http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chipset
Chipset
A chipset is a set of electronic components in an integrated circuit that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. It is usually found in the motherboard of a computer. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance.
Computers[edit]
In computing, the term chipset is commonly used to refer to a set of specialized chips on a computer's motherboard or an expansion card. In personal computers, the first chipset for theIBM PC AT was the NEAT chipset by Chips and Technologies for the Intel 80286 CPU.
In home computers, game consoles and arcade game hardware of the 1980s and 1990s, the term chipset was used for the custom audio and graphics chips. Examples include the Commodore Amiga's Original Chip Set or SEGA's System 16 chipset.
Based on Intel Pentium-class microprocessors, the term chipset often refers to a specific pair of chips on the motherboard: the northbridge and the southbridge. The northbridge links the CPU to very high-speed devices, especially RAM and graphics controllers, and the southbridge connects to lower-speed peripheral buses (such as PCIor ISA). In many modern chipsets, the southbridge contains some on-chip integrated peripherals, such as Ethernet, USB, and audio devices.
The manufacturer of a chipset often is independent from the manufacturer of the motherboard. Current manufacturers of chipsets for x86 motherboards include AMD,Broadcom, Intel, NVIDIA, SiS and VIA Technologies. Apple computers and Unixworkstations have traditionally used custom-designed chipsets. Some server manufacturers also develop custom chipsets for their products.
In the 1980s, Chips and Technologies pioneered the manufacturing of chipsets for PC-compatible computers. Computer systems produced since then often share commonly used chipsets, even across widely disparate computing specialties. For example, the NCR 53C9x, a low-cost chipset implementing a SCSI interface to storage devices, could be found in Unix machines such as the MIPS Magnum, embedded devices, and personal computers.
Move toward processor integration in PCs[edit]
Traditionally in x86 computers, the processor's primary connection to the rest of the machine is through the motherboard chipset's northbridge. The northbridge is directly responsible for communications with high-speed devices (System memory, and primary expansion buses such as PCIe, AGP, PCI cards being common examples) and conversely any system communication back to the processor. This connection between the processor and northbridge is traditionally known as the front side bus (FSB). Requests to resources not directly controlled by the northbridge are offloaded to the southbridge - with the northbridge being an intermediary between the processor and the southbridge. The southbridge traditionally handles "everything else," generally lower speed peripherals and board functions (the largest being hard disk and storage connectivity) such as USB, parallel and serial communications. The connection between the northbridge and southbridge does not have a common name, but is usually a high speed interconnect proprietary to the chipset vendor. Thus any interaction between a CPU and main memory, any expansion device such as a graphics card(s), whether AGP, PCI or integrated into the motherboard, was directly controlled by the northbridge IC on behalf of the processor. This made processor performance highly dependent on the system chipset - especially the northbridge's memory performance and ability to shuttle this information back to the processor.
However in 2003 AMD's introduction the Athlon 64-bit series of processors[1] changed this. The Athlon64 marked the introduction of an integrated memory controller being incorporated into the processor itself allowing the processor to directly access and handle memory, negating the need for a traditional northbridge to do so. Intel followed suit in 2008 with the release of its Core i series CPUs and the X58 platform." In newer processors integration has further increased, primarily inclusion of the system's primary PCIe controller and integrated graphics directly on the CPU itself. As fewer functions are left un-handled by the processor itself, chipset venders have condensed the remaining north and southbridge functions into a single chip. Intel's version of this is the "Platform Controller Hub" (PCH), effectively an enhanced southbridge for the remaining peripherals, as traditional northbridge duties such as memory controller, expansion bus (PCIe) interface, and even on-board video controller are integrated into the CPU itself.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_chipset
List of Intel chipsets
This is a list of motherboard chipsets made by Intel. It is divided into three main categories: those that use the PCI bus for interconnection (the 4xx series), those that connect using specialized "Hub Links" (the 8xx series), and those that connect using PCI Express (the 9xx series). The chipsets are listed in chronological order.
Contents
[hide]
Early chipsets[edit]
Intel licensed ZyMOS POACH chipset for Intel 80286 and Intel 80386SX processors (the 82230/82231 High Integration AT-Compatible Chip Set). This chipset can be used with a 82335 High-integration Interface Device to provide support for the Intel 386SX.[1]
List of early Intel chipset includes:[2][3]
- 82091AA EISA/ISA - Advanced Integrated Peripheral (AIP), includes: floppy disk controller, 2× UARTs, parallel port, IDE controller, oscillator, etc.[4]
- 82310 MCA - announced in April 1988.[5] Includes: 82306 Local Channel Support Chip, 82307 DMA Controller/Central Arbiter, 82308 Micro Channel Bus Controller, 82309 Address Bus Controller, 82706 VGA Graphics Controller.[1]
- 82350 EISA - announced in September 1988.[6][7]
- 82311 MCA - announced in November 1988.[8][9] Includes: 82303 and 82304 Local I/O Channel Support Chips, 82307 DMA Controller/Central Arbiter, 82308 Micro Channel Bus Controller, 82309 Address Bus Controller, 82706 VGA Graphics Controller, 82077 Floppy Disk Controller.[1][7]
- 82320 MCA - announced in April 1989.[10]
- 82340SX PC AT - announced in January 1990, it is the Topcat chipset licensed from VLSI.[11]
- 82340DX PC AT - announced in January 1990, it is the Topcat chipset licensed from VLSI.[11]
- 82360SL - announced in October 1990.[12] It was a chipset for the mobile 80386SL and 80486SL processors. It integrated DMA controller, an interrupt controller PIC, serial and parallel ports, and power-management logic for the processor.
- 82350DT EISA - announced in April 1991.[13]
4xx chipsets[edit]
80486 chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code Name | Part Numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Parity/ECC | L2 Cache Type | PCI support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 420TX | Saturn | 82424TX, 82423TX | SIO | November 1992 | 5 V 486 | Up to 33 MHz | No | FPM | 128 MB[14] | Parity | Async. | 2.0 |
| 420EX | Aries | 82425EX | 82426EX | March 1994 | 5 V/3.3 V 486 | Up to 50 MHz | No | FPM | 128 MB | Parity | Async. | 2.0 |
| 420ZX | Saturn II | 82424ZX, 82423TX | SIO | March 1994 | 5 V/3.3 V 486 | Up to 33 MHz | No | FPM | 160 MB | Parity | Async. | 2.1 |
Pentium chipsets[edit]
While not an actual Intel chipset bug, the Mercury and Neptune chipsets could be found paired with RZ1000 and CMD640 IDE controllers with data corruption bugs. L2 caches are direct-mapped with SRAMtag RAM, write-back for 430FX, HX, VX, and TX.
| Chipset | Code Name | Part Numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Max. cacheable | Parity/ECC | L2 Cache Type | PCI support | AGP support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 430LX | Mercury[15] | 82434LX, 82433LX | SIO (ISA) PCEB/ESC (EISA) | March 1993 | P60/66 | 60/66 MHz | No | FPM | 192 MB | 192 MB | Parity | Async. | 2.0 | No |
| 430NX | Neptune[16] | 82434NX, 82433NX | SIO (ISA) SIO.A (DP ISA) PCEB/ESC (EISA) | March 1994 | P75+ | 50/60/66 MHz | Yes | FPM | 512 MB | 512 MB | Parity | Async. | 2.0 | No |
| 430FX | Triton[17][18] | SB82437FX-66 SB82437JX | PIIX | January 1995 | P75+ | 50/60/66 MHz | No | FPM/EDO | 128 MB | 64 MB | Neither | Async./Pburst | 2.0 | No |
| 430MX | Mobile Triton | 82437MX | MPIIX | October 1995 | P75+ | 50/60/66 MHz | No | FPM/EDO | 128 MB | 64 MB | Neither | Async./Pburst | 2.0 | No |
| 430HX | Triton II[18][19] | FW82439HX FW82439JHX | PIIX3 | February 1996 | P75+ | 50/60/66 MHz | Yes | FPM/EDO | 512 MB | 512/64 MB depending on tag RAMused | Both | Async./Pburst | 2.1 | No |
| 430VX | Triton II[18][20] | SB82437VX SB82438VX | PIIX3 | February 1996 | P75+ | 60/66 MHz | No | FPM/EDO/SDRAM | 128 MB | 64 MB | Neither | Async./Pburst | 2.1 | No |
| 430TX[21] | FW82439TX | PIIX4 | February 1997 | P75+ | 60/66 MHz | No | FPM/EDO/SDRAM | 256 MB | 64 MB | Neither | Async./Pburst | 2.1 | No |
Pentium Pro/II/III chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code Name | Part numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Processors1 | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Memory banks | Parity/ECC | PCI support | AGP support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450KX | Mars | 82451KX, 82452KX, 82453KX, 82454KX | SIO, SIO.A (ISA) PCEB/ESC (EISA) | November 1995 | Pentium Pro | 60/66 MHz | Yes | FPM | 1 GB | Both | 2.0 | No | |
| 450GX | Orion | 82451GX, 82452GX, 82453GX, 82454GX | SIO.A (ISA) PCEB/ESC (EISA) | November 1995 | Pentium Pro | 60/66 MHz | Yes (up to four) | FPM | 8 GB | Both | 2.0 | No | |
| 440FX | Natoma | 82441FX, 82442FX | PIIX3 (ISA) PCEB/ESC (EISA) | May 1996 | Pentium Pro/Pentium II | 60/66 MHz | Yes | FPM/EDO/BEDO | 1 GB | 4 | Both | 2.1 | No |
| 440LX | Balboa | 82443LX | PIIX4 | August 1997 | Pentium II/Celeron | 66 MHz | Yes | FPM/EDO/SDRAM | 1 GB EDO/512 MB SDRAM | 4 | Both | 2.1 | AGP 2× |
| 440EX | n/a | 82443EX | PIIX4E | April 1998 | Celeron/Pentium II | 66 MHz | No | EDO/SDRAM | 256 MB | 2 | Neither | 2.1 | AGP 2× |
| 440BX | Seattle | 82443BX | PIIX4E | April 1998 | Pentium II/III, Celeron | 66/100 MHz | Yes | EDO/SDRAM | 1 GB | 4 | Both | 2.1 (64-bit optional) | AGP 2× |
| 440GX | n/a | 82443GX | PIIX4E | June 1998 | Pentium II/III, Xeon | 100 MHz | Yes | SDRAM | 2 GB | 4 | Both | 2.1 | AGP 2× |
| 450NX | n/a | 82451NX, 82452NX, 82453NX, 82454NX | PIIX4E | June 1998 | Pentium II/III, Xeon | 100 MHz | Yes (up to four) | FPM/EDO | 8 GB | 4 | Both | 2.1 (64-bit optional) | No |
| 440ZX/440ZX-66 | n/a | 82443ZX | PIIX4E | November 1998 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100 MHz (440ZX), 66 MHz (440ZX-66) | No | SDRAM | 512 MB | 2 | Neither | 2.1 | AGP 2× |
| 440ZX-M | n/a | 82443ZX-M | PIIX4M | Pentium III/mobile Celeron | 66/100 MHz | No | SDRAM | 256 MB | 2 | Neither | 2.1 | AGP 2× | |
| 440MX | Banister | 82443MX | Same chip | Pentium II/III, mobile Celeron | 66/100 MHz | No | SDRAM | 256 MB | 2 | Neither | 2.2 | No |
Southbridge 4xx chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Part Number | ATA support | USB support | CMOS/clock | ISA support | LPC support | Power management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIO | 82378IB/ZB | None | None | No | Yes | No | SMM |
| SIO.A | 82379AB | None | None | No | Yes | No | SMM |
| PIIX | 82371FB | PIO/WDMA | None | No | Yes | No | SMM |
| MPIIX | 82371MX | PIO | None | No | Yes | No | SMM |
| PIIX3 | 82371SB | PIO/WDMA | 1 Controller, 2 Ports | No | Yes | No | SMM |
| PIIX4 | 82371AB | PIO/UDMA 33 | 1 Controller, 2 Ports | Yes | Yes | No | SMM |
| PIIX4E | 82371EB | PIO/UDMA 33 | 1 Controller, 2 Ports | Yes | Yes | No | SMM |
| PIIX4M | 82371MB | PIO/UDMA 33 | 1 Controller, 2 Ports | Yes | Yes | No | SMM |
8xx chipsets[edit]
Pentium II/III chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Memory banks | Parity or ECC | PCI | Ext. AGP/speed | IGP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 810 | Whitney | 82810 | ICH/ICH0 | April 1999 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100 MHz | No | EDO/PC100 SDRAM | 512 MB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes |
| 810E | Whitney | 82810E | ICH | September 1999 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes |
| 810E2 | Whitney | 8210E | ICH2 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes | |
| 820 | Camino | 82820 | ICH | November 1999 | Pentium II/III, Celeron | 66/100/133 MHz | Yes | PC800 RDRAM/PC100 SDRAM (with MTH) | 1 GB | 2 | Both | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
| 840 | Carmel | 82840 | ICH | October 1999 | Pentium III, Xeon | 66/100/133 MHz | Yes | Dual-Channel PC800 RDRAM | 4 GB | 2×4 | Both | v2.2/33 MHz+PCI-X/66 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
| 820E | Camino | 82820 | ICH2 | June 2000 | Pentium II/III, Celeron | 66/100/133 MHz | Yes | PC800 RDRAM/PC100 SDRAM (with MTH) | 1 GB | 2 | Both | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
| 815 | Solano | 82815 | ICH | June 2000 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | Yes |
| 815E | Solano | 82815 | ICH2 | June 2000 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100/133 MHz | Yes (2) | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 6* | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | Yes |
| 815EP | Solano | 82815EP | ICH2 | November 2000 | Celeron, Pentium II/III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 3 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
| 815P | Solano | 82815EP | ICH/ICH0 | March 2001 | Celeron, Pentium III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 3 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
| 815G | Solano | 82815G | ICH/ICH0 | September 2001 | Celeron, Pentium III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 3 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes |
| 815EG | Solano | 82815G | ICH2 | September 2001 | Celeron, Pentium III | 66/100/133 MHz | No | PC100/133 SDRAM | 512 MB | 3 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes |
(*)Relevant Gigabyte website Gigabyte's website states that the 815E has six memory banks. .
