goods组件显示的区域是固定的,也没有滚动条,所以是采用绝对布局的,左右分为menu栏和foods栏,左边固定布局,右边自适应布局,采用flex布局。
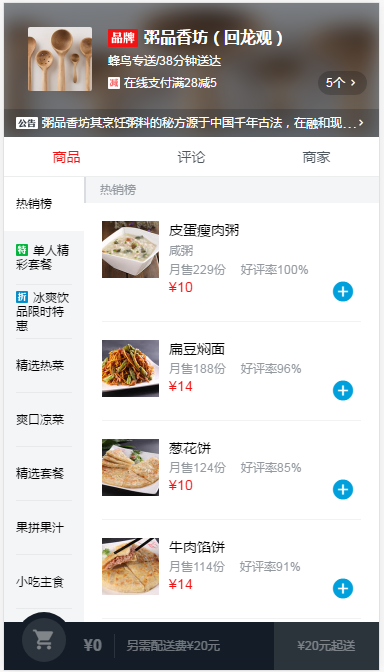
写CSS样式的时候,尽量用class,少用tag,因为class的查找效率优于tag,尤其是嵌套层级比较多的时候。左边的menu栏有些是一行有些是多行,要做到不管单行还是多行都是垂直是居中,可以用display:table,table布局是实现垂直居中的有效布局。menu-item设置display:table,text设置display:table-cell,vertical-align:center
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in goods" class="menu-item" :class="{'current':currentIndex===index}" @click="selectMenu(index, $event)">
<span class="text border-1px">
<span v-show="item.type>0" class="icon" :class="classMap[item.type]"></span>
{{item.name}}
</span>
</li>
</ul>
右边的food栏用两个<ul v-for="XXX">来实现遍历
每个食品的显示分为左边icon和右边的content,用flex布局来实现,左边固定宽度,右边自适应布局。goods组件的右边的food栏,除了最后一个食品的下面都有1px的border,要去掉最后一个食品的border,课程中是在mixin中写了一个border-none()的样式,把after的伪类设置为display:none。也可以用另一种方式来实现,由于border是通过after伪类来实现的,那么如果给最后一个食品的after伪类设置为border:none应该就可以去掉border了。
border-none()
&:after
display: none
food-item设置了18px的margin,但是由于相邻两个food-item的上下margin是会重合的,所以要再设置一个padding-bottom,但是最后一个food-item就会有一个18px的margin-bottom和18px的padding-bottom,所以最后一个fodd-tiem的margin-bottom要设置为0。
.food-item
display: flex
margin: 18px
padding-bottom: 18px
border-1px(rgba(7, 17, 27, 0.1))
用better scroll库实现滚动效果, new BScroll()有两个参数,第一个是dom对象,第二个是可选对象。给dom对象增加ref属性,<div class="foods-wrapper" ref="menuWrapper">,在js中用this.$refs获取dom对象,this.meunScroll = new BScroll(this.$refs.menuWrapper, {});
DOM对象是异步更新的,所以要把滚动的初始化函数放在¥nextTick()函数中,$nextTick 是在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调,在修改数据之后使用 $nextTick,则可以在回调中获取更新后的 DOM。
要实现左边的menu和右边的food的连动,要计算出右边每一个类的food的高度区间,用getElementsByClassNames获取每一个类food的DOM对象,用函数clientHeight得到的DOM对象的高度。
_calculateHeight() {
let foodList = this.$refs.foodsWrapper.getElementsByClassName('food-list-hook');
let height = 0;
this.listHeight.push(height);
for (let i = 0; i < foodList.length; i++) {
let item = foodList[i];
height += item.clientHeight;
this.listHeight.push(height);
}
}
然后拿到实时的y值与高度区间值对比,在BScroll函数中传入参数probeType:3就可以获取实时滚动的位置,用this.foodsscroll.on()监听滚动事件
this.foodsScroll = new BScroll(this.$refs.foodsWrapper, {
click: true,
probeType: 3
});
this.foodsScroll.on('scroll', (pos) => {
this.scrollY = Math.abs(Math.round(pos.y));
});
},
当food栏滚动时,获取当前的坐标,与区间对比,得到对应的index,更新左边的menu栏,对应index的menu-item会获得一个current的class。用better Scroll之后,点击时会有两个事件,一个是浏览器原生事件,一个是better Scroll派发的时间,其中浏览器原生事件都没有_constructed属性,better scroll派发的事件有_constructed属性。
<li v-for="(item, index) in goods" class="menu-item" :class="{'current':currentIndex===index}" @click="selectMenu(index, $event)">
computed: {
currentIndex() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.listHeight.length; i++) {
let height1 = this.listHeight[i];
let height2 = this.listHeight[i + 1];
if (!height2 || (this.scrollY >= height1 && this.scrollY < height2)) {
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
点击左边的menu列表时,根据index,通过scrollToElement把右边的列表滚动到对应的位置
selectMenu(index, event) {
if (!event._constructed) {
return;
}
