复习
1.枚举
枚举
enum -> public enum Score{ 全大写的英文单词:A,B,C,D }
最普通的枚举元素 -> 名称(字符串),序数(从0开始,标记先后顺序)
获得一个枚举对象 Score score = Score.A
valueOf(枚举类型-.class,枚举元素名称)
String s = "A";
Score score = Score.valueOf(Score.class,s);
switch(score/Score.A) case:"A","B","C"
枚举类型中可以定义构造器(枚举元素记录更多的信息),自定义方法
枚举元素的定义中重写某些方法(@OverWrite)
2.异常
throw -> 出现位置:方法体 -> new XXXException()/("message") -> super(String message);
throws -> 出现位置:参数列表后 -> 向上抛 -> 方法的调用者 -> jvm(打印异常-程序终止)
try - catch -> try{ 要执行的代码块 } - catch (XXXException e ){ 异常的解决方案 } - 范围由小到大(子父类)
try当中即使可能出现多个异常,当遇到第一个异常时就会进入catch阶段(多个try-catch结果解决每一个具体的异常)
finally{ 一定会执行的代码-(try/catch) }
当try - catch - finally结构中均有return,直接返回一个常量,返回同一个变量时,以finally为准
当try - catch - finally结构中try - catch有return变量(基本数据类型-字符串),finally中修改了return变量,以try/catch为准
当try - catch - finally结构中try - catch有return变量(引用类型),finally中修改了return变量,以finally为准
3.集合
Collection,Map,Iterator 集合框架的三大接口
Collection -> List,Set,Vetor -> ArrayList,LinkedList,HashSet,TreeSet,LinkedHashSet
Map -> HashMap,TreeMap,HashTable,LinkedHashMapArrayList:add(E e) -> 1.扩容 2.追加列表末尾 3.return true; get(int index)
remove(E e)/(int index) contains(Object o) -> 底层equals()比较
set(int index, E element) 覆盖某一位置的元素 toArray() -> 转换成数组 -> 泛型约束(无:Object)
今日内容
1.泛型
1)使用位置
- 在方法定义中声明
- 在类定义中声明
- 在接口定义中声明

// 在类结构中声明一个泛型
// 当前的类结构中可以将其看做一个为知的类型
// 在实例化对象时,需要传入一个类型作为参数,可以使得每次实例化得到的对象都有不同的约束
// 可以在一个类当中声明多个泛型,使用逗号隔开
public class Person<T,E> {}2)注意事项
- 不能用于声明静态/常量属性
- 不能在类中实例化泛型数组
- 不能使用泛型参数构成重载方法
- 不同类型的泛型的引用不能直接赋值
3)受限泛型

// 耦合度:类与类之间的关联关系
// 高内聚,低耦合 -> 合理范围 -> 业务模块
// 优点:可以解耦,动态传入需要关联的实例
// 缺点:类成员变量的命名使用较差,随着泛型数量的增加,使用会逐渐复杂2.迭代器
1)初始化