Pentium III-M mobile chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Memory banks | Parity or ECC | PCI | Ext. AGP/speed | IGP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 830M | Almador | 82830M | ICH3M | July 2001 | Celeron, Pentium III-M | 100/133 MHz | No | PC133 SDRAM | 1 GB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | Yes |
| 830MG | Almador | 82830MG | ICH3M | Celeron, Pentium III-M | 100/133 MHz | No | PC133 SDRAM | 1 GB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | No | Yes | |
| 830MP | Almador | 82830MP | ICH3M | Celeron, Pentium III-M | 100/133 MHz | No | PC133 SDRAM | 1 GB | 2 | Neither | v2.2/33 MHz | Yes/AGP 4× | No |
Pentium 4 chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Parity/ECC | PCI Type | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 850 | Tehama | 82850 (MCH) | ICH2 | November 2000 | Pentium 4 | 400 MHz | No | PC800/600 RDRAM | 2 GB | Yes/Yes | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| 860 | Colusa | 82860 (MCH) | ICH2 | May 2001 | Xeon | 400 MHz | Yes | PC800/600 RDRAM | 4 GB (w. 2 repeaters) | Yes/Yes | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| 845 | Brookdale | 82845 (MCH) | ICH2 | January 2002 | Celeron, Pentium 4 | 400 MHz | No | either DDR 200/266 or PC133 | 2 GB DDR, 3 GB SDR | Yes/Yes | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| E7500 | Plumas | E7500 (MCH) | ICH3-S | Feb 2002 | Xeon | 400 MHz | Yes | Dual channel DDR 200/266 | 16 GB | Yes/Yes | PCI-X | ||
| 850E | Tehama-E | 82850E (MCH) | ICH2 | May 2002 | Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | PC1066/800 RDRAM | 2 GB | Yes/Yes | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| 845E | Brookdale-E | 82845E (MCH) | ICH4 | May 2002 | Celeron, Celeron D, Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 200/266 | 2 GB | Yes/Yes | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | 5.8 W |
| 845GL | Brookdale-GL | 82845GL (GMCH) | ICH4 | May 2002 | Celeron, Pentium 4 | 400 MHz | No | DDR 266, PC133 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated | 5.1 W (SDRAM), 5.8 W (DDR)[22] |
| 845G | Brookdale-G | 82845G (GMCH) | ICH4 | May 2002 | Celeron, Celeron D, Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 266,DDR 333(unofficial), PC133 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× &Intel Extreme Graphics | 5.1 W (SDRAM), 5.7 W (DDR)[22] |
| 845GE | Brookdale-GE | 82845GE (GMCH) | ICH4 | October 2002 | Celeron, Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× & integrated | 6.3 W |
| 845PE | Brookdale-PE | 82845PE (MCH) | ICH4 | October 2002 | Celeron, Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | 5.6 W |
| 845GV | Brookdale-GV | 82845GV (GMCH) | ICH4 | October 2002 | Celeron, Celeron D, Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 266/333, PC133 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | integrated | 5.1 W (SDRAM), 5.7 W (DDR)[22] |
| E7505 | Placer | E7505 (MCH) | ICH4 | Nov 2002 | Xeon | 400/533 MHz | Yes | DDR 200/266 | 16 GB | Yes/Yes | AGP 8x | ||
| E7205 | Granite Bay | E7205 (MCH) | ICH4 | Nov 2002 | Pentium 4 | 400/533 MHz | No | Dual channel DDR 200/266 | 4 GB | Yes/Yes | AGP 8x | ||
| E7501 | Plumas 533 | E7500 (MCH) | ICH3-S | Dec 2002 | Xeon, Pentium M | 400/533 MHz | Yes | DDR 200/266 | 16 GB Dual channel, 8GB single channel | Yes/Yes | PCI-X | ||
| 875P | Canterwood | 82875P (MCH) | ICH5/ICH5R | April 2003 | Pentium 4, Pentium Extreme Edition, Celeron, Celeron D, Xeon | 400/533/800 MHz | Yes | Dual channel DDR 266/333/400 | 4 GB | Yes/Yes | v2.3/33 MHz | AGP 8× | 12.1 W |
| 865G | Springdale | 82865G (GMCH) | ICH5/ICH5R | May 2003 | Pentium 4, Pentium Extreme Edition, Celeron, Celeron D | 400/533/800 MHz | No | Dual channel DDR 266/333/400 | 4 GB | No/No | v2.3/33 MHz | AGP 8× &Intel Extreme Graphics 2 | 12.9 W |
| 865P | Springdale-P | 82865P | ICH5 | May 2003 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 400/533 MHz | No | Dual channel DDR 266/333 | 4 GB | No/No | v2.3/33 MHz | AGP 8× | 10.3 W |
| 865PE | Springdale-PE | 82865PE | ICH5/ICH5R | May 2003 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Pentium Extreme Edition, Celeron, Celeron D | 400/533/800 MHz | No | Dual channel DDR 266/333/400 | 4 GB | No/No | v2.3/33 MHz | AGP 8× | 11.3 W |
| 848P | Breeds Hill | 82848P (MCH) | ICH5/ICH5R | August 2003 | Celeron, Celeron D, Pentium 4 | 400/533/800 MHz | No | DDR 266/333/400 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.3/33 MHz | AGP 8× | 8.1 W |
| 865GV | Springdale-GV | 82865GV (GMCH) | ICH5/ICH5R | September 2003 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Pentium Extreme Edition, Celeron, Celeron D | 400/533/800 MHz | No | Dual channel DDR 266/333/400 | 4 GB | No/No | v2.3/33 MHz | Integrated |
Summary:
- 845 (Brookdale)
- 875P (Canterwood)
- Similar to E7205, but adds support for 800 MHz bus, DDR at 400 MHz, Communication Streaming Architecture (CSA), Serial ATA (with RAID in certain configurations) and Performance Acceleration Technology (PAT), a mode purported to cut down memory latency.
- SMP capability exists only on Xeon-based (socket 604) motherboards using the 875P chipset. FSB is rated at 533 MHz on these motherboards.
- 865PE (Springdale)
- 875P without PAT, though it was possible to enable PAT in some early revisions. Also lacks ECC Memory support.
- Sub-versions:
- 865P - The same as 865PE, but supports only 400/533 MHz bus and 333 MHz memory.
- 848P - Single memory channel version of 865PE.
- 865G (Springdale-G)
- 865PE with integrated graphics (Intel Extreme Graphics 2). PAT never supported in any revisions.
- Sub-versions:
- 865GV - 865G without external AGP slot.
Pentium 4-M/Pentium M/Celeron M mobile chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors | FSB | SMP | Memory types | Max. memory | Parity/ECC | PCI Type | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 845MP | Brookdale-M | 82845 (MCH) | ICH3-M | March 2002 | Mobile Celeron, Pentium 4-M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266 | 1 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| 845MZ | Brookdale-MZ | 82845 (MCH) | ICH3-M | March 2002 | Mobile Celeron, Pentium 4-M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200 | 1 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 4× | |
| 852GM | Montara-GM | 82852GM (GMCH) | ICH4-M | Q2, '04 | Pentium 4-M, Celeron,Celeron M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266 | 1 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated 32-bit 3D Core @ 133 MHz | 3.2 W |
| 852GMV | Montara-GM | 82852GMV (GMCH) | ICH4-M | Pentium 4-M, Celeron, Celeron M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266 | 1 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated 32-bit 3D Core @ 133 MHz | 3.2 W | |
| 852PM | Montara-GM | 82852PM (MCH) | ICH4-M | Pentium 4-M, Celeron,Celeron D | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 200/266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 1x/2×/4× | 5.7 W | |
| 852GME | Montara-GM | 82852GME (GMCH) | ICH4-M | Q4, '03 | Pentium 4-M, Celeron, Celeron D | 400/533 MHz | No | DDR 200/266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated Extreme Graphics 2 graphics core | 5.7 W |
| 854 [25] | 82854 (GMCH) | ICH4-M | March 2005 | Celeron M ULV | 400 MHz | No | DDR 266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated Extreme Graphics 2 graphics core | 5.7 W | |
| 855GM | Montara-GM | 82855GM (GMCH) | ICH4-M | March 2003 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated Extreme Graphics 2 graphics core | 3.2 W |
| 855GME | Montara-GM | 82855GME (MCH) | ICH4-M | March 2003 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | Integrated Extreme Graphics 2 graphics core | 4.3 W |
| 855PM | Odem | 82855PM (MCH) | ICH4-M | March 2003 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400 MHz | No | DDR 200/266/333 | 2 GB | No/No | v2.2/33 MHz | AGP 2×/4× | 5.7 W |
Southbridge 8xx chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Part Number | ATA | SATA | RAID Level | USB | PCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICH | 82801AA | UDMA 66/33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 2 Ports | Rev 2.2, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH0 | 82801AB | UDMA 33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 2 Ports | Rev 2.2, 4 PCI slots |
| ICH2 | 82801BA | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 4 Ports | Rev 2.2, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH2-M | 82801BAM | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 2 Ports | Rev 2.2, 2 PCI slots |
| ICH3-S | 82801CA | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 6 Ports | Rev 2.2, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH3-M | 82801CAM | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 1.1, 2 Ports | Rev 2.2, 2 PCI slots |
| ICH4 | 82801DB | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 2.0, 6 Ports | Rev 2.2, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH4-M | 82801DBM | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | Rev 2.2, 3 PCI slots |
| ICH5 | 82801EB | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 6 Ports | Rev 2.3, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH5R | 82801ER | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | RAID0, RAID1 | Rev 2.0, 6 Ports | Rev 2.3, 6 PCI slots |
| ICH5-M | 82801EBM | UDMA 100/66/33 | No | No | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | Rev 2.3, 4 PCI slots |
| 6300ESB | 6300ESB | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | RAID0, RAID1 | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | Rev 2.2, 4 PCI slots, Rev 1.0, 2 PCI-X slots + 2 PCI-X devices |
9xx chipsets and 3/4 Series chipsets[edit]
Pentium 4/Pentium D/Pentium EE chipsets[edit]
All Chipsets listed in the table below:
- Do not support SMP
- Support (-R and -DH) variants for South Bridges
| Chipset | Code Name | Part numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Supported Processors | FSB (MHz) | Memory Types | Max. Memory | Parity/ECC | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 910GL | Grantsdale-GL | 82910GL (GMCH) | ICH6 | September 2004 | Pentium 4, Celeron, Celeron D | 533 | DDR 333/400 | 2 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 16.3 W |
| 915P | Grantsdale | 82915P (MCH) | ICH6 | June 2004 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 533/800 |
| 4 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× | 16.3 W |
| 915PL | Grantsdale-PL | 82915PL (MCH) | ICH6 | March 2005 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 533/800 | DDR 333/400 | 2 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× | 16.3 W |
| 915G | Grantsdale-G | 82915G (GMCH) | ICH6 | June 2004 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 533/800 |
| 4 GB | No/No |
| 16.3 W |
| 915GL | Grantsdale-GL | 82915GL (GMCH) | ICH6 | March 2005 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 533/800 | DDR 333/400 | 4 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 16.3 W |
| 915GV | Grantsdale-GV | 82915GV (GMCH) | ICH6 | June 2004 | Pentium 4, Celeron D | 533/800 |
| 4 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 16.3 W |
| 925X | Alderwood | 82925X (MCH) | ICH6 | June 2004 | Pentium 4, Pentium 4 EE | 800 | DDR2 400/533 | 4 GB | Yes/Yes | PCI Express 16× | 12.3 W |
| 925XE | Alderwood-XE | 82925XE (MCH) | ICH6 | November 2004 | Pentium 4, Pentium 4 EE | 800/1066 | DDR2 400/533 | 4 GB | Yes/Yes | PCI Express 16× | 13.3 W |
| 955X | Lakeport-X | 82955X (MCH) | ICH7 | April 2005 | Pentium 4, Pentium 4 EE, Pentium D, Pentium XE | 800/1066 | DDR2 533/667 | 8 GB | Yes/Yes | PCI Express 16× | 13.5 W |
| 945P | Lakeport | 82945P (MCH) | ICH7 | May 2005 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Extreme, Core 2 Duo | 533/800/1066 | DDR2 400/533/667 | 4 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× | 15.2 W |
| 945PL | Lakeport-PL | 82945PL (MCH) | ICH7 | March 2006 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D | 533/800 | DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× | 15.2 W |
| 945G | Lakeport-G | 82945G (GMCH) | ICH7 | May 2005 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Extreme, Core 2 Duo | 533/800/1066 | DDR2 400/533/667 | 4 GB | No/No |
| 22.2 W |
Summary:
- 915P (Grantsdale)
- Supports Pentium 4 on an 800 MHz bus. Uses DDR memory up to 400 MHz, or DDR2 at 533 MHz. Replaces AGP and CSA with PCI Express, and also supports "Matrix RAID", a RAID mode designed to allow the usage of RAID levels 0 and 1 simultaneously with two hard drives. (Normally RAID1+0 would have required four hard drives)
- Sub-versions:
- 915PL - Cut-down version of 915P with no support for DDR2 and only supporting 2 GB of memory.
