Picture
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 12522 | Accepted: 6605 |
Description
A number of rectangular posters, photographs and other pictures of the same shape are pasted on a wall. Their sides are all vertical or horizontal. Each rectangle can be partially or totally covered by the others. The length of the boundary of the union of all rectangles is called the perimeter.
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
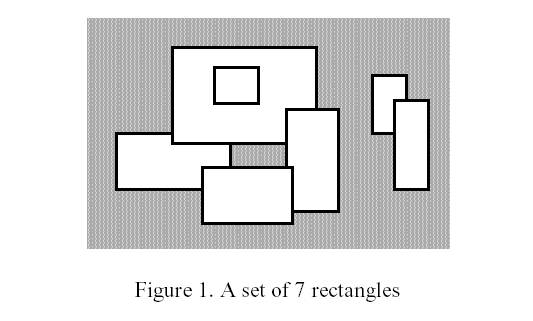
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.
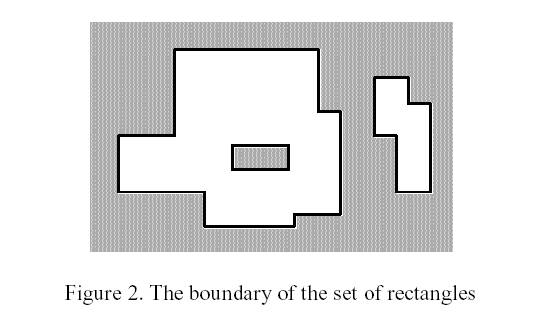
The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.

The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.

The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
Input
Your program is to read from standard input. The first line contains the number of rectangles pasted on the wall. In each of the subsequent lines, one can find the integer coordinates of the lower left vertex and the upper right vertex of each rectangle. The values of those coordinates are given as ordered pairs consisting of an x-coordinate followed by a y-coordinate.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Output
Your program is to write to standard output. The output must contain a single line with a non-negative integer which corresponds to the perimeter for the input rectangles.
Sample Input
7 -15 0 5 10 -5 8 20 25 15 -4 24 14 0 -6 16 4 2 15 10 22 30 10 36 20 34 0 40 16
Sample Output
228
题意:求几个矩形并的周长
对横着的和竖着的分别求一次
暴力算法:
对于每一条横边从左到右扫一遍,如果是矩形的下边,先判断当前坐标覆盖数为0,ans+,然后当前坐标覆盖数+1(覆盖数不为0也要加)
如果是矩形的上边,先判断当前坐标覆盖数为1,ans++,然后当前坐标覆盖数-1(覆盖数不为1也要减)
对于每一条竖边,同理(下边改成左边,上边改成右边)
注:1、边[l,r]的扫描范围为[l,r-1]
2、排序时,若几条横边的高度一样,上边优先。同理,竖边左边优先。
原因:这种情况下是一个矩形的下边和另一个矩形的上边重合,两条边的长度都不能算。
如果先扫下边,扫下边之前一定扫了上边,坐标覆盖可能为1,导致答案错误累加
线段树做法:
类似于求矩形并的面积:http://www.cnblogs.com/TheRoadToTheGold/p/6828162.html
不同点:累加答案累加与上一次的差,不需要再乘高度
注:1、边[l,r]的扫描范围是[l,r-1]
2、排序时,若几条边高度一样,谁在前无所谓。因为累加与上一次的差
暴力法:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define delta 10001 using namespace std; int n,x1,x2,y1,y2; int g[20005],ans; struct ways { int s,t,h,f; }x[20005],y[20005]; bool cmp(ways p,ways q) { if(p.h!=q.h) return p.h<q.h; return p.f>q.f; } int main() { scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); x1+=delta; y1+=delta; x2+=delta; y2+=delta; x[i*2-1].s=x1; x[i*2-1].t=x2; x[i*2-1].h=y1; x[i*2-1].f=1; x[i*2].s =x1; x[i*2].t =x2; x[i*2].h =y2; x[i*2].f=-1; y[i*2-1].s=y1; y[i*2-1].t=y2; y[i*2-1].h=x1; y[i*2-1].f=1; y[i*2].s =y1; y[i*2].t =y2; y[i*2].h =x2; y[i*2].f=-1; } sort(x+1,x+2*n+1,cmp); sort(y+1,y+2*n+1,cmp); int l,r; for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) { l=x[i].s; r=x[i].t; for(int j=l;j<r;j++) if(x[i].f==1) { if(!g[j]) ans++; g[j]++; } else { if(g[j]==1) ans++; g[j]--; } } memset(g,0,sizeof(g)); for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) { l=y[i].s; r=y[i].t; for(int j=l;j<r;j++) if(y[i].f==1) { if(!g[j]) ans++; g[j]++; } else { if(g[j]==1) ans++; g[j]--; } } printf("%d",ans); }
线段树法:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define delta 10001 using namespace std; int n,x1,x2,y3,y2; int ans; int opl,opr,maxnx,maxny; struct ways { int s,t,h,f; }x[20005],y[20005]; struct node { int sum,f; }tr[20005*4]; bool cmp(ways p,ways q) { return p.h<q.h; } void up(int k,int l,int r) { if(tr[k].f) tr[k].sum=r-l+1; else if(l==r) tr[k].sum=0; else tr[k].sum=tr[k<<1].sum+tr[k<<1|1].sum; } void solve(int k,int l,int r,int w) { if(l>=opl&&r<=opr) { tr[k].f+=w; up(k,l,r); return ; } int mid=l+r>>1; if(opl<=mid) solve(k<<1,l,mid,w); if(opr>mid) solve(k<<1|1,mid+1,r,w); up(k,l,r); } int main() { scanf("%d",&n); ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y3,&x2,&y2); x1+=delta; y3+=delta; x2+=delta; y2+=delta; x[i*2-1].s=x1; x[i*2-1].t=x2; x[i*2-1].h=y3; x[i*2-1].f=1; x[i*2].s =x1; x[i*2].t =x2; x[i*2].h =y2; x[i*2].f=-1; y[i*2-1].s=y3; y[i*2-1].t=y2; y[i*2-1].h=x1; y[i*2-1].f=1; y[i*2].s =y3; y[i*2].t =y2; y[i*2].h =x2; y[i*2].f=-1; maxnx=max(maxnx,x2); maxny=max(y2,maxny); } sort(x+1,x+2*n+1,cmp); sort(y+1,y+2*n+1,cmp); int last=0; for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) { opl=x[i].s; opr=x[i].t-1; if(x[i].f==1) solve(1,1,maxnx,1); else solve(1,1,maxnx,-1); ans+=abs(last-tr[1].sum); last=tr[1].sum;; } memset(tr,0,sizeof(tr)); last=0; for(int i=1;i<=2*n;i++) { opl=y[i].s; opr=y[i].t-1; if(y[i].f==1) solve(1,1,maxny,1); else solve(1,1,maxny,-1); ans+=abs(last-tr[1].sum); last=tr[1].sum; } printf("%d",ans); }




 本文介绍了一种计算多个矩形粘贴在墙上形成图形的周长的方法,通过水平和垂直扫描线算法来确定边界长度,提供了两种实现方式:暴力算法和线段树算法。
本文介绍了一种计算多个矩形粘贴在墙上形成图形的周长的方法,通过水平和垂直扫描线算法来确定边界长度,提供了两种实现方式:暴力算法和线段树算法。
















 423
423

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








