Shiro简介
Apache Shiro是一个强大易用的Java安全框架,提供了认证、授权、加密和
会话管理等功能。
对于任何一个应用程序,Shiro都可以提供全面的安全管理服务。其不仅可
以用在JavaSE环境,也可以用在JavaEE环境。
二、Shiro架构图
1.从外部来看Shiro,即从应用程序角度来观察如何使用Shiro完成工作。如
下图:
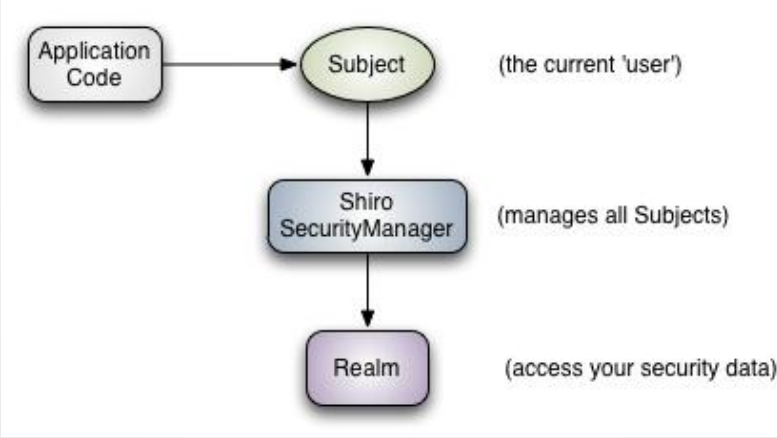
2.从Shiro内部看Shiro的架构,如下图所示:
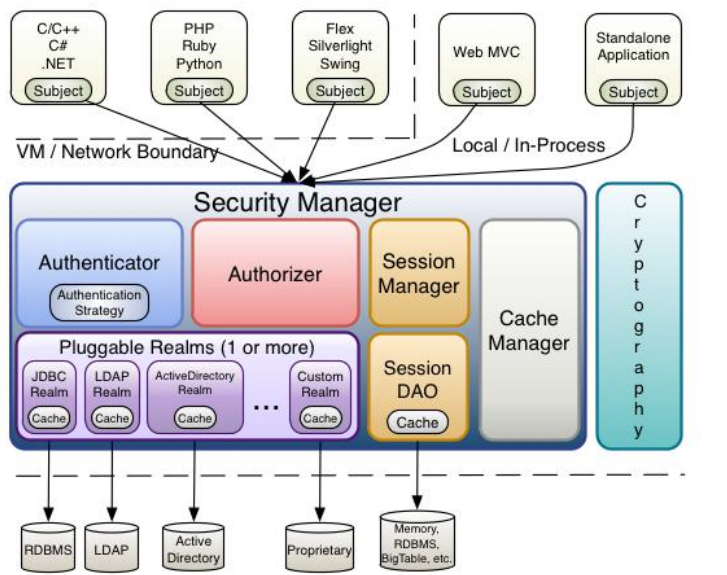
三、Shiro涉及常见名词