- 915G (Grantsdale-G)
- 915P with an integrated GMA 900. This core contains Pixel Shader version 2.0 only, it does not contain Vertex Shaders nor does it feature Transform & Lighting (T&L) capabilities and therefore is not Direct X 8.1 or 9.0 complaint.
- Sub-versions:
- 915GL - Same feature reductions as 915PL, but supports 4 GB of memory. No support for external graphics cards.
- 915GV - Same as 915G, but has no way of adding an external graphics card.
- 910GL - No support for external graphics cards or 800 MHz bus.
- 925X (Alderwood)
- Higher end version of 915. Supports another PAT-like mode and ECC memory, and exclusively uses DDR-II RAM.
- Sub-versions:
- 925XE - Supports a 1066 MHz bus.
- 945P (Lakeport)
- Update on 915P, with support for Serial ATA II, RAID mode 5, an improved memory controller with support for DDR-II at 667 MHz and additional PCI Express lanes. Support for DDR-I is dropped. Formal dual-core support was added to this chipset.
- Sub-versions:
- 945PL - No support for 1066 MHz bus, only supports 2 GB of memory.
- 945G (Lakeport-G)
- A version of the 945P that has a GMA 950 integrated, supports a 1066 MHz bus.
- Sub-versions:
- 945GZ - Same feature reductions as 945PL but with an integrated . No support for external graphics cards.
- 955X (Lakeport)
- Update for 925X, with additional features of "Lakeport" (e.g., PAT features and ECC memory), and uses DDR2.
Pentium M/Celeron M mobile chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code Name | Part numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Supported Processors | FSB (MHz) | Memory Types | Max. Memory | Parity/ECC | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 910GML | Alviso-GM | 82910GML (GMCH) | ICH6-M | January 2005 | Celeron M | 400 MHz | DDR 333, DDR2 400 | 2 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 6 W |
| 915GMS | Alviso-GM | 82915GMS (GMCH) | ICH6-M | January 2005 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400 MHz | DDR2 400 | 2 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 4.8 W |
| 915GM | Alviso-GM | 82915GM (GMCH) | ICH6-M | January 2005 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400/533 MHz | DDR 333, DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | No/No | Integrated GMA 900 | 6 W |
| 915PM | Alviso | 82915PM (MCH) | ICH6-M | January 2005 | Pentium M, Celeron M | 400/533 MHz | DDR 333, DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× | 5.5 W |
Core/Core 2 mobile chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors supported (official) | FSB | Memory types | Max. memory | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 940GML | Calistoga | 82940GML (GMCH) | ICH7-M | January 2006 | Celeron M, Core Solo, Pentium Dual-Core | 533 MHz | DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | Integrated GMA 950 graphics core (Max. 166 MHz 3D Render) | 7 W |
| 943GML | Calistoga | 82943GML (GMCH) | ICH7-M | January 2006 | Celeron M, Core Solo, Pentium Dual-Core2 | 533 MHz | DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | Integrated GMA 950 graphics core (Max. 200 MHz 3D Render) | |
| 945GMS | Calistoga | 82945GMS (GMCH) | ICH7-M | January 2006 | Core 2 Duo, Core Duo, Pentium Dual-Core, Core Solo, Celeron M | 533/667 MHz | DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | Integrated GMA 950 graphics core (Max. 166 MHz 3D Render) | 7 W |
| 945GSE | Calistoga | 82945GSE (GMCH) | ICH7-M | Q2, '08 | Intel Atom | 533/667 MHz | DDR2 400/533 | 2 GB | Integrated GMA 950 graphics core (Max. 166 MHz 3D Render) | 6 W |
| 945GM/E | Calistoga | 82945GM/E (GMCH) | ICH7-M | January 2006 | Core 2 Duo, Core Duo, Pentium Dual-Core, Core Solo, Celeron M | 533/667 MHz | DDR2 400/533/667 | 4 GB* | Integrated GMA 950 graphics core (Max. 250 MHz 3D Render) | 7 W |
| 945PM | Calistoga | 82945PM (MCH) | ICH7-M | January 2006 | Core 2 Duo, Core Duo, Pentium Dual-Core, Core Solo, Celeron M | 533/667 MHz | DDR2 400/533/667 | 4 GB* | PCI Express 16× | 7 W |
[*] Remapping of PCIE/APIC memory ranges not supported,[26] some physical memory might not be accessible (e.g. limited to 3.5 GB or similar).
Core 2 chipsets[edit]
All Core 2 Duo chipsets support the Pentium Dual-Core and Celeron processors based on the Core architecture. Support for all NetBurst based processors was officially dropped starting with the P35 chipset family.[27] However, some vendors' boards still support the older processors.[28]
| Chipset | Code Name | Part numbers | South Bridge | Release Date | Processors | Process support | Hardware Virtualization (Intel VT-d)[29] | FSB | Memory types | Max. memory | Parity/ECC | Graphics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 945GC | Lakeport-GC | 82945GC (MCH) | ICH7/ICH7R/ICH7-DH | 2007.01 (or Q1'05?)[30] | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core, Atom | Support for 45 nm | No | 533/800 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 2 GB[31] | No/No |
|
| 945GZ | Lakeport-GZ | 82945GZ (GMCH) | ICH7 | 2005.06 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800 MHz | DDR2 400/533 | 2 (or 4?)GB[31] | No/No | Integrated GMA 950 |
| 946PL | Lakeport-PL | 82946PL (MCH) | ICH7 | 2006.07 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 4 GB | No/No | PCI Express 16× |
| 946GZ | Lakeport-GZ | 82946GZ (GMCH) | ICH7 | 2006.07 | Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D, Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 4 GB | No/No |
|
| 975X | Glenwood | 82975X (MCH)[32] | ICH7/ICH7R/ICH7-DH | 2005.11 | Pentium D, Core 2 Quad, Core 2 Duo, Pentium Dual-Core | Support for 65 nm 45 nm unofficial2 | No | 533/667/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 533/667/8003 | 8 GB | Yes/Yes |
|
| P965 | Broadwater(P) | 82P965 (MCH) | ICH8/ICH8R/ICH8-DH | 2006.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 533/667/800 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| G965 | Broadwater(GC) | 82G965 (GMCH) | ICH8/ICH8R/ICH8-DH | 2006.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Duo | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 533/667/800 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| Q965 | Broadwater(G) | 82Q965 (GMCH) | ICH8/ICH8R/ICH8-DH | 2006.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Duo | Support for 65 nm | No | 533/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 533/667/800 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| P31 | Bearlake (P) | 82P31 (MCH) | ICH7 | 2007.08 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066 MHz | DDR2 667/800 | 4 GB | No/No |
|
| P35 | Bearlake (P+) | 82P35 (MCH) | ICH9/ICH9R/ICH9-DH | 2007.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 or DDR3 667/800/1066 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| G31 | Bearlake (G) | 82G31 (GMCH) | ICH7 | 2007.08 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo/Pentium Dual-Core | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 667/800 | 4 GB | No/No |
|
| G33 | Bearlake (G+) | 82G33 (GMCH) | ICH9/ICH9R/ICH9-DH | 2007.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 667/800 DDR3 800/1066 | 8 GB 4 GB | No/No |
Integrated GMA 3100 with: |
| G35 | Bearlake[33] | 82G35 (GMCH) | ICH8/ICH8R/ICH8-DH | 2007.08 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 667/800[34][35] | 8 GB | No/No |
IntegratedGMA X3500with: |
| Q33 | Bearlake (QF) | 82Q33 (MCH) | ICH9/ICH9R | 2007.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 667/800 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| Q35 | Bearlake (Q) | 82Q35 (MCH) | ICH9/ICH9R/ICH9-DO | 2007.06 | Pentium Dual-Core/Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | Yes4 | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR2 667/800 | 8 GB | No/No |
|
| X38 | Bearlake (X) | 82X38 (MCH) | ICH9/ICH9R/ICH9-DH | 2007.09[36] | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo/Core 2 Extreme | Support for 45 nm | Yes4 | 800/1066/1333 MHz[37] | DDR3 800/1066/1333 DDR2 667/800/1066 | 8 GB 16 GB | No/DDR2 only |
|
| X48 | Bearlake (X) | 82X48 (MCH) | ICH9/ICH9R/ICH9-DH | 2008.03 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo/Core 2 Extreme | Support for 45 nm | Yes4 | 800/1066/1333/1600 MHz | DDR3 1066/1333/1600 DDR2 533/667/800/1066 | 8 GB 16 GB | No/DDR2 only |
|
| P43 | Eaglelake (P) | 82P43 (MCH) | ICH10/ICH10R | 2008.06 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800 | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
|
| P45 | Eaglelake (P+) | 82P45 (MCH) | ICH10/ICH10R | 2008.06 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066/1333 DDR2 667/800/1066 | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
|
| G41 | Eaglelake (G) | 82G41 (GMCH) | ICH7 | 2008.09 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800 | 4 GB 8 GB | No/No |
|
| G43 | Eaglelake (G) | 82G43 (GMCH) | ICH10/ICH10R | 2008.06 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800 | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
|
| G45 | Eaglelake (G+) | 82G45 (GMCH) | ICH10/ICH10R | 2008.06 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800[38] | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
|
| B43 | Eaglelake (B) | 82B43 (GMCH) | ICH10D | 2008.12 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800 | 16 GB | No/No |
|
| Q43 | Eaglelake (Q) | 82Q43 (GMCH) | ICH10/ICH10R/ICH10D | 2008.08 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | No | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800[39] | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
|
| Q45 | Eaglelake (Q) | 82Q45 (GMCH) | ICH10/ICH10R/ICH10-DO | 2008.08 | Core 2 Quad/Core 2 Duo | Support for 45 nm | Yes4 | 800/1066/1333 MHz | DDR3 800/1066 DDR2 667/800[40] | 8 GB 16 GB | No/No |
Summary:
- 975X (Glenwood)
- Update of 955, with support for ATI Crossfire Dual Graphics systems and 65 nm processors, including Core 2 Duo.
