In this chapter, we will cover:
- Computing the image histogram
- Applying look-up tables to modify image appearance
- Equalizing the image histogram
- Backprojecting a histogram to detect specific image content
- Using the mean shift algorithm to find an object
- Retrieving similar images using histogram comparison
Computing the image histogram
Using the cv::calcHist function.
Caculate 1D Histogram
Histogram1D.h
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
class Histogram1D {
private:
int histSize[1]; // number of bins
float hranges[2]; // min and max pixel value
const float* ranges[1];
int channels[1]; // only 1 channel used here
public:
Histogram1D() {
// Prepare arguments for 1D histogram
histSize[0] = 256;
hranges[0] = 0.0;
hranges[1] = 255.0;
ranges[0] = hranges;
channels[0] = 0; // by default, we look at channel 0
}
// Computes the 1D histogram
cv::MatND getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image);
// Computes the 1D histogram and returns an image of it.
cv::MatND getHistogramImage(const cv::Mat &image);
};
Histogram.cpp
#include "Histgram1D.h"
// Computes the 1D histogram
cv::MatND Histogram1D::getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::MatND hist;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&image,
1, // histogram from 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
1, // it is a 1D histgram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
cv::Mat Histogram1D::getHistogramImage(const cv::Mat &image) {
// Compute histogram first
cv::MatND hist = getHistogram(image);
// Get min and max bin values
double maxVal = 0;
double minVal = 0;
cv::minMaxLoc(hist, &minVal, &maxVal, 0, 0);
// Image on which to display histogram
cv::Mat histImg(histSize[0], histSize[0], CV_8U, cv::Scalar(255));
// Set highest point at 90% of nbins
int hpt = static_cast <int >(0.9 * histSize[0]);
// Draw a vertical line for each bin
for ( int h = 0; h < histSize[0]; h++ ) {
float binVal = hist.at<float>(h);
int intensity = static_cast <int >(binVal * hpt / maxVal);
// This function draws a line between 2 points
cv::line(histImg, cv::Point(h, histSize[0]),
cv::Point(h, histSize[0] - intensity),
cv::Scalar::all(0));
}
return histImg;
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Histgram1D.h"
int main() {
// Read input image
cv::Mat image = cv::imread( "group.jpg", 0); // open in b&w
// The histogram object
Histogram1D h;
// Compute the histogram
cv::MatND histo = h.getHistogram(image);
// Loop over each bin
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
std::cout << "Value " << i << " = " <<
histo.at<float >(i) << std::endl;
}
// Draw histogram image
cv::Mat histoImage = h.getHistogramImage(image);
cv::namedWindow( "histogram", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "histogram", histoImage);
// threshold the image
cv::Mat thresholded;
cv::threshold(image, thresholded, 60, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow( "Binary image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "Binary image", thresholded);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
the result as follows:
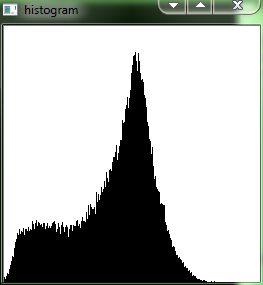

Caculate Color image histogram
ColoHistogram.h
#include <iostream>
#include "Histgram1D.h"
int main() {
// Read input image
cv::Mat image = cv::imread( "group.jpg", 0); // open in b&w
// The histogram object
Histogram1D h;
// Compute the histogram
cv::MatND histo = h.getHistogram(image);
// Loop over each bin
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
std::cout << "Value " << i << " = " <<
histo.at<float >(i) << std::endl;
}
// Draw histogram image
cv::Mat histoImage = h.getHistogramImage(image);
cv::namedWindow( "histogram", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "histogram", histoImage);
// threshold the image
cv::Mat thresholded;
cv::threshold(image, thresholded, 60, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow( "Binary image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "Binary image", thresholded);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
ColorHistogram.cpp
#include "ColorHistogram.h"
// Computes the 1D histogram
cv::MatND ColorHistogram::getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::MatND hist;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&image,
1, // histogram from 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
3, // it is a 3D histgram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
cv::SparseMat ColorHistogram::getSpareHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
// Compute histogram first
cv::SparseMat hist(3, histSize, CV_32F);