四、Shiro配置文件详解
shiro.ini文件放在classpath下,shiro会自动查找。其中格式是key/value
键值对配置。INI配置文件一般适用于用户少且不需要在运行时动态创建的
情景下使用。
ini文件中主要配置有四大类:main,users,roles,urls
示例:
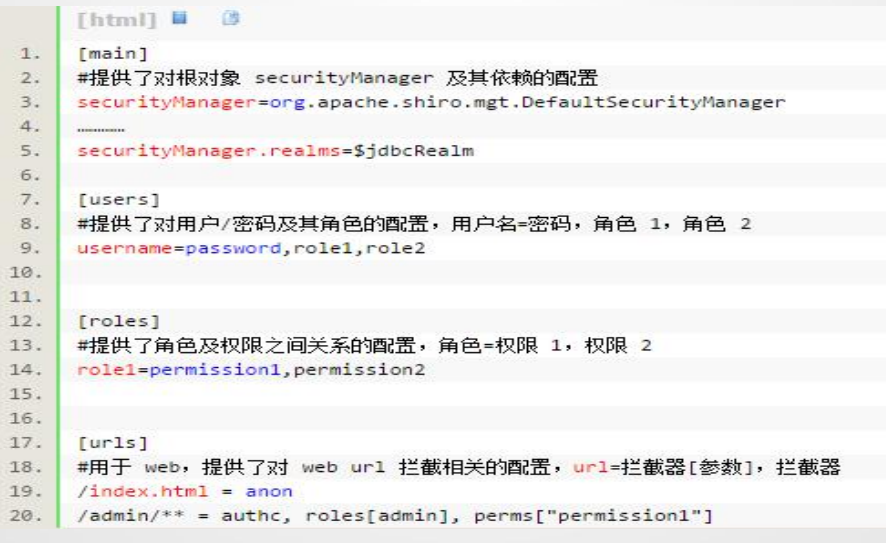
1、[main]
main主要配置shiro的一些对象,例如securityauthenticator,authcStrategy 等等,例如:
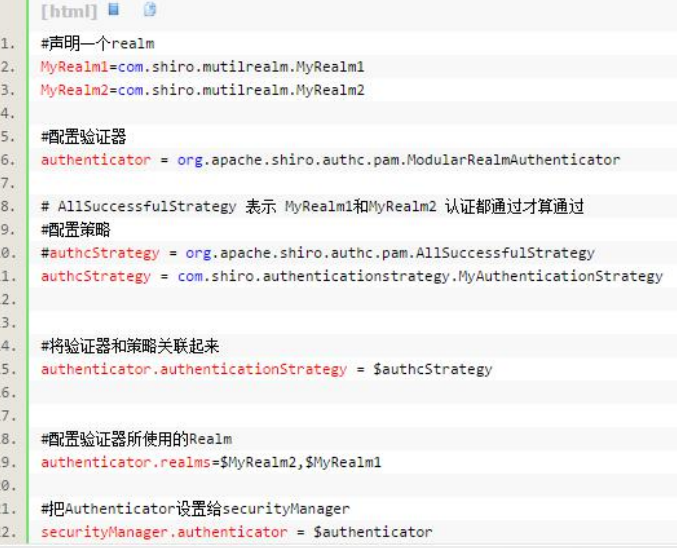
2、[users]
[users]允许你配置一组静态的用户,包含用户名,密码,角色,一个用户
可以有多个角色,可以配置多个角色,例如:
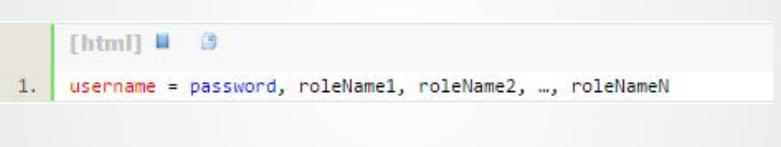
3、[roles]
[roles]将角色和权限关联起来,格式为:角色名=权限字符串1,权限字符
串2…..,例如:
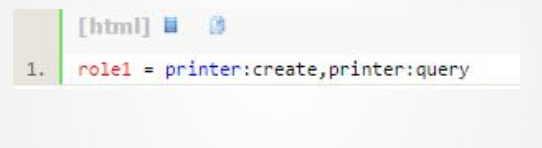

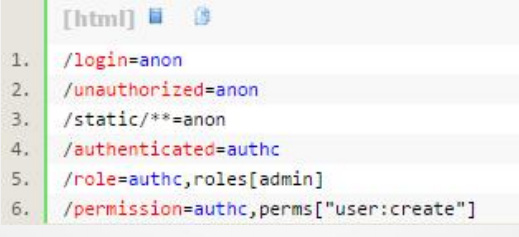
4、[urls]
这部分配置主要在web应用中,格式为:url=拦截器[参数],拦截器[参
数]……,例如
五、认证实现
认证:验证用户是否合法
在 shiro 中,用户需要提供principals (身份)和credentials(凭证)
给shiro,从而实现对用户身份的验证。
5.1.principals
身份,即主体的标识属性,可以是任何东西,如用户名、邮箱等,唯一即可。
例如:用户名/邮箱/手机号等。
5.2.credentials
凭证,即只有主体知道的安全值,如密码/数字证书等。
最常见的principals和credentials组合就是用户名/密码了。
5.3 实现步骤
5.3.1 导入jar包
5.3.2 从源码的示例项目quickstart中拷贝shiro.ini放到src下,并配置
5.3.3 编写代码


package com.bjsxt.test; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; import org.junit.Test; //实现简单认证 public class AuthenticationTest { @Test public void testAuthentication(){ //1.构建SecurityManager工厂 IniSecurityManagerFactory securityManagerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //2.通过securityManagerFactory工厂获取SecurityManager实例 SecurityManager securityManager = securityManagerFactory.getInstance(); //3.将securityManager设置到运行环境当中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //4.获取subject实例 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5.创建用户名密码验证令牌Token UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("victor","123456"); //6.进行身份验证 subject.login(token); //7.判断是否认证通过 System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated()); } }
shiro.ini