- P965 (Broadwater)
- Update on 945P, no native PATA support, improved memory controller with support for DDR-II at 800 MHz and formal Core 2 Duo support.
- G965 (BroadwaterG)
- A version of P965 that has a GMA X3000 integrated graphics core.
- Q965 (Broadwater)
- Expected G965 intended for Intel's vPro office computing brand, with GMA 3000 instead of GMA X3000. Supports an ADD2 card to add a second display.
- Sub-versions:
- Q963 - Q965 without an external graphics interface or support for ADD2.
- P35 (Bearlake)
- The P35 chipset provides updated support for the new Core 2 Duo E6550, E6750, E6800, and E6850. Processors with a number ending in "50" have a 1333 MT/s FSB. Support for all NetBurst based chips is dropped with this chipset.[27]
- G33 (BearlakeG)
- A version of P35 with a GMA 3100 integrated graphics core and uses an ICH9 South Bridge, no DDR3 Support.
- Sub-versions:
- G35 - G33 with a GMA x3500 integrated graphics core and uses an ICH8 South Bridge, no DDR3 Support.
- Q35 (BearlakeG)
- Expected G33 intended for Intel's vPro office computing brand, no DDR3 Support.
- Sub-versions:
- Q33 - Q35 without vPro support.
- P31 (BearlakeG)
- A version of P35 with an ICH7 South Bridge and only supporting 4 GB RAM,no 1333 FSB nor DDR3 Support.
- G31 (BearlakeG)
- A version of P31 with a GMA 3100 integrated graphics core, but supports a 1333 FSB.
- P45 (Eaglelake)
- Update of P35, with PCIe 2.0, Hardware Virtualization, Extreme Memory Profile (XMP) and support for ATI Crossfire (8x+8x).
- Sub-versions:
- P43 - P45 without Crossfire support and no DDR2-1066/DDR3-1333 support.
- G45 (EaglelakeG)
- A version of P45 that has a GMA X4500HD integrated graphics core, Also lacks Crossfire support.
- Sub-versions:
- G43 - Same feature reductions as P43, but with a GMA X4500 integrated graphics core.
- Q45 (EaglelakeQ)
- Expected G43 intended for Intel's vPro office computing brand, Also supports Hardware Virtualization Technology and Intel® Trusted Platform Module 1.2 feature.
- Sub-versions:
- Q43 - Q45 without vPro support, Also lacks Intel® Trusted Platform Module 1.2 support.
- B43 - Q43 with an ICH10D South Bridge.
- G41 (EaglelakeG)
- Update of G31 with a GMA X4500 integrated graphics core and DDR3 800/1066 support.
[1] 975X chipset only supports 16x PCIe (electrical) in the top slot when the slot below it is unpopulated. Otherwise it and the lower slot (both attached to the Memory Controller Hub) operate at 8x electrical.
[2] Officially 975X supports a maximum of 1066FSB. Unofficially third party motherboards (Asus, Gigabyte) support certain 1333FSB 45 nm Core2 processors, usually with later BIOS updates.
[3] The 975X chipset technical specification shows only 533/667 memory support. Actual implementations of 975X do support DDR2 800.
[4] VT-d is inherently supported on these chipsets, but may not be enabled by individual OEMs. Always read the motherboard manual and check for BIOS updates. X38/X48 VT-d support is limited to certain Intel, Supermicro, DFI (LanParty) and Tyan boards. VT-d is broken or non existent on some boards until the BIOS is updated. Note that VT-d is a chipset Memory Controller Hub technology, not a processor feature, but this is complicated by later processor generations (i series) moving the MCH from the motherboard to the processor package, making only certain i series CPUs support VT-d.
Core 2 mobile chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Code name | Part numbers | South bridge | Release date | Processors supported (official) | FSB | Memory types | Max. memory | Graphics | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL960 | Crestline | 82960GL (GMCH) | ICH8-M | May 2007 | Celeron M, Pentium Dual-Core | 533 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 3 GB | Integrated GMA X3100 graphics core (Max. 400 MHz 3D Render) | 13.5 W |
| GM965 | Crestline | 82965GM (GMCH) | ICH8-M | May 2007 | Core 2 Duo | 533/667/800 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 4 GB/8GB1 | Integrated GMA X3100 graphics core (Max. 500 MHz 3D Render) | 13.5 W |
| PM965 | Crestline | 82965PM (MCH) | ICH8-M | May 2007 | Core 2 Duo | 533/667/800 MHz | DDR2 533/667 | 4 GB/8GB1 | PCIe 16× | 8 W |
| GL40 | Cantiga | 82GL40 (GMCH) | ICH9-M | Sep 2008 | Core 2 Duo, Celeron, Celeron M, Pentium Dual-Core | 667/800 MHz | DDR2 667/800, DDR3 667/800 | 8 GB | Integrated GMA X4500HD graphics core (Max. 400 MHz 3D Render) | 12 W |
| GS40 | Cantiga | 82GS40 (GMCH) | ICH9-M | Sep 2008 | Core 2 Duo, Celeron, Celeron M?, Pentium Dual-Core | 667?/800 MHz | DDR2 667/800, DDR3 667/800 | 4 GB | Integrated GMA X4500HD graphics core (Max. 400 MHz 3D Render) | 12 W |
| GS45 | Cantiga | 82GS45 (GMCH)(For CULV) | ICH9-M | Sep 2008 | Core 2 Solo, Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Extreme, Celeron M | 800/1066 MHz | DDR2 667/800, DDR3 667/800/1066 | 8 GB | Integrated GMA X4500HD graphics core (Max. 533 MHz 3D Render) | 7 W (low power mode), 8W (HD playback mode), 12W (Full performance mode) |
| GM45 | Cantiga | 82GM45 (GMCH) | ICH9-M | Sep 2008 | Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Extreme, Celeron M | 667/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 667/800, DDR3 667/800/1066 | 8 GB | Integrated GMA X4500HD graphics core (Max. 533 MHz 3D Render) | 12 W |
| PM45 | Cantiga | 82PM45 (MCH) | ICH9-M | Sep 2008 | Core 2 Duo, Core 2 Extreme | 667/800/1066 MHz | DDR2 667/800, DDR3 667/800/1066 | 8 GB | PCIe 16× | 7 W |
[1] Officially only 4GB is supported. Unofficially many laptops with this chipset support 8GB.
Southbridge 9xx and 3/4 Series chipsets[edit]
| Chipset | Part Number | Parallel ATA | Serial ATA | RAID Level | USB | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICH6 | 82801FB | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 6 Ports | 3.8 W |
| ICH6R | 82801FR | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 6 Ports | 3.8 W |
| ICH6-M | 82801FBM | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | 3.8 W |
| ICH7 | 82801GB | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 8 Ports | 3.3 W |
| ICH7R | 82801GR | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 8 Ports | 3.3 W |
| ICH7DH | 82801GDH | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 8 Ports | 3.3 W |
| ICH7-M | 82801GBM | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 1.5 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | 3.3 W |
| ICH7-M DH | 82801GHM | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 4 Ports | 3.3 W |
| ICH8 | 82801HB | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 3.7 W |
| ICH8R | 82801HR | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 3.7 W |
| ICH8DH | 82801HH | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 3.7 W |
| ICH8DO | 82801HO | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 3.7 W |
| ICH8M | 82801HM | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 3 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 2.4 W |
| ICH8M-E | 82801HEM | UDMA 100/66/33 | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 3 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | 2.4 W |
| ICH9 | 82801IB | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.3 W |
| ICH9R | 82801IR | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.3 W |
| ICH9DH | 82801IH | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.3 W |
| ICH9DO | 82801IO | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.3 W |
| ICH9M | 82801IBM | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 8 Ports | 2.5 W |
| ICH9M-E | 82801IEM | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 8 Ports | 2.5 W |
| ICH10 | 82801JB | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.5 W |
| ICH10R | 82801JR | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.5 W |
| ICH10D | 82801JH | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | No | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.5 W |
| ICH10DO | 82801JO | No | SATA 3.0 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10, Matrix RAID | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | 4.5 W |
5/6/7/8 Series chipsets[edit]
The Nehalem microarchitecture, moves the memory controller on to the processor. For high-end Nehalem processors, the X58 IOH acts as a bridge from the QPI to PCI Express peripherals and DMI to the ICH10 southbridge. For mainstream and lower-end Nehalem processors, the integrated memory controller (IMC) is an entire northbridge (some even having GPUs), and the PCH (Platform Controller Hub) acts as a southbridge.
Not listed below is the 3450 chipset (see Xeon chipsets) which is compatible with Nehalem mainstream and high-end processors but does not claim core iX-compatibility. With either a Core i5 or i3 processor, the 3400-series chipsets enable the ECC functionality of unbuffered ECC memory.[41] Otherwise these chipsets do not enable unbuffered ECC functionality.
The Cougar Point Intel 6 series chipsets with step B2 were recalled due to a hardware bug that causes their 3 Gbit/s Serial ATA to degrade over time until they become unusable. Step B3 of the Intel 6 series chipsets will have the fix for this. The Z68 chipset which supports CPU overclocking and use of the integrated graphics does not have this hardware bug.[42] The Z68 also added support for transparently caching hard disk data on to solid-state drives (up to 64GB), a technology called Smart Response Technology.[43]
LGA 1150[edit]
Chipsets supporting LGA 1150 CPUs (Haswell).
| Chipset | Code Name | sSpec Number | Part numbers | Release Date | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | PCI Express lanes | PCI | SATA | USB | FDI support | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z87 | Lynx Point | SR13A(C1) SR176(C2) | DH82Z87 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 3.0, 6 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
| H87 | Lynx Point | SR139(C1) SR175(C2) | DH82H87 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 3.0, 6 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
| H81 | Lynx Point | SR13B(C1) SR177(C2) | DH82H81 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 6 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 3.0, 2 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
| Q87 | Lynx Point | SR137(C1) SR173(C2) | DH82Q87 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 3.0, 6 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
| Q85 | Lynx Point | SR138(C1) SR174(C2) | DH82Q85 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 4 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | Rev 3.0, 6 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
| B85 | Lynx Point | SR13C(C1) SR178(C2) | DH82B85 (PCH) | June 2013 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 4 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 2 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 4.1 W |
LGA 1155[edit]
Chipsets supporting LGA 1155 CPUs (Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge).
| Chipset | Code Name | sSpec Number | Part numbers | Release Date | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | PCI Expresslanes | PCI | SATA | USB | FDI support | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H613 | Cougar Point | SLH83(B2) SLJ4B(B3) | BD82H61 (PCH) | February 20, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 6 PCIe 2.0[44] | No | 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 2.0, 10 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| P673 | Cougar Point | SLH84(B2) (Recalled) SLJ4C (B3) | BD82P67 (PCH) | January 9, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0[45] | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | No | 6.1 W |
| H673 | Cougar Point | SLH82(B2) (Recalled) SLJ49 (B3) | BD82H67 (PCH) | January 9, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| Z683 | Cougar Point | SLJ4F(B3) | BD82Z68 (PCH) | May 11, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| Q673 | Cougar Point | SLH85(B2) SLJ4D(B3) | BD82Q67 (PCH) | February 20, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0[46] | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| Q653 | Cougar Point | SLH99(B2) SLJ4E(B3) | BD82Q65 (PCH) | Q2 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 1 Port & 3 Gbit/s, 5 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| B653 | Cougar Point | SLH98(B2) SLJ4A(B3) | BD82B65 (PCH) | February 20, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 1 Port & 3 Gbit/s, 5 Ports | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | Yes | 6.1 W |
| Z775 | Panther Point | SLJC7(C1) | BD82Z77 (PCH) | April 8, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
| Z755 | Panther Point | SLJ87(C1) | BD82Z75 (PCH) | April 8, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
| H775 | Panther Point | SLJ88(C1) | BD82H77 (PCH) | April 8, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
| Q775 | Panther Point | SLJ83(C1) | BD82Q77 (PCH) | May 13, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
| Q755 | Panther Point | SLJ84(C1) | BD82Q75 (PCH) | May 13, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 1 Port & 3 Gbit/s, 5 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
| B755 | Panther Point | SLJ85(C1) | BD82B75 (PCH) | May 13, 2012 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | Yes | 6 Gbit/s, 1 Port & 3 Gbit/s, 5 Ports | Rev 3.0, 4 Ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | Yes | 6.7 W |
LGA 1156[edit]
Chipsets supporting LGA 1156 CPUs (Nehalem).