2)使用方法

// remove使用迭代器移除当前指向的元素,作用在集合本身3)list接口中的迭代器

4)ListIterator
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();
// 游标处在初始位置时,获取前一个索引值,返回-1
System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex());// -1
// 游标处在初始位置时,后续后一个索引值,返回下一个元素的索引
System.out.println(listIterator.nextIndex());// 0
//移动一次
listIterator.next();
// 游标移动一次后,获取前一个索引值,返回当前指向元素的下标
System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex());// 0
// 游标移动一次后,获取后一个索引值,返回下一元素的索引
System.out.println(listIterator.nextIndex());// 1
// 移动两次
listIterator.next();
listIterator.next();
// 游标移动到末尾,获取前一个索引值,返回当前指向元素的下标
System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex());// 2
// 游标移动到末尾,获取后一个索引值,返回当前集合的元素个数
System.out.println(listIterator.nextIndex());// 3
- ArrayList和LinkedList的大致区别如下:
1.ArrayList是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList基于链表的数据结构。
2.对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。
3.对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
3.Set集合
1)常用方法
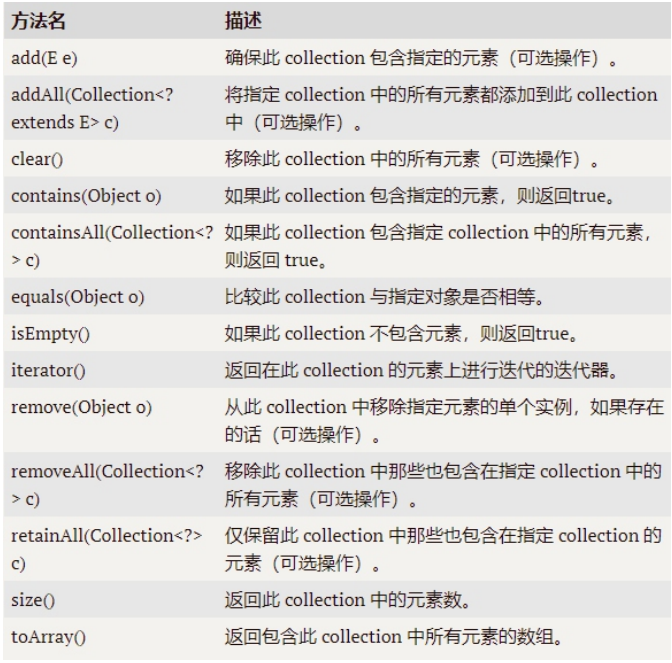
2)存储特点

3)常用实现类

HashSet
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add("123ddd"); System.out.println(set.add("111"));// true set.add("369"); // 1.不能出现重复的元素,只需确保当前集合中有此元素 System.out.println(set.add("111"));// false // 2.存储顺序和元素放入的顺序并不相同 -> hash算法决定 Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); }Set<Student> set2 = new HashSet<>(); // 引用类型的实例:当对象的各个属性完全一致时,只要new关键字(HashCode不同时) -> 不同的对象 Student student = new Student("sand", "123"); set2.add(new Student("sand", "123")); set2.add(new Student("sand", "123")); // 引用类型的实例:向集合当中添加同一个实例的引用时 -> 相同的对象 set2.add(student); set2.add(student); for (Student temp : set2) { System.out.println(temp);// 输出只有三个对象 }Set set3 = new HashSet<>(); // 基本数据类型的包装类的hashCode直接返回拆箱后的值 System.out.println(new Integer(1).hashCode()); System.out.println(new Integer(1).hashCode()); // 基本数据类型的包装类 -> 出现相同值时,认定相同 set3.add(new Integer(1)); set3.add(new Integer(1)); set3.add(new Integer(500)); set3.add(new Integer(500)); // 基本数据类型和字符串 -> 出现重复元素时,认定相同 set3.add("123"); set3.add("123"); set3.add(2); set3.add(2); for (Object object : set3) { System.out.println(object);//1 500 2 123 只添加了4个元素 }TreeSet
// Hash结构的排序 - hashCode编码
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add("1");
hashSet.add("2ad");
hashSet.add("a3df");
hashSet.add("i5");
hashSet.add("f4asd");
for (String string : hashSet) {
System.out.println(string); //输出相对无序
} // TreeSet的排序 - 元素和元素之间的比较
// TreeSet默认的排序规则 - 自然升序
TreeSet<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add(200);
treeSet.add(500);
treeSet.add(300);
for (Integer integer : treeSet) {
System.out.println(integer);
}






 本文深入讲解Java中的枚举、异常处理、集合框架等基础知识,并详细分析ArrayList与LinkedList的区别,以及Set集合的特点和实现。
本文深入讲解Java中的枚举、异常处理、集合框架等基础知识,并详细分析ArrayList与LinkedList的区别,以及Set集合的特点和实现。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