let foodList = this.$refs.foodsWrapper.getElementsByClassName('food-list-hook');
let el = foodList[index];
this.foodsScroll.scrollToElement(el, 300);
},
购物车组件开发
购物车组件fixed布局,由于购物车是一直显示的所以要之一z-index的设置。购物车也可以分为左右两部分用flex布局,左边固定宽度,右边自适应。左边包括logo,price和desc,用display:inline-block
.shopcart
position: fixed
left: 0
bottom: 0
z-index: 50
width: 100%
height: 48px
background: #000
购物车的logo-wrapper是一个超出购物车一部分的圆形,用relative布局和负的top值实现超出购物车,圆形可通过相同的width和height和border-radius:50%实现。其中用到了box-sizing: border-box,这是指用IE下的盒子模型,这种方法在移动端布局比较常用,可以省去计算width。price的右边有border,设置line-height:24px和maring-top: 12px,这样子能使border的高度是24px. 在App组件中,seller数据要在router-view中传递过来<router-view :seller="seller"></router-view>。
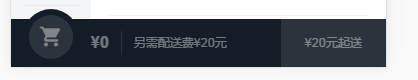
购物车的状态是由选择的商品决定的,购物车要根据goods组件选择的商品来改变样式,selectFoods是一个数组元素,保存了选择的商品种类和数量,在props中如果数据时数组或者对象,default是一个函数。
selectFoods: {
type: Array,
default() {
return [
{
price: 10,
count: 10
}
];
}
v-show可以等于一个表达式,当表达式是true的时候,就显示DOM元素<div class="num" v-show="totalCount>0">{{totalCount}}</div>
cartcontrol组件
cartcontrol从父组件接收数据food,<cartcontrol @add="addFood" :food="food"></cartcontrol>
为了美观,按钮很小,为了方便增加有效的点击区域便于用户点击操作,可以给cart-decrase,cart-increase增加padding。
要为food添加一个count属性时,不能直接添加,要用Vue的set方法
addCart(event) {
if (!event._constructed) {
return;
}
if (!this.food.count) {
Vue.set(this.food, 'count', 1);
} else {
this.food.count++;
}
this.$emit('add', event.target);
},
个减号出现时,添加一个滚动出现的动画,这个动画包含了平移和滚动,所以要有两个层,外层实现平移,内层实现滚动。
<transition name="move">
<div class="cart-decrease" v-show="food.count>0" @click.stop.prevent="decreaseCart">
<span class="inner icon-remove_circle_outline"></span>
</div>
</transition>
.cart-decrease
display: inline-block
padding: 6px
opacity: 1
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0)
.inner
display: inline-block
line-height: 24px
font-size: 24px
color: rgb(0, 160, 220)
transition: all 0.4s linear
transform: rotate(0)
&.move-enter-active, &.move-leave-active
transition: all 0.4s linear
&.move-enter, &.move-leave-to
opacity: 0
transform: translate3d(24px, 0, 0)
.inner
transform: rotate(180deg)
计算属性selectFoods通过两个forEach来遍历goods,把count大于0的food push到数组中,返回这个数组,这样子就拿到了和shopcart状态显示有关的的selectFoods数组
小球落入购物车的动画,用一个balls数组来控制小球的显示,一共有5个小球。小球是相对于视口做动画的,所以用fixed布局,小球在屏幕上方,z-index要大于shopcart的z-index。有水平方向和竖直方向的动画,所以也需要内外两层来实现两个方向上的动画
.ball-container
.ball
position: fixed
left: 32px
bottom: 22px
z-index: 200
transition: all 0.4s cubic-bezier(0.49, -0.29, 0.75, 0.41)
.inner
width: 16px
height: 16px
border-radius: 50%
background: rgb(0, 160, 220)
transition: all 0.4s linear
这个动画中起始点的位置需要动态计算,要获取加按钮的相对于屏幕的位置。这个动画不是通过设置enter和leave实现的。点击加号时,向父组件goods发送一个add事件,把这个dom元素传递给父组件this.$emit('add', event.target);在父组件goods中对这个事件做处理,获取加号DOM对象,<cartcontrol @add="addFood" :food="food"></cartcontrol>
addFood(target) {
this._drop(target);
},
_drop(target) {
// 体验优化,异步执行下落动画
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs.shopcart.drop(target);
});
在shopcart组件中获取加号的DOM。在drop函数中遍历balls数组,取出第一个不可见的小球,设为可见,放入dropBalls数组中。用钩子函数before-enter,enter和after-enter实现动画效果。