| Chipset | Code Name | sSpec Number | Part numbers | Release Date | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | PCI Express lanes | PCI | SATA | USB | FDI support | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P55 | Ibex Peak | SLH24 (B3), SLGWV (B2) | BD82P55 (PCH) | Sep 2009 | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 at 2.5 Gbit/s | Yes | 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | No | 4.7 W |
| H55 | Ibex Peak | SLGZX(B3) | BD82H55 (PCH) | Jan 2010 | DMI | 2 GB/s | 6 PCIe 2.0 at 2.5 Gbit/s | Yes | 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | Yes | 5.2 W |
| H57 | Ibex Peak | SLGZL(B3) | BD82H57 (PCH) | Jan 2010 | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 at 2.5 Gbit/s | Yes | 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 5.2 W |
| Q57 | Ibex Peak | SLGZW(B3) | BD82Q57 (PCH) | Jan 2010 | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 at 2.5 Gbit/s | Yes | 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | Yes | 5.1 W |
LGA 1366 & LGA 2011[edit]
Chipsets supporting LGA 1366 and LGA 2011 CPUs.
| Chipset | Code Name | sSpec Number | Part numbers | Release Date | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | PCI Express lanes | PCI | SATA | USB | FDI support | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X58 (Northbridge)1 | Tylersburg | SLGBT (B2), SLGMX (B3), SLH3M (C2) | AC82X58 (IOH) | Nov 2008 | QPI | Up to 12.8 GB/s | 36 PCIe 2.0 at 5 Gbit/s (IOH); 6 PCIe 1.1 (ICH) | Yes | 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 2.0, 12 Ports | No | 28.6 W2 |
| X794 | Patsburg | SLJHW(C0)[47] | BD82X79 (PCH)[48] | November 14, 2011 | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | No | 6 Gbit/s, 2 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 Ports[49] | Rev 2.0, 14 Ports | No | 7.8 W |
- 1 X58 South Bridge is ICH10/ICH10R.
- 2 X58 TDP includes the X58 IOH TDP in addition to the ICH10/ICH10R TDP.
- 3 For Sandy Bridge mainstream desktop and business platforms. Sandy Bridge CPUs provide 16 PCIe 2.0 lanes for direct GPU connectivity.
- 4 For Sandy Bridge enthusiast desktop platform. Sandy Bridge CPUs will provide up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes for direct GPU connectivity and an additional 4 PCIe 2.0 lanes.
- 5 For Ivy Bridge mainstream desktop platform. Ivy Bridge CPUs will provide 16 PCIe 3.0 lanes for direct GPU connectivity and an additional 4 PCIe 2.0 lanes.[50]
Mobile chipsets[edit]
All Core i series mobile chipsets are integrated south bridge.
| Chipset | Code Name | sSpec Number | Part numbers | Release Date | Process support | Bus Interface | Bus Speed | PCI Expresslanes | SATA | USB | TDP | FDI support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM55 | Ibex Peak-M | SLGWN(B2), SLH23(B3), SLGWP | BD82PM55 (PCH)[51] | Sep 2009 | 45 nm, 32 nm | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 3 Gbit/s, 6 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.5 W | No |
| HM55 | Ibex Peak-M | SLGZS(B3) | BD82HM55 (PCH)[52] | Jan 2010 | 45 nm, 32 nm | DMI | 2 GB/s | 6 PCIe 2.0 | 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 12 ports | 3.5 W | Yes |
| HM57 | Ibex Peak-M | SLGZR(B3) | BD82HM57 (PCH)[53] | Jan 2010 | 45 nm, 32 nm | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 3 Gbit/s, 6 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.5 W | Yes |
| QM57 | Ibex Peak-M | SLGZQ(B3) | BD82QM57 (PCH)[54] | Jan 2010 | 45 nm, 32 nm | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 3 Gbit/s, 6 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.5 W | Yes |
| QS57 | Ibex Peak-M | SLGZV(B3) | BD82QS57 (PCH)[55] | Jan 2010 | 45 nm, 32 nm | DMI | 2 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 3 Gbit/s, 6 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.4 W | Yes |
| HM65 | Cougar Point-M | SLH9D(B2) (Recalled) SLJ4P(B3) | BD82HM65 (PCH)[56] | January 9, 2011 | 32 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 12 ports | 3.9 W | Yes |
| HM67 | Cougar Point-M | SLH9C(B2) (Recalled) SLJ4N(B3) | BD82HM67 (PCH)[57] | January 9, 2011 | 32 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.9 W | Yes |
| UM67 | Cougar Point-M | SLH9U(B2) SLJ4L(B3) | BD82UM67 (PCH)[58] | February 20, 2011 | 32 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.4 W | Yes |
| QM67 | Cougar Point-M | SLH9B(B2) SLJ4M(B3) | BD82QM67 (PCH)[59] | February 20, 2011 | 32 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.9 W | Yes |
| QS67 | Cougar Point-M | SLHAG(B2) SLJ4K(B3) | BD82QS67 (PCH)[60] | February 20, 2011 | 32 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 2.0, 14 ports | 3.4 W | Yes |
| NM70 | Panther Point-M | SLJTA(C1) | BD82NM70 (PCH) | August 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 4 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 1 port & 3 Gbit/s, 3 Ports | Rev 3.0, 0 ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| HM70 | Panther Point-M | SJTNV(C1) | BD82HM70 (PCH)[61] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 1 port & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 6 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| HM75 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8F(C1) | BD82HM75 (PCH)[62] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 0 ports & Rev 2.0, 12 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| HM76 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8E(C1) | BD82HM76 (PCH)[63] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| HM77 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8C(C1) | BD82HM77 (PCH)[64] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| UM77 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8D(C1) | BD82UM77 (PCH)[65] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 4 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 1 port & 3 Gbit/s, 3 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 6 ports | 3.0 W | Yes |
| QM77 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8A(C1) | BD82QM77 (PCH)[66] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | 4.1 W | Yes |
| QS77 | Panther Point-M | SLJ8B(C1) | BD82QS77 (PCH)[67] | April 8, 2012 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 2 ports & 3 Gbit/s, 4 ports | Rev 3.0, 4 ports & Rev 2.0, 10 ports | 3.0 to 3.6 W | Yes |
| QM87 | Lynx Point-M | SR13G(C1) SR17C(C2) | DH82QM87 (PCH) | June 2013 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 4 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | Rev 3.0, 6 ports & Rev 2.0, 8 ports | 2.7 W | Yes |
| HM87 | Lynx Point-M | SR13H(C1) SR17D(C2) | DH82HM87 (PCH) | June 2013 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 4 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | 14 ports | 2.7 W | Yes |
| HM86 | Lynx Point-M | SR13J(C1) SR17E(C2) | DH82HM86 (PCH) | June 2013 | 22 nm | DMI 2.0 | 4 GB/s | 8 PCIe 2.0 | 6 Gbit/s, 4 Ports & 3 Gbit/s, 6 Ports | 14 ports | 2.7 W | Yes |
Server and workstation chipsets[edit]
http://www.intel.com/products/server/chipsets/
Embedded chipsets[edit]
http://www.intel.com/products/embedded/chipsets.htm
Notes[edit]
Note 1: The Pentium Pro, Pentium II/III, and the Celerons based on them are essentially the same design with minor internal revisions and varying cache designs. Because of this, the same chipset can be used for Socket 8, Socket 370, Slot 1, or Slot 2 designs with any CPU in the P6 family. In practice however, newer chipset designs are usually only made for the newer processor packages, and older ones may not be updated to accommodate for recent package designs. In addition, certain chipsets may be implemented in motherboards with different processor packages, much like how the 440FX could be used either with a Pentium Pro (Socket 8) or Pentium II (Slot 1). A new feature for the latest Intel chipsets is hardware virtualization support (Intel VT-d).[68] The chipset support for this technology is not very clear for the moment.[69]
Note 2: The Intel 82943GML mobile chipset unofficially supports Core Duo, Core 2 Duo, and Pentium Dual Core processors as well as 667 MHz FSB, which is a popular upgrade for many older notebook computers such as certain models of Acer Aspire 3680.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_5_Series
Intel 5 Series
Intel 5 Series is a computing architecture introduced in 2008 that improves the efficiency and balances the use of communication channels in the motherboard. The architecture consists primarily of a central processing unit (CPU) (connected to the graphics card and memory) and a single chipset (connected to motherboard components). All motherboard communications and activities circle around these two devices.
The architecture is a product of adjustments made to the Intel 4 Series to deliver higher performance motherboards while maintaining efficiency and low power. The changes revolve around chipset and processor design, in conjunction with a rearrangement of functions and controllers. The result is the first major change in many years of computing.
Contents
[hide]Design concept[edit]
The concept of the architecture was to improve motherboard mechanics to keep pace with the CPU as it gained more speed and multiplied in number of cores. In the previous architecture, the CPU was communicating heavily with the motherboard's central component, the Northbridge chipset, as it was the intermediary between the CPU, memory, and, in most cases, graphics card. The CPU would communicate with the Northbridge chipset when it needed data from the memory or when it needed to output graphics to the display. This arrangement caused the communication channel known as the front-side bus (FSB) to be heavily used. It was not long till either the FSB would reach full capacity or operate inefficiently with more cores. With the memory controller and/or graphics core moved into the processor, the reliance of separate motherboard chipsets for these functions are reduced.
Ibex Peak[1][2][edit]
The Ibex Peak chipset includes only Platform Controller Hub (PCH) per model, which provides peripheral connections, and display controllers for CPU with integrated graphics via Flexible Display Interface (excluding P-models). Additionally, the PCH is connected to the CPU via Direct Media Interface (DMI).