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&image,
1, // histogram from 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
3, // it is a 3D histgram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
Applying look-up tables to modify image appearance
A look-up table is a simple one-to-one (or many-to-one) function that defines how pixel values are transformed into new values. It is a 1D array with, in the case of regular gray-level images, 256 entries. Entry i of the table gives the new intensity value of the corresponding gray level, that is:
newIntensity= lookup[oldIntensity];
Function cv::LUT in OpenCV applies a look-up table to an image in order to produce a new image. We can add this function to our Histogram1D class:
cv::Mat Histogram1D::applyLookUp(const cv::Mat& image, // input image
const cv::Mat& lookup) { // 1*256 uchar matrix
// the output image
cv::Mat result;
// apply the lookup table
cv::LUT(image, lookup, result);
return result;
}
cv::Mat Histogram1D::strech(const cv::Mat &image, int minValue /* = 0 */) {
// Compute histogram first
cv::MatND hist = getHistogram(image);
// find left extremity of the histogram
int imin = 0;
for ( ; imin < histSize[0]; imin ++) {
std::cout << hist.at<float>(imin) << std::endl;
if (hist.at<float >(imin) > minValue) {
break;
}
}
// find right extremity of the histogram
int imax = histSize[0] - 1;
for ( ; imax >= 0; imax --) {
if (hist.at<float >(imax) > minValue)
break;
}
// Create lookup table
int dim(256);
cv::Mat lookup(1, // 1 dimension
&dim, // 256 entries
CV_8U // uchar
);
// Build lookup table
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
// stretch between imin and imax
if (i < imin) lookup.at<uchar>(i) = 0;
else if (i > imax) lookup.at<uchar>(i) = 255;
//linear mapping
else lookup.at<uchar>(i) = static_cast <uchar>(255.0 * (i - imin) / (imax - imin) + 0.5);
}
// Apply lookup table
cv::Mat result;
result = applyLookUp(image, lookup);
return result;
}
Using the function as follows:
cv::Mat streched = h.strech(image, 100);
cv::namedWindow( "streched image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "streched image", streched);
cv::Mat strechedHistoImage = h.getHistogramImage(streched);
cv::namedWindow( "strechedHistoImage", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "strechedHistoImage", strechedHistoImage);
results as follows:


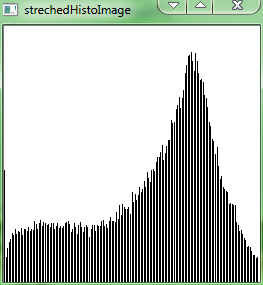
Equalizing the image histogram
OpenCV offers an easy-to-use function that performs histogram equalization. It can be called as follows:
cv::Mat Histogram1D::equalize(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::Mat result;
cv::equalizeHist(image, result);
return result;
}
result as follows:

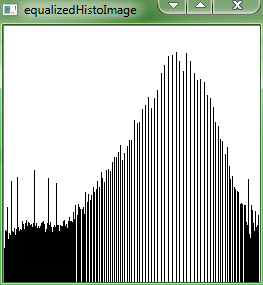
Backprojecting a histogram to detect specific image content
ContentFinder.h
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
class ContentFinder {
private:
float hranges[2];
const float* ranges[3];
int channels[3];
float threshold;
cv::MatND histogram;
public:
ContentFinder() : threshold(-1.0f) {
ranges[0] = hranges; // all channels have same range
ranges[1] = hranges;
ranges[2] = hranges;
}
// Sets the threshold on histogram values [0, 1]
void setThreshold(float t) {
threshold = t;
}
// Gets the threshold
float getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
// Sets the reference histogram
void setHistogram(const cv::MatND &h) {
histogram = h;
cv::normalize(histogram, histogram, 1.0);
}
cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat &image, float minValue, float maxValue, int *channels, int dim);
};
ContentFinder.cpp
#include "ContentFinder.h"
cv::Mat ContentFinder::find(const cv::Mat &image,
float minValue,
float maxValue,
int *channels,
int dim) {
cv::Mat result;
hranges[0] = minValue;
hranges[1] = maxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < dim; i++) {
this->channels[i] = channels[i];
}
cv::calcBackProject(&image, 1, // input image
channels, // list of channels used
histogram, // the histogram we are using
result, // the resulting backprojection
ranges, // the range of values
255.0 // the scaling factor
);
// Threshold back projection to obtain a binary image
if (threshold > 0.0)
cv::threshold(result, result, 255 * threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
return result;
}
Let's now use a BGR histogram on the color version of the image we used above. This time, we will try to detect the blue sky area. We will first load the color image, reduce the number of color using the color reduction function of Chapter 2, and define the region of interest: ColorHistogram hc;
