0.简介(在以下环境下运行通过):
运行环境:Linux(ubuntu12.10);
编译器:gcc;
语言:C语言;
作者:Catcher24。
1.问题描述:
使用链表实现多项式的表示和运算(加法、减法、乘法)。
2.数据结构描述与设计:
2.1 使用链表的原因:
有两个多项式:
P1 = 6x^4+4x^2-x;
P2 = -7x^5+x^2;
如果要对两个多项式进行操作(多项式相加、除法等等......),可以采用数组的存储方式。设多项式P(n) = a1xn+a2xn-1+...an;如果采用数组A[n]来存储P(n)的系数,当P(n)中有的ai为0时,数组储存在空间上会带来很大的浪费。而采用链表存储,每个节点存储系数和指数信息。
用链表来表示多项式,节点信息如下图:
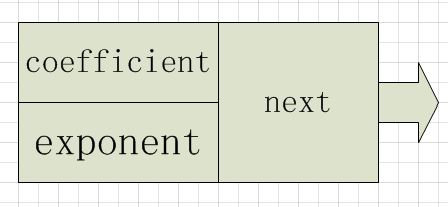
图:链表节点信息
2.2 多项式的链表实现:
下面给出polynomial.h文件,里面包含了节点的定义和函数定义;
1 #include <stdlib.h> 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 #ifndef _List_H 5 typedef int bool; 6 typedef int exp_type; 7 typedef float coe_type; 8 #define true 1 9 #define false 0 10 typedef struct node { 11 coe_type coefficient; 12 exp_type exponent; 13 struct node* next; 14 }node; 15 typedef struct node* polynomial; 16 17 node* init(node* l); 18 node* make_empty(node* l); 19 bool is_empty(node* l); 20 bool is_last(node* p,node* l); 21 node* find(coe_type x,node* l); 22 node* find_previous(coe_type x,node *l); 23 void delete_node(coe_type x, node* l); 24 void insert(coe_type x,exp_type y,node* l); 25 void delete_list(node* l); 26 node* header(node* l); 27 node* first(node* l); 28 void print_list(node* l); 29 30 polynomial create(polynomial poly,coe_type coe[],exp_type exp[],int n); 31 polynomial plus_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial polyprod); 32 polynomial sub_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial polyprod); 33 polynomial mult_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial polyprod); 34 void print_poly(const polynomial poly); 35 36 #endif
其中通过create()函数创建一个新的多项式,用一个float类型的数组来表示多项式的系数,用int型的数组来表示多项式的指数。plus_poly()函数实现多项式加法,sub_poly()函数实现多项式减法,mult_poly()函数实现多项式乘法。
下面给出polynomial.c文件:
1 #include "polynomial.h" 2 3 node* init(node* l) 4 { 5 l = malloc(sizeof(node)); 6 l->next = NULL; 7 return l; 8 } 9 node* make_empty(node* l) 10 {//Make list which l pointer to empty 11 node* nptr = l; 12 if(nptr->next == NULL) 13 return nptr; 14 nptr = nptr->next; 15 while(nptr->next != NULL){ 16 node* ptr = nptr; 17 nptr = nptr->next; 18 free(ptr); 19 } 20 l->next = NULL; 21 return l; 22 } 23 bool is_empty(node* l) 24 { 25 return (l->next == NULL)?true:false; 26 } 27 bool is_last(node* plast,node* l) 28 { 29 node* nptr = l; 30 while(nptr->next != NULL) 31 nptr = nptr->next; 32 return (nptr == plast)?true:false; 33 } 34 node* find(coe_type x,node* l) 35 { 36 node* nptr = l; 37 if(is_empty(nptr)) 38 return NULL; 39 nptr = nptr->next; 40 while(nptr->next != NULL){ 41 if(nptr->coefficient == x) 42 return nptr; 43 nptr = nptr->next; 44 } 45 return NULL; 46 } 47 node* find_previous(coe_type x,node* l) 48 { 49 node* nptr = l; 50 if(is_empty(nptr)) 51 return NULL; 52 node* ptr = nptr; 53 nptr = nptr->next; 54 while(nptr->next != NULL){ 55 if(nptr->coefficient == x){ 56 return ptr; 57 } 58 ptr = nptr; 59 nptr = nptr->next; 60 } 61 return NULL; 62 } 63 void delete_node(coe_type x, node* l) 64 { 65 node* nptr = find(x,l); 66 if(nptr == NULL) 67 return; 68 node* pptr = find_previous(x,l); 69 pptr->next = nptr->next; 70 free(nptr); 71 return; 72 } 73 void insert(coe_type x,exp_type y,node* l) 74 { 75 node* nptr = malloc(sizeof(node)); 76 node* newptr = l; 77 while(newptr->next != NULL) 78 newptr = newptr->next; 79 nptr->coefficient = x; 80 nptr->exponent = y; 81 nptr->next = NULL; 82 newptr->next = nptr; 83 return ; 84 } 85 void delete_list(node* l) 86 { 87 l = make_empty(l); 88 free(l); 89 return; 90 } 91 node* header(node* l) 92 { 93 return l; 94 } 95 node* first(node* l) 96 { 97 return l->next; 98 } 99 void print_list(node* l) 100 { 101 if(is_empty(l)){ 102 printf("List is empty!