Taking advantage of Intel Nehalem CPUs with integrated graphics and PCI Express ports, the Intel management engine (ME) and a display controller for integrated graphics, once housed in north bridge, are moved into the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). The I/O Controller Hub (ICH) function is integrated into the PCH, removing the need for separate north bridge and south bridge.
| [hide]Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| P55 Express | BD82P55 |
| H55 Express | BD82H55 |
| H57 Express | BD82H57 |
| Q57 Express | BD82Q57 |
| B55 Express | ? |
| [hide]Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| PM55 Express | BD82PM55 |
| QM57 Express | BD82QM57 |
| HM55 Express | BD82HM55 |
| HM57 Express | BD82HM57 |
| QS57 Express | BD82QS57 |
| [hide]Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| 3400 | BD3400 |
| 3420 | BD3420 |
| 3450 | BD3450 |
Tylersburg[edit]
Unlike the Ibex Peak chipsets, The Tylersburg family of chipsets do not include PCH, and the I/O Hub mainly provides extra PCI Express 2.0 ports. Peripheral connections are provided by I/O Controller Hub (ICH) connected to DMI interface. Intel 5 series IOH support ICH10, while Intel 5500 Series IOH support ICH9 or ICH10.
| [hide]Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| X58 | AC82X58 (B2), AC82X58 SLGMX 901076 (B3), AC82X58 SLH3M 904727 (C2) |
| [hide]Model | Top marking |
|---|---|
| 5520 | AC5520 SLGMU 901037 (B-3), AC5520 SLH3P 904729 (C-2) |
| 5500 | AC5500 SLGMT 901036 (B-3), AC5500 SLH3N 904728 (C-2) |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
External links[edit]
Ibex Peak[edit]
- Intel 5 series: H55, H57, P55, Q57
- Mobile Intel 5 series: HM55, HM57, PM55, QM57, QS57
- Intel 3400 and 3420 Chipsets Overview
- Intel 5 Series Chipset and Intel 3400 Series Chipset
- Support for the Intel 5 Series Chipset
- Intel's "Ibex Peak"
Tylersburg[edit]
- Intel X58 Express Chipset
- Intel 5500 series: 5500, 5520
- Intel 5500 and 5520 Chipset
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1366
LGA 1366
 | |
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | Flip-chip land grid array |
| Contacts | 1366 |
| FSB protocol | Intel QuickPath Interconnect |
| FSB frequency | 1× to 2× QuickPath |
| Processor dimensions | 1.77 × 1.67 inches (44.958mm x 42.418mm) [1] |
| Processors | Intel Core i7 (9xx series) Intel Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) Intel Celeron P1053 |
| Predecessor | LGA 775 LGA 771 |
| Successor | LGA 2011 LGA 1356 |
|
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
LGA 1366, also known as Socket B,[2][3] is an Intel CPU socket. This socket supersedes Intel's LGA 775 (Socket T) in the high-end and performance desktop segments. It also replaces the server-oriented LGA 771 (Socket J) in the entry level and is superseded itself by LGA 2011. LGA stands for land grid array. This socket has 1,366 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor (CPU)[4] and accesses up to three channels of DDR3 memory via the processor's internal memory controller.
Socket 1366 (Socket B) uses QPI to connect the CPU to a reduced-function northbridge that serves mainly as a PCI-Express controller. A slower DMI is used to connect Intel's most recent northbridge and southbridge components. By comparison, Intel's socket 1156 (Socket H) moves the QPI link and PCI-Express controller onto the processor itself, using DMI to interface a single-component "chipset" (now called PCH) that serves traditional southbridge functions. The difference in pin number is mostly a reflection of the number of memory channels served.
In November 2008, Intel released Core i7, which was the first processor requiring this socket.
LGA 1366 socket and processors were discontinued sometime in 2012,[5] and superseded by the LGA 2011 socket, on November 14, 2011, supporting Sandy Bridge E-series processors. LGA 1156 was discontinued at the same time.
Socket B mechanical load limits[edit]
Socket B processors have the following mechanical maximum load limits which should not be exceeded during heatsink assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use. Load above those limits will crack the processor die and make it unusable.
| Location | Dynamic | Static |
|---|---|---|
| IHS Surface | 890 N (200 lbf) (90 kp) | 266 N (60 lbf) (27 kp) |
Processors using this socket have a lower static load limit than previous models using LGA 775.
Supported chipsets[edit]
The desktop chipset that supports LGA 1366 is Intel's X58.
LGA 2011
| This article is outdated. (September 2013) |
 | |
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | Flip-chip land grid array |
| Contacts | 2011 |
| FSB protocol | Intel QuickPath Interconnect DMI 2.0 |
| FSBfrequency | 1× to 2× QuickPath, DMI 2.0 |
| Processors | Sandy Bridge-E/EP Ivy Bridge-E |
| Predecessor | LGA 1366 |
| Successor | LGA 2011-3 |
|
This article is part of the CPU socketseries | |
LGA 2011, also called Socket R, is a CPU socket by Intel. It replaces Intel's LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567 in the performance and high-end desktop and server platforms.[1] The socket has 2011 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor.
Socket R uses QPI to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0 is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCIe lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366 there is no provision for integrated graphics.
The socket was released on 14 November 2011[2], and supports 4 DDR3 SDRAM memory channels with 1 unbuffered DIMM per channel, as well as 40× PCIe 2.0 or 3.0 lanes.[3] LGA 2011 also has to ensure platform scalability beyond eight cores and 20 MB of cache.[4]
LGA 2011 is compatible with Sandy Bridge-E, Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), and Xeon processors, subject to motherboard manufacturers adding support for the new CPUs on their LGA 2011 motherboards;[5] however Intel has confirmed that it will not be updating its own range of X79 motherboards which therefore will not be compatible with Ivy Bridge-E processors.[6]
Contents
[hide]
Chipsets[edit]
Information for the Intel X79 chipset can be found in the table below.
| Name | X79[7] |
|---|---|
| CPU Support | Sandy Bridge-E, Ivy Bridge-E[5] |
| Maximum DDR3 slots | 8 |
| Overclocking | Yes |
| Embedded GPU | No |
| RAID 0/1/5/10 | Yes |
| Maximum USB Ports (USB 3.0) | 14 (0)[8] |
| Maximum SATA Ports (SATA 6 Gbit/s) | 6 (2)[8] |
| Main PCIe configuration | 40 × PCIe lanes[9] |
| Secondary PCIe | 8 × PCIe 2.0 (5GT/s) |
| PCI | Yes |
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology | Yes |
| Smart Response Technology | No |
| Release Date (Y-M-D) | 2011-11-14 |
Compatible processors[edit]
Desktop (Sandy Bridge-E/Ivy Bridge-E)[edit]
Information for the desktop LGA 2011 socket processors can be found in the table below.
- All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AVX, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bitimplementation), TXT, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, Turbo Boost, AES-NI, Smart Cache, Hyper-threading, except the C1 stepping models, which lack VT-d.[10]
- Sandy Bridge-E processors are not bundled with standard air cooled CPU-coolers. Intel is offering a standard CPU-cooler, and a liquid-cooling CPU-cooler, which are both sold separately.[11]
| Name | Cores | Threads | Frequency | Turbo Boost | Multiplier | L2 cache | L3 cache | TDP | Release Date (Y-M-D)[12] | Price (US)[13] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy Bridge-E | ||||||||||
| Core i7-3820 | 4 | 8 | 3.60 GHz | 3.80 GHz | Partially Unlocked 1 | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 130W | 2012-02-14 | $305 [14] |
| Core i7-3930K | 6 | 12 | 3.20 GHz | 3.80 GHz | Unlocked | 6 x 256KB | 12MB | 130W | 2011-11-14 | $555[15] |
| Core i7-3960X Extreme Edition | 6 | 12 | 3.30 GHz | 3.90 GHz | Unlocked | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 130W | 2011-11-14 | $990[15] |
| Core i7-3970X Extreme Edition | 6 | 12 | 3.50 GHz | 4.00 GHz | Unlocked | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 150W | Q4'12 | $999 |
| Ivy Bridge-E | ||||||||||
| Core i7-4820K Extreme Edition | 4 | 8 | 3.70 GHz | 3.90 GHz | Unlocked | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 130W | Q3'13 | |
| Core i7-4930K Extreme Edition | 6 | 12 | 3.40 GHz | 3.90 GHz | Unlocked | 6 x 256KB | 12MB | 130W | Q3'13 | |
| Core i7-4960X Extreme Edition | 6 | 12 | 3.60 GHz | 4.00 GHz | Unlocked | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 130W | Q3'13 | |
1 The X79 chipset allows for increasing the base clock(bclk), Intel calls it CPU Strap, by 1.00x, 1.25x, 1.66x or 2.50x. The CPU frequency is derived by the bclk times the CPU multiplier.
Server (Xeon E5-16xx/26xx)[edit]
Information for the server LGA 2011 socket processors can be found in the table below.
- All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AVX, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bitimplementation), TXT, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, AES-NI, Smart Cache. Not all support Hyper-threading and Turbo Boost.
- Independent Loading Mechanism (ILM) in 2 variants Square and Narrow[16]
| Name | Cores | Threads | Frequency | Turbo Boost | Multiplier | L2 cache | L3 cache | TDP | Release Date | Price (US)[17][18] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xeon E5 1620 | 4 | 8 | 3.60 GHz | 3.90 GHz | 38 | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 130W | Q1 2012[19][20] | $294 |
| Xeon E5 1650 | 6 | 12 | 3.20 GHz | 3.80 GHz | 38 | 6 x 256KB | 12MB | 130W | Q1 2012 | $583 |
| Xeon E5 1660 | 6 | 12 | 3.30 GHz | 3.90 GHz | 39 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 130W | Q1 2012 | $1080 |
| Xeon E5 2603 | 4 | 4 | 1.8 GHz | not supported[21] | 18 | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 80W | Q1'12 | $198 |
| Xeon E5 2609 | 4 | 4 | 2.4 GHz | not supported[22] | 24 | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 80W | Q1'12 | $294 |
| Xeon E5 2620 | 6 | 12 | 2.0 GHz | 2.5 GHz | 25 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $406 |
| Xeon E5 2630 | 6 | 12 | 2.3 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 28 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $612 |
| Xeon E5 2630L | 6 | 12 | 2.0 GHz | 2.5 GHz | 20 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 60W | Q1'12 | $662 |
| Xeon E5 2637 | 2 | 4 | 3.0 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 30 | 2 x 256KB | 5MB | 80W | Q1'12 | $885 |
| Xeon E5 2640 | 6 | 12 | 2.5 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 30 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $885 |
| Xeon E5 2643 | 4 | 8 | 3.3 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 33 | 4 x 256KB | 10MB | 130W | Q1'12 | $885 |
| Xeon E5 2650 | 8 | 16 | 2.0 GHz | 2.8 GHz | 28 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $1107 |
| Xeon E5 2658 | 8 | 16 | 2.1 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $1141 | |
| Xeon E5 2650L | 8 | 16 | 1.8 GHz | 2.3 GHz | 18 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 70W | Q1'12 | $1107 |
| Xeon E5 2660 | 8 | 16 | 2.2 GHz | 3.0 GHz | 30 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 95W | Q1'12 | $1329 |
| Xeon E5 2665 | 8 | 16 | 2.4 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 31 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 115W | Q1'12 | $1440 |
| Xeon E5 2667 | 6 | 12 | 2.9 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 29 | 6 x 256KB | 15MB | 130W | Q1'12 | $1552 |
| Xeon E5 2670 | 8 | 16 | 2.6 GHz | 3.3 GHz | 33 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 115W | Q1'12 | $1552 |
| Xeon E5 2680 | 8 | 16 | 2.7 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 35 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 130W | Q1'12 | $1723 |
| Xeon E5 2687W | 8 | 16 | 3.1 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 31 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 150W | Q1'12 | $1885 |
| Xeon E5 2690 | 8 | 16 | 2.9 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 38 | 8 x 256KB | 20MB | 135W | Q1'12 | $2057 |
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1156
LGA 1156
 | |
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Chip form factors | Flip-chip land grid array |
| Contacts | 1156 |
| FSBprotocol | PCIe 16× (video) + 4× (DMI) + 2 DP (FDI), 2 DDR3 channels |
| Processor dimensions | 37.5 × 37.5 mm[1] |
| Processors | Intel Celeron Intel Pentium Intel Core i3 Intel Core i5 Intel Core i7 Intel Xeon |
| Predecessor | LGA 775 |
| Successor | LGA 1155 |
|
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
LGA 1156, also known as Socket H[2][3] or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. LGA stands for land grid array. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155.
LGA 1156, along with LGA 1366, were designed to replace LGA 775. Whereas LGA 775 processors connect to anorthbridge using the Front Side Bus, LGA 1156 processors integrate the features traditionally located on a northbridge on the processor itself. The LGA 1156 socket allows the following connections to be made from the processor to the rest of the system:
- PCI-Express 2.0 ×16 for communication with a graphics card. Some processors allow this connection to be divided into two ×8 lanes to connect two graphics cards. Some motherboard manufacturers use Nvidia's NF200 chip to allow even more graphics cards to be used.
- DMI for communication with the Platform Controller Hub (PCH). This consists of a PCI-Express 2.0 ×4 connection.
- FDI for communication with the PCH. This consists of two DisplayPort connections.
- Two memory channels for communication with DDR3 SDRAM. The clock speed of the memory that is supported will depend on the processor.
LGA 1156 socket and processors were discontinued sometime in 2012,[4] and superseded by the LGA 1155 socket. LGA 1366 was discontinued at the same time.
