codeforces 407D Largest Submatrix 3
题意
找出最大子矩阵,须满足矩阵内的元素互不相等。
题解
官方做法
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/11333
- \(O(n^6)\)
- 枚举子矩阵,暴力check。
- \(O(n^4)\)
- 枚举上下边界,双指针。
- \(O(n^3log_2n)\)
- 假设当前上边界 \(up\), 下边界 \(down\),\(R_i\) 表示当 \(i\) 为左边界时,右边界最大是 \(R_i\)。
- 当 \(down->down+1\) 时,\(R_i\) 要么不变,要么减小。
- 减小的情况:\(a_{down+1, j}(i<=j<=R_i)\) 在矩阵 \((up, i, down, R_i)\) 中出现。
- 因此对于每个 \(a_{down+1, j}(i<=j<=R_i)\),我们需要寻找在矩阵 \((up, i, down, R_i)\) 中出现的,从左边最靠近 \(j\),和从右边最靠近 \(j\) 的两个位置。这个可以用set维护。
- \(O(n^3)\)
- 如何优化掉 \(O(n^3log_2n)\) 做法的 \(log_2n\) ?
- 从大到小枚举 \(up\)。当 \(up->up-1\) 时,\(O(n^2)\) 更新 \((up, 1, n, m)\) 中所有点的从左边最靠近,和从右边最靠近的两个位置。
区间dp做法
\(f_{i, l, r}\)表示下边界是 \(i\), 左右边界是 \(l, r\) 时,上边界的值。
\(f_{i, l, r}=max\{f_{i-1, l, r}, f_{i, l+1, r}, f_{i, l, r-1}, a_{i, l}与a_{1-i, r}的限制, a_{i, r}与a_{1-i, l}的限制\}\)
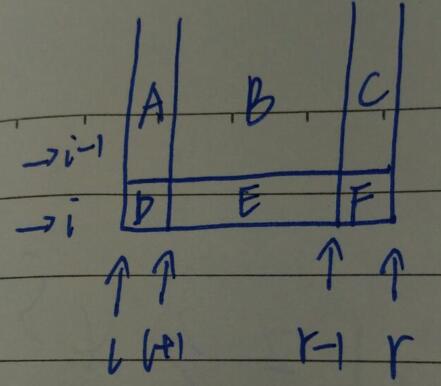
可以这样理解:\(f_{i, l, r}\) 需要维护A、B、C、D、E、F这六个块之间的关系,\(f_{i-1, l, r}\) 只维护了A、B、C之间的关系,\(f_{i, l+1, r}\) 只维护了B、C、E、F之间的关系,\(f_{i, l, r-1}\) 只维护了A、B、D、E之间的关系,剩下的还需维护A与F、C与D、D与F的关系。
// 代码实现可以省掉第一维。
代码
\(O(n^3log_2n)\)做法
T了 不知道有没有写错
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); i++)
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define de(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<endl
#define dd(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<" "
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef vector<int> vi;
const int N=404;
int n,m;
int a[N][N], R[N], cnt[N*N];
set<int> pos[N*N];
int solve() {
int ans=1;
rep(up,1,n+1) {
rep(i,0,N*N) pos[i].clear();
rep(i,0,m+1) R[i]=m;
rep(down,up,n+1) {
int r=0;
rep(i,1,m+1) {
while(r<m&&!cnt[a[down][r+1]]) {
++r;
++cnt[a[down][r]];
}
R[i]=min(R[i], r);
--cnt[a[down][i]];
}
rep(j,1,m+1) {
int c=a[down][j];
auto it1=pos[c].upper_bound(j);
auto it2=pos[c].lower_bound(j);
if(it1!=pos[c].begin()) {
--it1;
if(*it1<=j) R[*it1]=min(R[*it1], j-1);
}
if(it2!=pos[c].end()) {
if(j<=*it2) R[j]=min(R[j], *it2-1);
}
}
for(int i=m-1;i;--i) R[i]=min(R[i], R[i+1]);
rep(i,1,m+1) if(i<=R[i]) ans=max(ans, (down-up+1)*(R[i]-i+1));
rep(i,1,m+1) pos[a[down][i]].insert(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) {
///read
rep(i,1,n+1) rep(j,1,m+1) scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
///solve
printf("%d\n",solve());
}
return 0;
}\(O(n^3)\) 做法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); i++)
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define de(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<endl
#define dd(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<" "
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef vector<int> vi;
const int N=404;
int n, m;
int a[N][N], p[N*N], l[N][N], r[N][N], R[N];
void Min(int &a, int b) {
if(a>b) a=b;
}
void Max(int &a, int b) {
if(a<b) a=b;
}
int solve() {
int ans=1;
rep(i,0,n+1) rep(j,0,m+1) l[i][j]=0, r[i][j]=m+1;
for(int u=n;u;--u) {
rep(i,1,m+1) p[a[u][i]]=0;
rep(i,1,m+1) l[u][i]=p[a[u][i]], p[a[u][i]]=i;
rep(i,1,m+1) p[a[u][i]]=m+1;
for(int i=m;i;--i) r[u][i]=p[a[u][i]], p[a[u][i]]=i;
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
rep(i,1,m+1) {
p[a[u][i]]=i;
rep(v,u+1,n+1) Max(l[v][i], p[a[v][i]]);
}
rep(i,0,N*N) p[i]=m+1;
for(int i=m;i;--i) {
p[a[u][i]]=i;
rep(v,u+1,n+1) Min(r[v][i], p[a[v][i]]);
}
rep(i,1,m+1) R[i]=m+1;
rep(v,u,n+1) {
rep(i,1,m+1) {
Min(R[l[v][i]], i);
Min(R[i], r[v][i]);
}
for(int i=m-1;i;--i) Min(R[i], R[i+1]);
rep(i,1,m+1) {
Max(ans, (v-u+1)*(R[i]-i));
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) {
///read
rep(i,1,n+1) rep(j,1,m+1) scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
///solve
printf("%d\n",solve());
}
return 0;
}区间dp做法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<(b); i++)
#define sz(x) (int)x.size()
#define de(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<endl
#define dd(x) cout<< #x<<" = "<<x<<" "
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef vector<int> vi;
const int N=404;
int n,m;
int a[N][N], f[N][N], p[N][160004];
int main() {
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)) {
rep(i,1,n+1) rep(j,1,m+1) scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
int ans=1;
rep(i,1,n+1) {
rep(len,1,m+1) {
for(int l=1, r=len;r<=m;++l, ++r) {
if(l==r) {
f[l][r]=max(f[l][r], p[l][a[i][l]]);
} else {
f[l][r]=max(f[l][r], max(f[l][r-1], f[l+1][r]));
f[l][r]=max(f[l][r], max(p[l][a[i][r]], p[r][a[i][l]]));
if(a[i][l]==a[i][r]) f[l][r]=i;
}
ans=max(ans, (i-f[l][r])*(r-l+1));
}
}
rep(j,1,m+1) p[j][a[i][j]]=i;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}



 本文介绍了 CodeForces 平台上的题目 407D,该题要求找出最大的子矩阵,其中所有元素各不相同。文章提供了多种解题思路,包括 O(n^6), O(n^4), O(n^3log_2n), O(n^3) 的复杂度解法,并给出了具体的实现代码。
本文介绍了 CodeForces 平台上的题目 407D,该题要求找出最大的子矩阵,其中所有元素各不相同。文章提供了多种解题思路,包括 O(n^6), O(n^4), O(n^3log_2n), O(n^3) 的复杂度解法,并给出了具体的实现代码。
















 731
731

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