ColorHistogram hc;// load color imagecv::Mat color = cv::imread( "waves.jpg");//reduce colorscolor = hc.colorReduce(color, 32);// blue sky areacv::Mat imageROI = color(cv::Rect(0, 0, 165, 75));
Next, you compute the histogram and use the findmethod to detect the sky portion
of the image:
cv::MatND hist = hc.getHistogram(imageROI);ContentFinder finder;finder.setHistogram(hist);finder.setThreshold(0.05f);//Get back-projection of color histogramcv::Mat result = finder.find(color);cv::namedWindow( "original image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);cv::imshow( "original image", color);cv::namedWindow( "color back projection result", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);cv::imshow( "color back projection result", result);
The result of the detection on the color version of the image, of the previous section is seen
here:

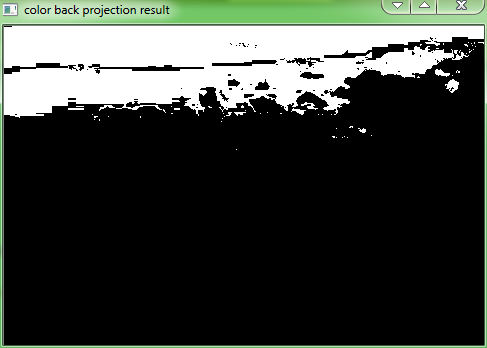
Using the mean shift algorithm to find an object
colorhistogram.h
#if !defined COLHISTOGRAM
#define COLHISTOGRAM
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
class ColorHistogram {
private:
int histSize[3];
float hranges[2];
const float* ranges[3];
int channels[3];
public:
ColorHistogram() {
// Prepare arguments for a color histogram
histSize[0]= histSize[1]= histSize[2]= 256;
hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG range
hranges[1]= 255.0;
ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range
ranges[1]= hranges;
ranges[2]= hranges;
channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
channels[1]= 1;
channels[2]= 2;
}
// Computes the histogram.
cv::MatND getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::MatND hist;
// BGR color histogram
hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG range
hranges[1]= 255.0;
channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
channels[1]= 1;
channels[2]= 2;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&image,
1, // histogram of 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
3, // it is a 3D histogram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
// Computes the histogram.
cv::SparseMat getSparseHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::SparseMat hist(3,histSize,CV_32F);
// BGR color histogram
hranges[0]= 0.0; // BRG range
hranges[1]= 255.0;
channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
channels[1]= 1;
channels[2]= 2;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&image,
1, // histogram of 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
3, // it is a 3D histogram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
// Computes the 2D ab histogram.
// BGR source image is converted to Lab
cv::MatND getabHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::MatND hist;
// Convert to Lab color space
cv::Mat lab;
cv::cvtColor(image, lab, CV_BGR2Lab);
// Prepare arguments for a 2D color histogram
hranges[0]= -128.0;
hranges[1]= 127.0;
channels[0]= 1; // the two channels used are ab
channels[1]= 2;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&lab,
1, // histogram of 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
2, // it is a 2D histogram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
// Computes the 1D Hue histogram with a mask.
// BGR source image is converted to HSV
cv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image) {
cv::MatND hist;
// Convert to Lab color space
cv::Mat hue;
cv::cvtColor(image, hue, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Prepare arguments for a 1D hue histogram
hranges[0]= 0.0;
hranges[1]= 180.0;
channels[0]= 0; // the hue channel
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&hue,
1, // histogram of 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
cv::Mat(), // no mask is used
hist, // the resulting histogram
1, // it is a 1D histogram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
cv::Mat colorReduce(const cv::Mat &image, int div=64) {
int n= static_cast<int >(log(static_cast <double >(div))/log(2.0));
// mask used to round the pixel value
uchar mask= 0xFF<<n; // e.g. for div=16, mask= 0xF0
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator it= image.begin<cv::Vec3b>();
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator itend= image.end<cv::Vec3b>();
// Set output image (always 1-channel)
cv::Mat result(image.rows,image.cols,image.type());
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::iterator itr= result.begin<cv::Vec3b>();
for ( ; it!= itend; ++it, ++itr) {
(*itr)[0]= ((*it)[0]&mask) + div/2;
(*itr)[1]= ((*it)[1]&mask) + div/2;
(*itr)[2]= ((*it)[2]&mask) + div/2;
}
return result;
}
// Computes the 1D Hue histogram with a mask.