Supported processors[edit]
| Code name | Brand name | Model (list) | Frequency | Cores/Threads | Max Memory Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lynnfield | Core i5 | i5-7xx | 2.66-2.8 GHz | 4/4 | DDR3-1333 |
| Core i7 | i7-8xx | 2.8-3.07 GHz | 4/8 | ||
| Xeon | L34xx | 1.86 GHz | 4/4 or 4/8 | ||
| X34xx | 2.4-2.93 GHz | ||||
| Clarkdale | Celeron | G1xxx | 2.26 GHz | 2/2 | DDR3-1066 |
| Pentium | G6xxx | 2.80 GHz | 2/2 | ||
| Core i3 | i3-5xx | 2.93-3.2 GHz | 2/4 | DDR3-1333 | |
| Core i5 | i5-6xx | 3.2-3.6 GHz | 2/4 |
All LGA 1156 processors and motherboards made to date are interoperable, making it possible to switch between a Celeron, Pentium, Core i3 or Core i5 with integrated graphics and a Core i5 or Core i7 without graphics. However, using a chip with integrated graphics on a P55 motherboard will (in addition to likely requiring a BIOS update) not allow use of the on-board graphics processor, and likewise, using a chip without integrated graphics on a H55, H57 or Q57 motherboard will not allow use of the motherboard's graphics ports.[5]
Supported chipsets[edit]
The Desktop chipsets that support LGA 1156 are Intel's H55, H57, P55, and Q57. Server chipsets supporting the socket are Intel's 3400, 3420 and 3450.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1155#Original_Sandy_Bridge_chipsets
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1155#Ivy_Bridge_chipsets
LGA 1155
 | |
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Contacts | 1155 |
| Processor dimensions | 37.5mm × 37.5mm[1] |
| Processors | Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge |
| Predecessor | LGA 1156 |
| Successor | LGA 1150 |
|
This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which supports Intel Sandy Bridgeand Ivy Bridge microprocessors.
It's incompatible high-performance counterpart for Intel desktops and servers is the LGA 2011.
LGA 1155 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1156 (known as Socket H). LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. Processors of LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compatible with each other since they have different socket notches. However, cooling systems are compatible between both LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets, as the processor has the same dimensions, profile and construction, and similar heat production.[2]
Integrated USB 3.0 support is present in the Z75, Z77, H77, Q75, Q77 and B75 chipsets intended for Ivy Bridge CPUs. Refer to list of Intel chipsets for the complete list of socket 1155 chipsets.
LGA 1150 has succeeded LGA 1155.
Original Sandy Bridge chipsets[edit]
Sandy Bridge chipsets, except Q65, Q67 and B65, support both Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge CPUs through a BIOS upgrade.[3] Sandy Bridge based processors officially support up to DDR3-1333 memory, however in practice speeds up to DDR3-2133 have been tested to work successfully.[4]
The H61 chipset only supports one double-sided DIMM per memory-channel and therefore is limited to 16 GB instead of the 32 GB like the others support.[5] On motherboards with four DIMM slots, only four single-sided DIMMs can be installed.[6]
| Name | B65 | H61 | Q67 | H67[7] | P67 | Z68[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overclocking | GPU | CPU + RAM | CPU + GPU + RAM | |||
| Allows using built-in GPUwith Intel Clear Video Technology | Yes | No | Yes | |||
| Maximum USB 2.0 ports1 | 12 | 10 | 14 | |||
| Maximum SATA 2.0/3.0 ports | 4 / 1 | 4 / 0 | 4 / 2 | |||
| Main PCIe Configuration | 1 × PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 1 × PCIe 2.0 ×16 or 2 × PCIe 2.0 ×8 | ||||
| Secondary PCIe | 8 × PCIe 2.0 | 6 × PCIe 2.0 | 8 x PCIe 2.0 | |||
| Conventional PCI support2 | Yes | No | Yes | No | ||
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RAID) | No | Yes | ||||
| Smart Response Technology | No | Yes | ||||
| Ivy Bridge Processor Support | No | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Intel Active Management,Trusted Execution, Anti-Theft, and vPro Technology | No | Yes | No | |||
| Release Date | February 2011 | May 2011 | January 2011 | May 2011 | ||
| Max TDP | 6.1 W | |||||
| Chipset lithography | 65 nm | |||||
[9] Table updated with the latest information from Intel ARK
1 USB 3.0 is not supported by any of these chipsets. Motherboard manufacturers may use external hardware to add USB 3.0 support.
2 Although some of the chipsets do not support conventional PCI, motherboard manufacturers may include support through the addition of third party chips.
Ivy Bridge chipsets[edit]
All Ivy Bridge chipsets and motherboards support both Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge CPUs. Ivy Bridge based processors will officially support up to DDR3-1600, up from DDR3-1333 of Sandy Bridge. Some consumer Ivy Bridge chipsets will also allow overclocking of K-series processors.[10]
| Name | B75 | Q75 | Q77 | H77 | Z75 | Z77 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overclocking | CPU(Bclk) + GPU | CPU + GPU + RAM | ||||
| Allows using built-in GPU | Yes | |||||
| Intel Clear Video Technology | Yes | |||||
| RAID | No | Yes | ||||
| Maximum USB 2.0/3.0 ports | 8 / 4 | 10 / 4 | ||||
| Maximum SATA 2.0/3.0 ports | 5 / 1 | 4 / 2 | ||||
| Main PCIe Configuration3 | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 or 2 × PCIe 3.0 ×8 | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 or 2 × PCIe 3.0 ×8 or 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×8 + 2 × PCIe 3.0 ×4 | |||
| Secondary PCIe | 8 × PCIe 2.0 | |||||
| Conventional PCI4 | Yes [11] | No | ||||
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology | No | Yes | ||||
| Intel Anti-Theft Technology | Yes | |||||
| Smart Response Technology | No | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Intel vPro | No | Yes | No | |||
| Release Date | April 2012[12] | |||||
| Max TDP | 6.7 W | |||||
| Chipset lithography | 65 nm[13] | |||||
3 For PCIe 3.0 capability, the Ivy Bridge CPU must have the relevant PCIe 3.0 controller built in. Some Ivy Bridge CPUs only have a PCIe 2.0 controller built in.
4 Although some of the chipsets do not support conventional PCI, motherboard manufacturers may include support through the addition of third party chips.
| Intel CPU sockets and slots | |
|---|---|
| Desktop sockets | |
| Mobile sockets | |
| Server sockets | |
| Pre-Pentium II PGA Sockets | |
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LGA_1150#Original_Haswell_chipsets
LGA 1150
 | |
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Contacts | 1150 |
| Processor dimensions | 37.5 mm × 37.5 mm |
| Processors | Haswell, Broadwell |
| Predecessor | LGA 1155 |
|
This article is part of the CPU socketseries | |
LGA 1150,[1] also called Socket H3, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which supports the Intel Haswellmicroprocessor and its future successor, Broadwell.[2]
LGA 1150 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1155 (known as Socket H2). LGA 1150 has 1150 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. Cooling systems for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are compatible with LGA 1150, due to them having the same distance of 75 mm between each screw hole. All socket 1150 motherboards support varying video outputs (VGA, DVI, HDMI - depending on a model) and Intel Clear Video Technology.
Chipset for LGA 1150 is codenamed Lynx Point.[3] Future Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150 will use the Intel C228 chipset.[4]
Original Haswell chipsets[edit]
| Name | H81 | B85 | Q85 | Q87 | H87 | Z87 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overclocking | *CPU Ratio (ASRock, ECS, Biostar, Gigabyte, Asus,MSI[5][6][7][8][9][10]) + GPU | CPU + GPU + RAM | ||||
| Intel Clear Video Technology | No | Yes | ||||
| Maximum USB ports | 8 USB 2.0 and 2 USB 3.0 | 8 USB 2.0 and 4 USB 3.0 | 10 USB 2.0 and 4 USB 3.0 | 8 USB 2.0 and 6 USB 3.0 | ||
| Maximum SATA ports | 2 SATA 2.0 and 2 SATA 3.0 | 2 SATA 2.0 and 4 SATA 3.0 | 6 SATA 3.0 | |||
| Main PCIe Configuration | 1 × PCIe 2.0 ×16 | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 or 2 × PCIe 3.0 ×8 or 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×8 + 2 × PCIe 3.0 ×4 | |||
| Secondary PCIe | 6 × PCIe 2.0 | 8 x PCIe 2.0 | ||||
| Conventional PCI support1 | No | |||||
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RAID) | No | Yes | ||||
| Smart Response Technology | No | Yes | ||||
| Intel Anti-Theft Technology | Yes | |||||
| Intel Active Management,Trusted Execution, VT-d andvPro Technology | No | Yes | No | |||
| Release Date | 2 June 2013[11] | |||||
| Chipset TDP | 4.1W[12] | |||||
| Chipset lithography | 22 nm[13] | |||||
[14] Table updated with the latest information from Intel ARK. Additional details are in the Intel 8-Series Chipset Datasheet. [15]
1 Although chipsets do not support conventional PCI, motherboard manufacturers may include support through the addition of third party chips.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_Xeon_chipsets
Intel Xeon chipsets
Around the time that the Pentium 3 processor was introduced, Intel's Xeon line diverged from its line of desktop processors, which at the time was using the Pentium branding.
The divergence was implemented by using different sockets; since then, the sockets for Xeon chips have tended to remain constant across several generations of implementation.
The chipsets contain a 'memory controller hub' and an 'I/O controller hub', which tend to be called 'north bridge' and 'south bridge' respectively. The memory controller hub connects to the processors, memory, high-speed I/O such as PCI Express, and to the I/O controller hub by a proprietary link. The I/O controller hub on the other hand, connects to lower-speed I/O, such as hard discs, PCI slots, USB and Ethernet.
Contents
[hide]
P6-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Dual processor P6-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Intel's initial preferred chipset for Pentium III Xeon was the 840.
| Product name | Codename | Processor FSB supported | Memory type supported | High-speed interfaces provided | Preferred IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 440GX AGPset | Marlinespike | 100 | One 72-bit-wide channel of SDRAM, with ECC; up to four DIMMs | PIIX4E | |
| 840 | Carmel | 100 or 133 | Two channels RDRAM, two RIMMs per channel |
Four processor P6-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Pentium III Xeon bus protocol allowed four processors on the same bus, so the 440GX AGPset could be used in four-CPU systems; the limit of 2GB of main memory remained. These support Slot 2.
There was also the 450NX PCIset, which consisted of several chips: a single 82451NX Memory and IO Bridge Controller roughly analogous to the North Bridge, up to two 82454NX PCI Expander Bridges which converted the protocol used by 451NX to two 32-bit PCI33 or one 64-bit PCI33 bus, along with up to two memory cards each equipped with one 82452NX RAS/CAS Generator chip and two 82453NX Data Path Multiplexer chips. It supported PIIX3 and PIIX4E south bridges, and EDO DRAM.