\n"); 103 return; 104 } 105 node* nptr = l->next; 106 while(nptr != NULL){ 107 printf("%f\n",nptr->coefficient); 108 nptr = nptr->next; 109 } 110 } 111 112 /* 113 */ 114 polynomial create(polynomial poly,coe_type coe[],exp_type exp[],int n) 115 { 116 poly = init(poly);//Init poly:create a head; 117 int i,j; 118 for(i = 0;i < n;i++){ 119 int max = i; 120 for(j = i+1;j < n;j++){ 121 if(exp[j] > exp[max]){ 122 max = j; 123 } 124 } 125 if(max != i){ 126 coe_type temp = coe[i]; 127 coe[i] = coe[max]; 128 coe[max] = temp; 129 exp_type temp1 = exp[i]; 130 exp[i] = exp[max]; 131 exp[max] = temp1; 132 } 133 } 134 for(i = 0;i < n;i++) 135 insert(coe[i],exp[i],poly); 136 return poly; 137 } 138 polynomial plus_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial polyprod) 139 { 140 polynomial p1 = poly1->next; 141 polynomial p2 = poly2->next; 142 while(p1 != NULL && p2 != NULL){ 143 if(p1->exponent == p2->exponent){ 144 insert(p1->coefficient + p2->coefficient,p1->exponent,polyprod); 145 p1 = p1->next; 146 p2 = p2->next; 147 } 148 else if(p1->exponent > p2->exponent){ 149 insert(p1->coefficient,p1->exponent,polyprod); 150 p1 = p1->next; 151 } 152 else if(p1->exponent < p2->exponent){ 153 insert(p2->coefficient,p2->exponent,polyprod); 154 p2 = p2->next; 155 } 156 } 157 if(p1 == NULL && p2 == NULL) 158 return polyprod; 159 polynomial p3 = (p1 != NULL)? p1:p2; 160 while(p3 != NULL){ 161 insert(p3->coefficient,p3->exponent,polyprod); 162 p3 = p3->next; 163 } 164 return polyprod; 165 } 166 polynomial sub_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial polyprod) 167 { 168 polynomial p1 = poly1->next; 169 polynomial p2 = poly2->next; 170 while(p1 != NULL && p2 != NULL){ 171 if(p1->exponent == p2->exponent){ 172 insert(p1->coefficient - p2->coefficient,p1->exponent,polyprod); 173 p1 = p1->next; 174 p2 = p2->next; 175 } 176 else if(p1->exponent > p2->exponent){ 177 insert(p1->coefficient,p1->exponent,polyprod); 178 p1 = p1->next; 179 } 180 else if(p1->exponent < p2->exponent){ 181 insert(-p2->coefficient,p2->exponent,polyprod); 182 p2 = p2->next; 183 } 184 } 185 if(p1 == NULL && p2 == NULL) 186 return polyprod; 187 if(p1 == NULL){ 188 p1 = p2; 189 while(p1 != NULL){ 190 insert(-p1->coefficient,p1->exponent,polyprod); 191 p1 = p1->next; 192 } 193 return polyprod; 194 } 195 p2 = p1; 196 while(p2 != NULL){ 197 insert(p2->coefficient,p2->exponent,polyprod); 198 p2 = p2->next; 199 } 200 return polyprod; 201 202 } 203 polynomial mult_poly(const polynomial poly1,const polynomial poly2,polynomial ployprod) 204 { 205 polynomial p1 = poly1->next; 206 polynomial p2 = poly2->next; 207 polynomial p4 = NULL; 208 p4 = init(p4); 209 while(p1 != NULL){ 210 polynomial p3 = NULL; 