<transition name="drop" @before-enter="beforeDrop" @enter="dropping" @after-enter="afterDrop">
在beforeDrop函数中用getBoundingClientRect()函数获取加号DOM元素相对于视口的位置(这个方法返回一个矩形对象,包含四个属性:left、top、right和bottom。分别表示元素各边与页面上边和左边的距离),计算出小球在x方向和y方向需要移动的距离,设置内外两层小球的动画
beforeDrop(el) {
let count = this.balls.length;
while (count--) {
let ball = this.balls[count];
if (ball.show) {
let rect = ball.el.getBoundingClientRect();
let x = rect.left - 32;
let y = -(window.innerHeight - rect.top - 22);
ball.el.style.display = '';
el.style.webkitTransform = `translate3d(0, ${y}px, 0)`;
el.style.transform = `translate3d(0, ${y}px, 0)`;
let inner = el.getElementsByClassName('inner-hook')[0];
inner.style.webkitTransform = `translate3d(${x}px, 0, 0)`;
inner.style.transform = `translate3d(${x}px, 0, 0)`;
}
}
}
在dropping(el,done)函数中用let rf = el.offsetHeight;手动触发重绘
dropping(el, done) {
/* eslint-disable no-unused-vars */
let rf = el.offsetHeight;
this.$nextTick(() => {
el.style.webkitTransform = 'translate3d(0, 0, 0)';
el.style.transform = 'translate3d(0, 0, 0)';
let inner = el.getElementsByClassName('inner-hook')[0];
inner.style.webkitTransform = 'translate3d(0, 0, 0)';
inner.style.transform = 'translate3d(0, 0, 0)';
el.addEventListener('transitionend', done);
});
},
在afterDrop函数中重新把ball设置为不可见
afterDrop(el) {
console.log(el);
let ball = this.dropBalls.shift();
if (ball) {
ball.show = false;
el.style.display = 'none';
}
}
购物车详情页
购物车详情页由两部分组成list-header和list-content。shopcart-list用局对布局,注意高度的设置,高度的设置是在动画中设置为-100%,实现购物车详情页从底部向上显示出来的一个效果。
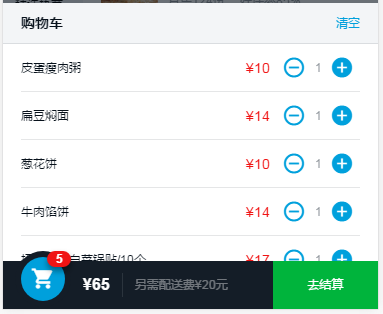
.shopcart-list
position: absolute;
left: 0
top: 0
z-index: -1
width: 100%
transform: translate3d(0, -100%, 0)
&.fold-enter-active, &.fold-leave-active
transition: all 0.5s
&.fold-enter, &.fold-leave-to
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0)
标题栏的左右两边的title和empty采用float布局

food中的price和cartcontrol-wrapper都使用绝对定位

用计算属性listShow控制购物车详情页是否可见。
listShow() {
if (!this.totalCount) {
this.fold = true;
return false;
}
let show = !this.fold;
if (show) {
this.$nextTick(() => {
if (!this.scroll) {
this.scroll = new BScroll(this.$refs.listContent, {
click: true
});
} else {
this.scroll.refresh();
}
});
}
return show;
}
给list-content添加滚动的效果,这部分内容也写在计算属性listShow中,如果scroll已经存在,则用refresh()进行刷新.
最后给empty按钮增加清空事件<span class="empty" @click="empty">清空</span>
empty()对selectFoods进行遍历,把count都置为0.
empty() {
this.selectFoods.forEach((food) => {
food.count = 0;
});
}
背景list-mask和shopcart同级,也由listShow控制显示,采用fixed布局,z-index要比shopcart的z-index小。
.list-mask
position: fixed
top: 0
left: 0
width: 100%
height: 100%
z-index: 40
backdrop-filter: blur(10px)
background: rgba(7, 17, 27, 0.6)
&.fade-enter-active, &.fade-leave-active
transition: all 0.5s
&.fade-enter, &.fade-leave-to
background: rgba(7, 17, 27, 0)
pay按钮增加点击结算事件,这个点击要阻止冒泡(stop)和默认事件(prevent),不然除了结算窗口还会弹出购物车详情页。
<div class="content-right" @click.stop.prevent="pay">




















 1704
1704

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