[users] victor=123456
六、JDBCRealm
Shiro默认使用自带的IniRealm,IniRealm从ini配置文件中读取用户的信息。
大部分情况下需要从系统的数据库中读取用户信息,所以需要使用JDBCRealm或自定义Realm。
需求:使用JDBCRealm提供数据源,从而实现认证
实现步骤:
6.1建users表(表名、字段对应上)
6.2添加jar包(数据库驱动、数据库连接池、beanutils等)
6.3编写shiro.ini
6.4编写测试代码
AuthenticationTest.java


package com.bjsxt.test; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; import org.junit.Test; //实现简单认证 public class AuthenticationTest { @Test public void testAuthentication(){ //1.构建SecurityManager工厂 IniSecurityManagerFactory securityManagerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //2.通过securityManagerFactory工厂获取SecurityManager实例 SecurityManager securityManager = securityManagerFactory.getInstance(); //3.将securityManager设置到运行环境当中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //4.获取subject实例 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5.创建用户名密码验证令牌Token UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("victor","123456"); //6.进行身份验证 subject.login(token); //7.判断是否认证通过 System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated()); } }
shiro.ini


[main] #配置Realm jdbcRealm = org.apache.shiro.realm.jdbc.JdbcRealm #配置数据源 dataSource = com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource dataSource.driverClass = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver dataSource.jdbcUrl = jdbc:mysql:///test dataSource.user = root dataSource.password = victor jdbcRealm.dataSource = $dataSource #将Realm注入给SecurityManager securityManager.realm = $jdbcRealm
七、如何自定义Realm
自定义Realm,可以注入给securityManager更加灵活的安全数据源(例如,
JDBCRealm中表和字段都限定了)
通过实现Realm接口,或根据需求继承他的相应子类即可。
需求:使用自定义Realm提供数据源,从而实现认证
实现步骤:
6.1添加jar包
6.2编写自定义Realm
6.3编写shiro.ini
6.4编写测试类
【代码示例】
realms


package com.bjsxt.realms; import java.net.ConnectException; import java.security.interfaces.RSAKey; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm; import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; public class CustomRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm { private String principal; private String credentials; private ResultSet rs; private Statement state; private Connection conn; @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //使用JDBC,从数据库获取数据 try { //1.注册驱动 Driver driver = new Driver(); DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); //2.获取连接对象 String url ="jdbc:mysql:///test"; String user = "root"; String password = "victor"; conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url , user , password ); state = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行sql语句 String sql = "select userName,passwd from starLogin"; rs = state.executeQuery(sql ); //5.处理结果集 while (rs.next()) { principal = rs.getString("userName"); credentials = rs.getString("passwd"); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(state != null){ try { state.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, "customRealm"); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } }
AuthenticationTest


package com.bjsxt.test; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; import org.junit.Test; //实现简单认证 public class AuthenticationTest { @Test public void testAuthentication(){ //1.构建SecurityManager工厂 IniSecurityManagerFactory securityManagerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //2.通过securityManagerFactory工厂获取SecurityManager实例 SecurityManager securityManager = securityManagerFactory.getInstance(); //3.将securityManager设置到运行环境当中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //4.获取subject实例 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5.创建用户名密码验证令牌Token UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("victor","123"); //6.进行身份验证 subject.login(token); //7.判断是否认证通过 System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated()); } }
Shrio.ini


[main] #配置Realm customRealm = com.bjsxt.realms.CustomRealm #将Realm注入给SecurityManager securityManager.realm = $customRealm
八、密码加密实现方案
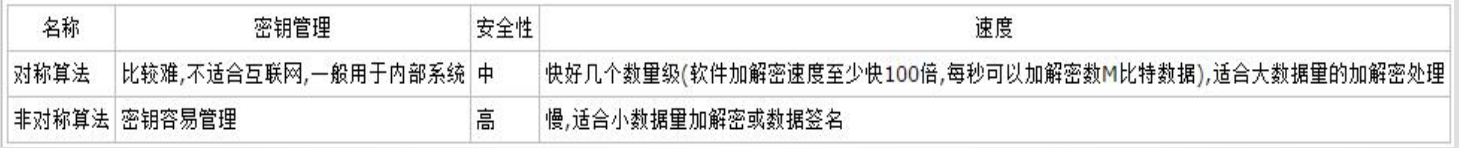
8.1几种常见加密算法比较
8.1.1对称加密算法(加密与解密密钥相同)

