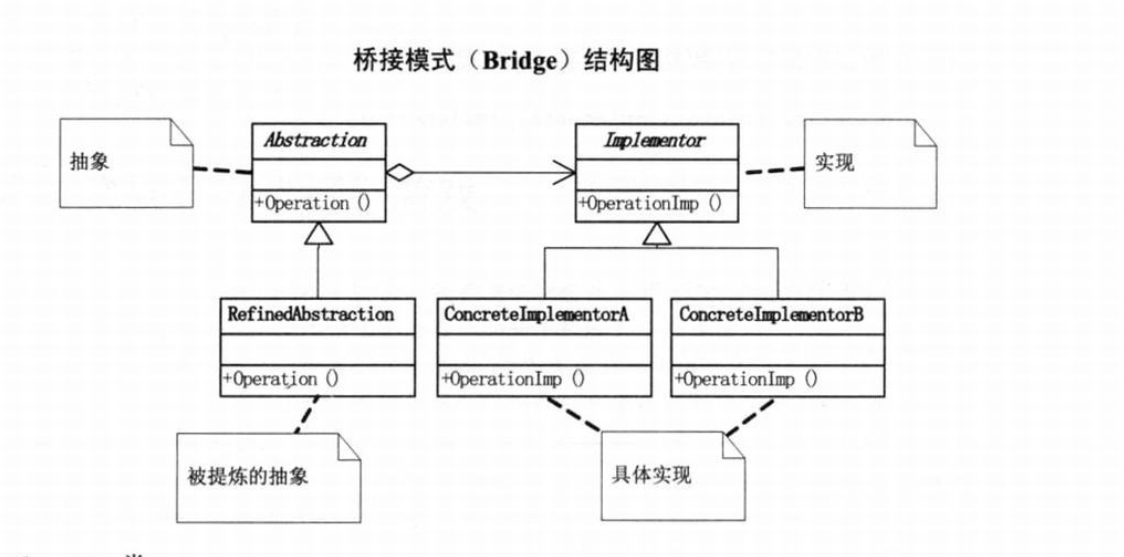
写在开头: 桥接模式主要用于一件事物分成了两个维度,进行排列组合,比如礼物,可以分成优雅的礼物(抽象),花(具体),排列组合优雅的花!
1.为什么使用桥接模式
小丁追小彭,送礼物必不可少。面向对象的思维,如何去实现这个礼物,先定义一个礼物的接口或抽象类,然后只要实现了这个接口那就算一个礼物。
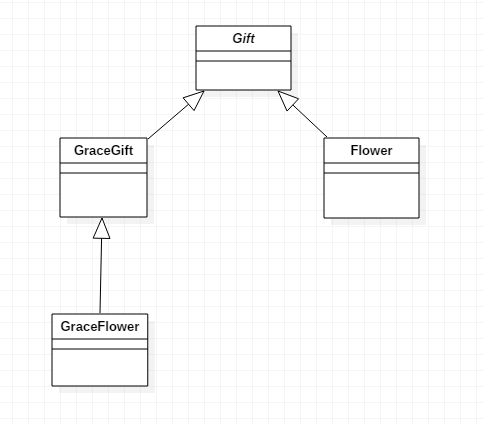
小彭是一个精致的女孩,我要送一个精致的礼物,好,按照上面的思路,实现礼物接口。小丁进了花店,哇,花朵,嗯,花朵也算礼物,实现礼物接口。
小丁想挑精致的花朵,用面向对象的思想,嗯,直接继承精致的礼物就实现了精致花朵。
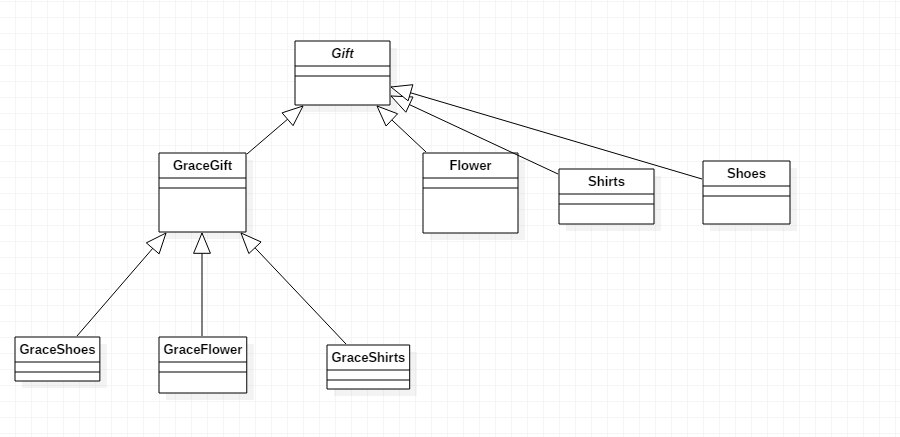
但是,小丁仔细一想,这只是花店,只有花朵,实现起来不复杂,如果进了一家百货商店,那么就要这样实现,相当麻烦。
2.使用桥接模式
使用前先解释上面图片中的话:
将抽象部分和实现部分分离 : 上面例子中,精致的礼物就是一个比较抽象的部分,精致的花就是一个实现部分,上面例子中,这两个是继承关系,现在需要进行分离。
使用聚合关系来替换继承关系
下面代码中Gift接口可去,去了后类的关系就和最上面那张UML一样
下面代码的UML类图
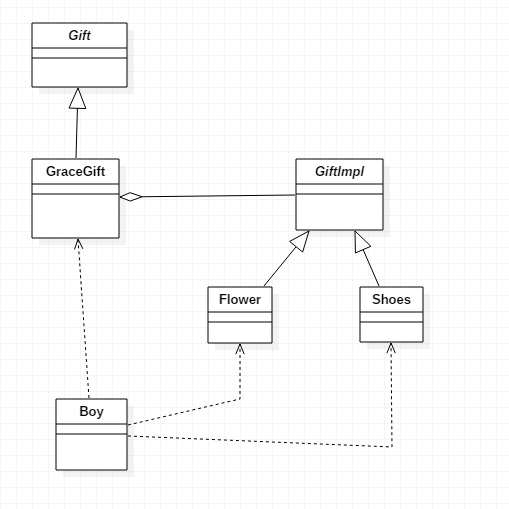
package com.dingyu; /** * 实现了这个接口,表示你是一个礼物 * @author dingyu * */ public interface Gift { }
package com.dingyu; /** * 一个精致的礼物 * 抽象部分有一个具体的部分 * @author dingyu * */ public class GraceGift implements Gift { private GiftImpl giftImpl; public GraceGift(GiftImpl giftImpl) { this.giftImpl = giftImpl; } public GiftImpl getGiftImpl() { return giftImpl; } public void setGiftImpl(GiftImpl giftImpl) { this.giftImpl = giftImpl; } }
package com.dingyu; /** * 具体的礼物 * @author dingyu * */ public interface GiftImpl { }
package com.dingyu; public class Flower implements GiftImpl { }
package com.dingyu; public class Shorts implements GiftImpl { }
package com.dingyu; /** * 男孩类 * * @author dingyu * */ public class Boy { private String name = "xiaoding"; public void sendGift() { Gift gift1; Gift gift2; gift1 = new GraceGift(new Shorts()); gift2 = new GraceGift(new Flower()); } }







 本文通过一个生动的例子,讲解了桥接模式的原理及其在实际场景中的应用。通过将抽象部分和实现部分分离,使用桥接模式可以有效地解决礼物选择的问题,使代码更加灵活和易于扩展。
本文通过一个生动的例子,讲解了桥接模式的原理及其在实际场景中的应用。通过将抽象部分和实现部分分离,使用桥接模式可以有效地解决礼物选择的问题,使代码更加灵活和易于扩展。
















 1400
1400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