// BGR source image is converted to HSV
// Pixels with low saturation are ignored
cv::MatND getHueHistogram(const cv::Mat &image,
int minSaturation=0) {
cv::MatND hist;
// Convert to HSV color space
cv::Mat hsv;
cv::cvtColor(image, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Mask to be used (or not)
cv::Mat mask;
if (minSaturation>0) {
// Spliting the 3 channels into 3 images
std::vector<cv::Mat> v;
cv::split(hsv,v);
// Mask out the low saturated pixels
cv::threshold(v[1],mask,minSaturation,255,
cv::THRESH_BINARY);
}
// Prepare arguments for a 1D hue histogram
hranges[0]= 0.0;
hranges[1]= 180.0;
channels[0]= 0; // the hue channel
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&hsv,
1, // histogram of 1 image only
channels, // the channel used
mask, // binary mask
hist, // the resulting histogram
1, // it is a 1D histogram
histSize, // number of bins
ranges // pixel value range
);
return hist;
}
};
#endif
bojectFinder.h
#if !defined OFINDER
#define OFINDER
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
class ObjectFinder {
private:
float hranges[2];
const float* ranges[3];
int channels[3];
float threshold;
cv::MatND histogram;
cv::SparseMat shistogram;
bool isSparse;
public:
ObjectFinder() : threshold(0.1f), isSparse(false) {
ranges[0]= hranges; // all channels have the same range
ranges[1]= hranges;
ranges[2]= hranges;
}
// Sets the threshold on histogram values [0,1]
void setThreshold(float t) {
threshold= t;
}
// Gets the threshold
float getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
// Sets the reference histogram
void setHistogram(const cv::MatND& h) {
isSparse= false;
histogram= h;
cv::normalize(histogram,histogram,1.0);
}
// Sets the reference histogram
void setHistogram(const cv::SparseMat& h) {
isSparse= true;
shistogram= h;
cv::normalize(shistogram,shistogram,1.0,cv::NORM_L2);
}
// Finds the pixels belonging to the histogram
cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image) {
cv::Mat result;
hranges[0]= 0.0; // range [0,255]
hranges[1]= 255.0;
channels[0]= 0; // the three channels
channels[1]= 1;
channels[2]= 2;
if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram type
cv::calcBackProject(&image,
1, // one image
channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
shistogram, // the histogram we are using
result, // the resulting back projection image
ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
);
} else {
cv::calcBackProject(&image,
1, // one image
channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
histogram, // the histogram we are using
result, // the resulting back projection image
ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
);
}
// Threshold back projection to obtain a binary image
if (threshold>0.0)
cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
return result;
}
cv::Mat find(const cv::Mat& image, float minValue, float maxValue, int *channels, int dim) {
cv::Mat result;
hranges[0]= minValue;
hranges[1]= maxValue;
for (int i=0; i<dim; i++)
this->channels[i]= channels[i];
if (isSparse) { // call the right function based on histogram type
cv::calcBackProject(&image,
1, // we only use one image at a time
channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
shistogram, // the histogram we are using
result, // the resulting back projection image
ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
);
} else {
cv::calcBackProject(&image,
1, // we only use one image at a time
channels, // vector specifying what histogram dimensions belong to what image channels
histogram, // the histogram we are using
result, // the resulting back projection image
ranges, // the range of values, for each dimension
255.0 // the scaling factor is chosen such that a histogram value of 1 maps to 255
);
}
// Threshold back projection to obtain a binary image
if (threshold>0.0)
cv::threshold(result, result, 255*threshold, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
return result;
}
};
#endif
finder.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2\video\tracking.hpp>
#include "objectFinder.h"
#include "colorhistogram.h"
int main()
{
// Read reference image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("../baboon1.jpg" );
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Define ROI
cv::Mat imageROI= image(cv::Rect(110,260,35,40));
cv::rectangle(image, cv::Rect(110,260,35,40),cv::Scalar(0,0,255));
// Display image
cv::namedWindow( "Image");
cv::imshow( "Image",image);
// Get the Hue histogram
int minSat=65;
ColorHistogram hc;
