As convention, I prefer to pass the object as const reference below.
void foo(const A& a)
In most of cases, normal conversions are applied to the arguments when the client invokes the function. For example.
A a;
c.foo(a);
Object a will convert to const reference of class A.
However, when we use template specializations, conversions are not applied to argument types. In a call to specialized version of a template, the argument types in the call must match the specialized version function parameter type(s) exactly. If they don't, then the complier will instantiate an instantiation for the argument(s) from the template definition.
class A
{
};
class C
{
public:
template<typename T>
void foo(T t)
{
printf("void foo(T t)\n");
}
template<>
void foo(const int i)
{
printf("void foo(int i)\n");
}
template<>
void foo(const A& a)
{
printf("void foo(const A a)\n");
}
};
TEST(TemplateTest, TemplateSpecializationTest)
{
C c;
int i = 2;
c.foo(i);
A a;
c.foo(a);
}
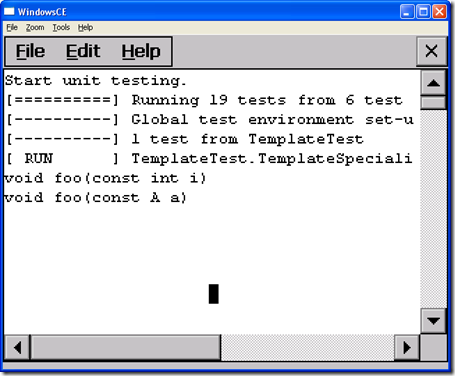
Because the parameter to call foo is (A a) install of (const A& a), the complier pick the template version void foo(T t) instead of specialized version void foo(const A& a) .
So, in such case, I prefer to use function overloading instead of template specializations.
class A
{
};
class C
{
public:
template<typename T>
void foo(T t)
{
printf("void foo(T t)\n");
}
template<>
void foo(const int i)
{
printf("void foo(const int i)\n");
}
void foo(const A& a)
{
printf("void foo(const A a)\n");
}
};
TEST(TemplateTest, TemplateSpecializationTest)
{
C c;
int i = 2;
c.foo(i);
A a;
c.foo(a);
}
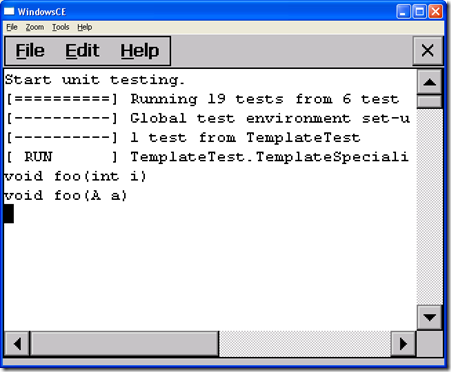
Works as I expect. Conversions are applied to argument when calls foo() function.
refer to C++ Primer.
Update
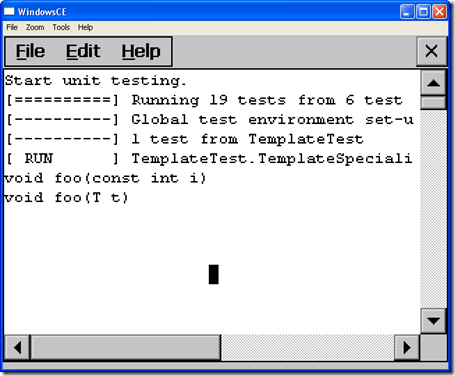
If we use template specializations and overloaded functions at the same time. The VC++(VS2005) complier will pick up the overloaded function.
class A
{
};
class C
{
public:
template<typename T>
void foo(T t)
{
printf("void foo(T t)\n");
}
template<>
void foo(const int i)
{
printf("void foo(int i)\n");
}
template<>
void foo(A a)
{
printf("template<> void foo(A a)\n");
}
void foo(A a);
};
TEST(TemplateTest, TemplateSpecializationTest)
{
C c;
int i = 2;
c.foo(i);
A a;
c.foo(a);
}
void C::foo(A a)
{
printf("void foo(A a)\n");
}
But I don’t recommend to use both function templates and nontemplate functions at the same time. Because it will surprise the users to use it.







 探讨了C++中模板特化与函数重载的区别,特别是在参数类型转换方面的行为差异。文章通过实例对比了两者在调用过程中的表现,指出模板特化在参数类型不完全匹配时的行为,以及为何在某些情况下,函数重载可能是更优的选择。
探讨了C++中模板特化与函数重载的区别,特别是在参数类型转换方面的行为差异。文章通过实例对比了两者在调用过程中的表现,指出模板特化在参数类型不完全匹配时的行为,以及为何在某些情况下,函数重载可能是更优的选择。
















 867
867

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