211 polynomial p5 = NULL; 212 p3 = init(p3); 213 p5 = init(p5); 214 p2 = poly2->next; 215 while(p2 != NULL){ 216 insert(p2->coefficient*p1->coefficient,p2->exponent + p1->exponent,p3); 217 p2 = p2->next; 218 } 219 if(p4->next == NULL){ 220 polynomial ptr = p3->next; 221 while(ptr != NULL){ 222 insert(ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent,p5); 223 ptr = ptr->next; 224 } 225 } 226 else{ 227 p5 = plus_poly(p3,p4,p5); 228 } 229 delete_list(p4); 230 p4 = p5; 231 delete_list(p3); 232 p1 = p1->next; 233 } 234 return p4; 235 } 236 void print_poly(const polynomial poly) 237 { 238 if(is_empty(poly)){ 239 printf("0\n"); 240 return ; 241 } 242 polynomial ptr = poly->next; 243 bool tag = false; 244 while(ptr->next != NULL){ 245 if(ptr->coefficient == -1){ 246 printf("-X^%d",ptr->exponent); 247 } 248 else if(ptr->coefficient < 0) 249 printf("%fX^%d",ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent); 250 else if(ptr->coefficient == 1){ 251 printf("X^%d",ptr->exponent); 252 } 253 else if(tag){ 254 printf("+%fX^%d",ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent); 255 } 256 else if(!tag){ 257 printf("%fX^%d",ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent); 258 } 259 ptr = ptr->next; 260 tag = true; 261 } 262 if(ptr->coefficient == -1) 263 printf("-X^%d",ptr->exponent); 264 else if(ptr->coefficient < 0) 265 printf("%fX^%d",ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent); 266 else if(ptr->coefficient == 1){ 267 printf("X^%d",ptr->exponent); 268 } 269 else 270 printf("+%fX^%d",ptr->coefficient,ptr->exponent); 271 printf("\n"); 272 }
上面polynomial.c为头文件中声明的各个函数的实现,下面给出测试函数main.c:
1 #include "polynomial.h" 2 3 int main() 4 { 5 /*poly1: 6X^5 + X^3 + 4X^2 6 */ 7 coe_type p1[] = {-1,4,6,-10}; 8 exp_type p1_e[] = {3,2,5,4}; 9 polynomial poly1 = NULL; 10 poly1 = create(poly1,p1,p1_e,4); 11 /*poly2: 9X^4 + 8X^2 12 */ 13 coe_type p2[] = {9,-8}; 14 exp_type p2_e[] = {4,2}; 15 polynomial poly2 = NULL; 16 poly2 = create(poly2,p2,p2_e,2); 17 18 printf("poly1:\t"); 19 print_poly(poly1); 20 printf("poly2:\t"); 21 print_poly(poly2); 22 23 printf("Now test plus....\n"); 24 polynomial poly3 = NULL; 25 poly3 = init(poly3); 26 poly3 = plus_poly(poly1,poly2,poly3); 27 printf("poly3 = poly1 + poly2 :\t"); 28 print_poly(poly3); 29 30 printf("now test sub....\n"); 31 polynomial poly4 = NULL; 32 poly4 = init(poly4); 33 poly4 = sub_poly(poly1,poly2,poly4); 34 printf("poly4 = poly1 - poly2 :\t"); 35 print_poly(poly4); 36 37 printf("now test mult....\n"); 38 polynomial poly5 = NULL; 39 poly5 = init(poly5); 40 poly5 = mult_poly(poly2,poly1,poly5); 41 printf("poly5 = poly1 * poly2 :\t"); 42 print_poly(poly5); 43 44 delete_list(poly1); 45 delete_list(poly2); 46 delete_list(poly3); 47 delete_list(poly4); 48 delete_list(poly5); 49 return 0; 50 }
3.问题解答:
测试与运行:
将上述三个文件放在同一个目录下并使用命令:
gcc polynomial.h polynomial.c main.c -o main
编译,然后运行:
./main
结果如下图:
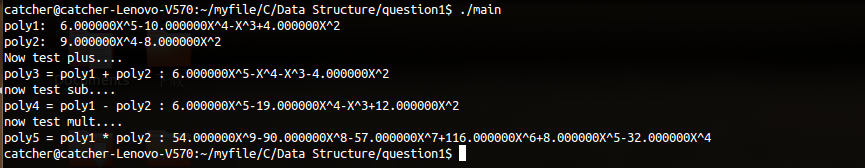
当然,也可以选择使用makefile来处理。




 本文介绍了一种使用链表来表示和计算多项式的数据结构和算法实现,包括加法、减法和乘法等基本运算,并提供了详细的C语言源代码示例。
本文介绍了一种使用链表来表示和计算多项式的数据结构和算法实现,包括加法、减法和乘法等基本运算,并提供了详细的C语言源代码示例。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