Eight processor P6-based Xeon chipset[edit]
In August 1999 Intel began shipping the Profusion PCIset.[1] The chipset was based on technology developed by Corollary.[2] It supported up to 8 Pentium III Xeon processors on two busses and maintained cache coherency between them.[3][4][5]
NetBurst-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Dual processor NetBurst-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
E7500 corresponded to the first Northwood-based Pentium4 Xeons, E7501 is essentially identical but supports faster FSB and memory. The E7320, E7520 and E7525 chipsets correspond to Prescott-based Pentium4 Xeons, and differ mainly in their PCI Express support. These support Socket 604.
| Product name | Codename | Processor FSB supported | Memory type supported | High-speed interfaces provided | Preferred IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E7205 | Granite Bay | 400 or 533 MHz | Two channels of DDR at 100 MHz or 133 MHz | AGP 8× port, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, 266 MHz 8-bit hub interface for ICH4 | ICH4 |
| E7320[6] | Lindenhurst VS | 800 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR SDRAM at 200 MHz (6.4GB/s peak) | One ×8 PCI Express interface with max theoretical bandwidth of 4 GB/s, which may be configured as two ×4 PCIe interfaces. A 6700PXH provides PCI-X 32-bit and/or 64-bit interfaces at 33 MHz, 66 MHz, 100 MHz, and 133 MHz. | 6300ESB, or 82801ER (ICH5R) |
| E7500 | Plumas | 400 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR SDRAM at 100 MHz (3.2GB/s peak) | Three ECC 1GB/s (66 MHz ×8, 16-bit) 'Hub Interface' channels, which connect to 82870P2 chips to provide two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI or PCI-X buses each, plus one ECC 533MB/s (66 MHz ×4) connector for ICH3-S | ICH3-S |
| E7501 | Plumas | 533 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR SDRAM at 133 MHz (4.2GB/s peak) | Three ECC 1GB/s (66 MHz ×8, 16-bit) 'Hub Interface' channels, which connect to 82870P2 chips to provide two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI or PCI-X buses each, plus one ECC 533MB/s (66 MHz ×4) connector for ICH3-S | ICH3-S |
| E7505 | Placer[7] | 533 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR SDRAM at 133 MHz (4.2GB/s peak) | AGP 8× port, three ECC 1GB/s (66 MHz ×8, 16-bit) 'Hub Interface' channels, which connect to 82870P2 chips to provide two 64-bit 66 MHz PCI or PCI-X buses each, plus one ECC 533MB/s (66 MHz ×4) connector for ICH4 | ICH4 |
| E7520[8] | Lindenhurst | 800 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR SDRAM at 200 MHz (6.4GB/s peak) | Three ×8 PCI Express interfaces each with max theoretical bandwidth of 4 GB/s, which may be configured as two ×4 PCIe interfaces. A 6700PXH provides PCI-X 32-bit and/or 64-bit interfaces at 33 MHz, 66 MHz, 100 MHz, and 133 MHz. | 6300ESB, or 82801ER (ICH5R) |
| E7525[9] | Tumwater | 800 MHz | Two channels of registered DDR333 or DDR2/400 SDRAM | One ×16 and one ×8 PCI Express interface. A 6700PXH can be attached. | 6300ESB, or 82801ER (ICH5R) |
Note that the 82870P2 chips mentioned above were initially designed for the Intel 870 chipset for Itanium 2, and that the summary page of the E7320 datasheet incorrectly claims three PCI Express interfaces.
Quad processor NetBurst-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
| Product name | Codename | Processor FSB supported | Memory type supported | High-speed interfaces provided | Preferred IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E8500 | Twin Castle | 667 MHz | DDR-266, DDR-333 or DDR2-400 | three ×8 and one ×4 PCI Express interface | 82801EB (ICH5), or 82801ER (ICH5R) |
| E8501 | Twin Castle | 667 and 800 MHz | DDR2-400 | 82801EB (ICH5), or 82801ER (ICH5R) |
Core-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Single processor Core-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
| Product name | Codename | Processor FSB supported | Memory type supported | High-speed interfaces provided | Preferred IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | Mukilteo | 533 or 800 or 1066 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR2-533 or DDR2-667 | PCI Express ×8 port, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for ICH7 | ICH7 |
| 3010 | Mukilteo 2 | 533 or 800 or 1066 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR2-533 or DDR2-667 | PCI Express 1 ×16 or 2 ×8 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for ICH7 | ICH7 |
| 3200 | Bigby | 800 or 1066 or 1333 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR2-667 or DDR2-800 | PCI Express ×8 port, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for ICH9 | ICH9 |
| 3210 | Bigby | 800 or 1066 or 1333 MHz | Two channels of ECC DDR2-667 or DDR2-800 | PCI Express 1 ×16 or 2 ×8 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for ICH9 | ICH9 |
Dual processor Core-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
These chipsets use a 'dual independent bus' design, in which each socket has its own connection to the chipset. These support LGA 771.
| Product name | Codename | Processor FSB supported | Memory type supported | High-speed interfaces provided | Preferred IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5000P | Blackford | 1066, 1333 | Four channels of FB-DIMM at 533 or 667 MHz | Two PCIe ×8 ports, plus two ×4 ports for communication with IOCH | 631xESB or 632xESB |
| 5000V | Blackford | 1066, 1333 | Two channels of FB-DIMM at 533 or 667 MHz | No PCI-e ports are exposed - connection is exclusively to the IOCH | 631xESB or 632xESB |
| 5000Z | Blackford | 1066, 1333 | Two channels of FB-DIMM at 533 or 667 MHz | One PCI-e ×8 port, plus two ×4 ports for communication with IOCH | 631xESB or 632xESB |
| 5000X | Greencreek | 1066, 1333 (has a snoop filter, comprising about 1MB of SRAM, to keep cache coherency traffic between the two sockets from appearing on the external bus) | Four channels of FB-DIMM at 533 or 667 MHz | One PCI-e ×16 port | 631xESB or 632xESB |
| 5100 | San Clemente | 1066, 1333 | Two channels of registered ECC DDR2 | 6 PCIe ×4 ports | 631xESB or 632xESB |
| 5400 | Seaburg | 1066, 1333, 1600; has a more advanced snoop filter than 5000X, comprising about 1.6MB of SRAM | Four channels of FB-DIMM at 533, 667 or 800 MHz | 9 PCIe ×4 ports | 631xESB or 632xESB |
Four processor Core-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
This chipset uses four independent buses, and is used by the Tigerton and Dunnington processors.
| Launch name | Codename | FSB speed | Memory speed | Fast I/O | IOCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7300[10] | Clarksboro | 1066. Very sophisticated snoop filter, comprising 4.5MB of SRAM. | Four channels of FB-DIMM at 533 or 667 MHz | 7 PCIe ×4 ports, of which two are usually used to connect to the IOCH | 631x or 632x |
Nehalem-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Single processor Nehalem-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The 3450 chipset is also compatible with an Intel Core i5 or Intel Core i3 processor.
| Product name | Codename | DMI | Fast I/O | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3400 | Ibex Peak | 1.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 6 ×1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 8× USB 2.0, 4× SATA, Integrated LAN |
| 3420 | Ibex Peak | 1.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 8 ×1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 12× USB 2.0, 6× SATA, Integrated LAN |
| 3450 | Ibex Peak | 1.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 8 ×1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 14× USB 2.0, 6× SATA, Integrated LAN |
Dual processor Nehalem-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Nehalem-based Xeons for dual-socket systems, initially launched as the Xeon 55xx series, feature a very different system structure: the memory controllers are on the CPU, and the CPUs can communicate with one another as peers without going via the chipset. This means that the 5500 and 5520 chipsets are essentiallyQPI to PCI Express interfaces; the 5520 is more intended for graphical workstations and the 5500 for servers that do not need vast amounts of PCI Express connectivity
| Launch name | Codename | QPI ports | QPI speed | Fast I/O | IOCH | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5500 | Tylersburg-24D | 2 | 4.8, 5.86 or 6.4 GT/s | 1 ×16 PCIe Gen 2, 2 ×4 PCIe Gen 1 to talk to southbridge | ICH10 (ICH9 also possible) | Integrated Management Engine with its own 100 Mbit Ethernet |
| 5520 | Tylersburg-36D | 2 | 4.8, 5.86 or 6.4 GT/s | 2 ×16 PCIe Gen 2, 1 ×4 PCIe Gen 1 to talk to southbridge | ICH10 (ICH9 also possible) | Integrated Management Engine with its own 100 Mbit Ethernet |
Four processor Nehalem-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
| Launch name | Codename | QPI ports | QPI speed | Fast I/O | IOCH | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7500 | Boxboro | 4 | 6.4 GT/s | 2 ×16 PCIe Gen 2, 1 ×4 PCIe Gen 1 to talk to southbridge | ICH10 (ICH9 also possible) | Integrated Management Engine with its own 100 Mbit Ethernet |
Sandy Bridge-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Single processor Sandy Bridge-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Intel C200 series chipsets that support the Intel Xeon E3-1200 CPU family.[11][12]
| Product name | Codename | DMI | Fast I/O | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C202 | Cougar Point | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 12 × USB 2.0, 6 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN |
| C204 | Cougar Point | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 12 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3/6 Gbit/s + 4 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN |
| C206 | Cougar Point | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 14 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3/6 Gbit/s + 4 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN, Integrated Graphics, Intel Anti-Theft Technology, Active Management Technology 7.0 |
Single processor Ivy Bridge-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Intel C200 series chipsets that support the Intel Xeon E3-1200v2 CPU family.[13]
| Product name | Codename | DMI | Fast I/O | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C216 | Panther Point | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 4 × USB 3.0 + 14 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3/6 Gbit/s + 4 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN, Integrated Graphics, Intel Anti-Theft Technology, Active Management Technology 8.0 |
Dual processor Sandy Bridge-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Intel C600 series chipsets support the Intel Xeon E5-2600 CPU family. Common to all C600 variants are the following features:
- DMI interface to CPU at 20 GT/s
- 8 PCIe 2.0 (5 GT/s) lanes, configurable by the board manufacturer as 8×1, 4×2, 2×4, or 1×8.
- 2 SATA ports supporting 6/3/1.5 Gbaud operation
- 4 SATA ports supporting 3/1.5 Gbaud operation
- one PCI 2.3 32-bit 33 MHz bus interface
- 14 USB 2.0 ports
- single-port Gigabit Ethernet controller
- Active Management Technology 7.0 and Anti-Theft Technology
- HD Audio controller
Some chipset variants have additional mass storage interfaces:
| Product name | Codename | additional mass storage capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| C602J | Patsburg | none |
| C602 | Patsburg | 4× SATA 1.5/3 Gbaud ports |
| C604 | Patsburg | 4× SAS/SATA 1.5/3 Gbaud ports |
| C606 | Patsburg | 8× SAS/SATA 1.5/3 Gbaud ports optionally through dedicated PCIe 2.0 ×4 (5 GT/s) interface, 1 additional SMBus |
| C608 | Patsburg | 8× SAS/SATA 1.5/3 Gbaud ports optionally through dedicated PCIe 2.0 ×4 (5 GT/s) interface, 2 additional SMBus |
Dual processor Gladden/Sandy Bridge-EP/EN-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Intel Communications 8900 series chipsets that support the Gladden Intel Xeon E3-11xx[14] or Sandy Bridge-EP/EN Intel Xeon E5-2xxx[15] CPU families.
| Product name | Codename | DMI | Fast I/O | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DH8900 | Cave Creek | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 ×16 + PCI Express 1.0 4 × 1 ports, DMI for processor | 6 × USB 2.0, 6 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, 4 × Integrated LAN |
| DH8903 | Cave Creek | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 ×8 + PCI Express 1.0 4 × 1 ports, DMI for processor | 6 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, 4 × Integrated LAN, 5 Gbit/s QuickAssist |
| DH8910 | Cave Creek | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 ×4 + PCI Express 1.0 4 × 1 ports, DMI for processor | 6 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, 4 × Integrated LAN, 10 Gbit/s QuickAssist |
| DH8920 | Cave Creek | 2.0, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 ×4 + PCI Express 1.0 4 × 1 ports, DMI for processor | 6 × USB 2.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, 4 × Integrated LAN, 20 Gbit/s QuickAssist |
Haswell-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
Single processor Haswell-based Xeon chipsets[edit]
The Intel C220 series chipsets support the Intel Xeon E3-1200v3 CPU family.[16]
| Product name | Codename | DMI | Fast I/O | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C222 | Lynx Point | 2.3, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 10 × USB 2.0/3.0, 2 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s + 4 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN, Integrated IDE, Rapid Storage Technology enterprise |
| C224 | Lynx Point | 2.3, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 12 × USB 2.0/3.0, 4 × SATA 1.5/3/6 Gbit/s + 2 × SATA 1.5/3 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN, Integrated IDE, Rapid Storage Technology enterprise |
| C226 | Lynx Point | 2.3, 100 MHz | PCI Express 2.0 8 × 1 ports, single 32-bit 33 MHz PCI bus, DMI for processor | 14 × USB 2.0/3.0, 6 × SATA 1.5/3/6 Gbit/s, Integrated LAN, Integrated Graphics, Rapid Storage Technology enterprise, Active Management Technology 9.0, Identity Protection Technology, VGA, Wireless Display |






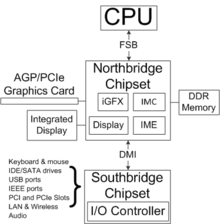


















 3408
3408

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