8.1.2非对称算法(加密密钥和解密密钥不同)

8.1.3 对称与非对称算法比较
8.1.4 散列算法比较‘

8.2 MD5加密、加盐与迭代
加盐:
使用MD5存在一个问题,相同的password生产的Hash值是相同的,如
果两个用户设置了相同的密码,那么数据库当就会存储相同的值,这样是极
不安全的。
加Salt可以一定程度上解决这一问题。所谓加Salt方法,就是加点
“佐料”。其基本想法是这样的:当用户首次提供密码时(通常是注册时),
由系统自动往这个密码里撒一些“佐料”,然后再散列。而当用户登录时,系统为用户提供的代码撒上同样的“佐料”,然后散列,再比较散列值,来确定密码是否正确。
加盐原理:
给原文加入随机数生成新的MD5值。
迭代:加密的次数
【代码示例】
md5Test


package com.bjsxt.test; import org.apache.shiro.crypto.hash.Md5Hash; import org.junit.Test; //MD5加密、加盐以及迭代 public class MD5Test { @Test public void testMD5(){ //md5加密 Md5Hash md5 = new Md5Hash("123456"); System.out.println(md5); //加盐 md5 = new Md5Hash("123456", "bjsxt"); System.out.println(md5); //迭代 md5 = new Md5Hash("123456", "bjsxt", 2); System.out.println(md5); } }
8.3 凭证匹配器
在Realm接口的实现类AuthenticatingRealm中有credentialsMatcher属性。
意为凭证匹配器。常用来设置加密算法及迭代次数等。
Shiro.ini


[main] #配置凭证匹配器 credentialsMatcher=org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher #设置凭证匹配器的相关属性 credentialsMatcher.hashAlgorithmName=MD5 credentialsMatcher.hashIterations=2 #配置Realm customRealm=com.bjsxt.realms.CustomRealm #配置Realm的凭证匹配器属性 customRealm.credentialsMatcher=$credentialsMatcher #将Realm注入给SecurityManager securityManager.realm=$customRealm
costomRealm


package com.bjsxt.realms; import java.net.ConnectException; import java.security.interfaces.RSAKey; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken; import org.apache.shiro.authc.SimpleAuthenticationInfo; import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthenticatingRealm; import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource; import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; public class CustomRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm { private String principal; private String credentials; private ResultSet rs; private Statement state; private Connection conn; private String salt; @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { //使用JDBC,从数据库获取数据 try { //1.注册驱动 Driver driver = new Driver(); DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); //2.获取连接对象 String url ="jdbc:mysql:///test"; String user = "root"; String password = "victor"; conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url , user , password ); state = conn.createStatement(); //4.执行sql语句 String sql = "select userName,passwd,passwd_salt from starLogin"; rs = state.executeQuery(sql ); //5.处理结果集 while (rs.next()) { principal = rs.getString("userName"); credentials = rs.getString("passwd"); salt = rs.getString("passwd_salt"); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if(rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(state != null){ try { state.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } ByteSource newSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(salt); SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials,newSalt , "customRealm"); return simpleAuthenticationInfo; } }
AutenticationTest


package com.bjsxt.test; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; import org.junit.Test; //实现简单认证 public class AuthenticationTest { @Test public void testAuthentication(){ //1.构建SecurityManager工厂 IniSecurityManagerFactory securityManagerFactory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //2.通过securityManagerFactory工厂获取SecurityManager实例 SecurityManager securityManager = securityManagerFactory.getInstance(); //3.将securityManager设置到运行环境当中 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //4.获取subject实例 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5.创建用户名密码验证令牌Token UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("victor","123456"); //6.进行身份验证 subject.login(token); //7.判断是否认证通过 System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated()); } }
 Apache Shiro安全框架全面解析
Apache Shiro安全框架全面解析







 本文介绍了Apache Shiro这一强大易用的Java安全框架,涵盖其架构、常见名词、配置文件。详细阐述认证实现,包括身份和凭证,还介绍了JDBCRealm、自定义Realm的使用及实现步骤。此外,对几种常见加密算法进行比较,讲解MD5加密、加盐与迭代及凭证匹配器。
本文介绍了Apache Shiro这一强大易用的Java安全框架,涵盖其架构、常见名词、配置文件。详细阐述认证实现,包括身份和凭证,还介绍了JDBCRealm、自定义Realm的使用及实现步骤。此外,对几种常见加密算法进行比较,讲解MD5加密、加盐与迭代及凭证匹配器。
















 1073
1073

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