cv::MatND colorhist= hc.getHueHistogram(imageROI,minSat);
ObjectFinder finder;
finder.setHistogram(colorhist);
finder.setThreshold(0.2f);
// Convert to HSV space
cv::Mat hsv;
cv::cvtColor(image, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Split the image
vector<cv::Mat> v;
cv::split(hsv,v);
// Eliminate pixels with low saturation
cv::threshold(v[1],v[1],minSat,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow( "Saturation");
cv::imshow( "Saturation",v[1]);
// Get back-projection of hue histogram
int ch[1]={0};
cv::Mat result= finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,ch,1);
cv::namedWindow( "Result Hue");
cv::imshow( "Result Hue",result);
cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);
cv::namedWindow( "Result Hue and");
cv::imshow( "Result Hue and",result);
// Second image
image= cv::imread("../baboon3.jpg");
// Display image
cv::namedWindow( "Image 2");
cv::imshow( "Image 2",image);
// Convert to HSV space
cv::cvtColor(image, hsv, CV_BGR2HSV);
// Split the image
cv::split(hsv,v);
// Eliminate pixels with low saturation
cv::threshold(v[1],v[1],minSat,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cv::namedWindow( "Saturation");
cv::imshow( "Saturation",v[1]);
// Get back-projection of hue histogram
result= finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,ch,1);
cv::namedWindow( "Result Hue");
cv::imshow( "Result Hue",result);
// Eliminate low stauration pixels
cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);
cv::namedWindow( "Result Hue and");
cv::imshow( "Result Hue and",result);
// Get back-projection of hue histogram
finder.setThreshold(-1.0f);
result= finder.find(hsv,0.0f,180.0f,ch,1);
cv::bitwise_and(result,v[1],result);
cv::namedWindow( "Result Hue and raw");
cv::imshow( "Result Hue and raw",result);
cv::Rect rect(110,260,35,40);
cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,0,255));
cv::TermCriteria criteria(cv::TermCriteria::MAX_ITER,10,0.01);
cout << "meanshift= " << cv::meanShift(result,rect,criteria) << endl;
cv::rectangle(image, rect, cv::Scalar(0,255,0));
// Display image
cv::namedWindow( "Image 2 result");
cv::imshow( "Image 2 result",image);
cv::waitKey();
return 0;
}
results:


Retrieving similar images using histogram comparison
imageComparator.h
#if !defined ICOMPARATOR
#define ICOMPARATOR
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp>
#include "colorhistogram.h"
class ImageComparator {
private:
cv::Mat reference;
cv::Mat input;
cv::MatND refH;
cv::MatND inputH;
ColorHistogram hist;
int div;
public:
ImageComparator() : div(32) {
}
// Color reduction factor
// The comparaison will be made on images with
// color space reduced by this factor in each dimension
void setColorReduction( int factor) {
div= factor;
}
int getColorReduction() {
return div;
}
void setReferenceImage(const cv::Mat& image) {
reference= hist.colorReduce(image,div);
refH= hist.getHistogram(reference);
}
double compare(const cv::Mat& image) {
input= hist.colorReduce(image,div);
inputH= hist.getHistogram(input);
return cv::compareHist(refH,inputH,CV_COMP_INTERSECT);
}
};
#endif
retrieve.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <opencv2\core\core.hpp>
#include <opencv2\highgui\highgui.hpp>
#include "imageComparator.h"
int main()
{
// Read reference image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("../waves.jpg" );
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Display image
cv::namedWindow( "Query Image");
cv::imshow( "Query Image",image);
ImageComparator c;
c.setReferenceImage(image);
// Read an image and compare it with reference
cv::Mat input= cv::imread("../dog.jpg" );
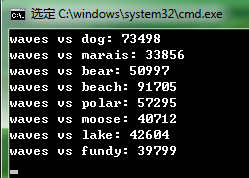
cout << "waves vs dog: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../marais.jpg");
cout << "waves vs marais: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../bear.jpg");
cout << "waves vs bear: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../beach.jpg");
cout << "waves vs beach: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../polar.jpg");
cout << "waves vs polar: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../moose.jpg");
cout << "waves vs moose: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../lake.jpg");
cout << "waves vs lake: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
// Read an image and compare it with reference
input= cv::imread("../fundy.jpg");
cout << "waves vs fundy: " << c.compare(input) << endl;
cv::waitKey();
return 0;
}
results:

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








