无监督学习 k-means
有关深层学习的FAU讲义 (FAU LECTURE NOTES ON DEEP LEARNING)
These are the lecture notes for FAU’s YouTube Lecture “Deep Learning”. This is a full transcript of the lecture video & matching slides. We hope, you enjoy this as much as the videos. Of course, this transcript was created with deep learning techniques largely automatically and only minor manual modifications were performed. Try it yourself! If you spot mistakes, please let us know!
这些是FAU YouTube讲座“ 深度学习 ”的 讲义 。 这是演讲视频和匹配幻灯片的完整记录。 我们希望您喜欢这些视频。 当然,此成绩单是使用深度学习技术自动创建的,并且仅进行了较小的手动修改。 自己尝试! 如果发现错误,请告诉我们!
导航 (Navigation)
Previous Lecture / Watch this Video / Top Level / Next Lecture

Welcome back to deep learning! So today, we finally want to look into the generative adversarial networks which are a key technology in unsupervised deep learning. So, let’s see what I have for you here.
欢迎回到深度学习! 因此,今天,我们终于要研究生成对抗网络,这是无监督深度学习中的一项关键技术。 所以,让我们在这里看看我有什么。

Well, the unsupervised deep learning part generative adversarial networks come from the key idea that GANs to play the following game: You have a generator and a discriminator. Now the generator, one could argue is somebody who generates a fake image. Then, the discrimination has to figure out whether the generator actually produced something that’s real or something which is fake. So, the discriminator can decide fake or real and in order to train the discriminator, he has access to many real data observations. So, the outcome of the discriminator then is whether the input was real or fake. Well, of course, this is difficult to ask persons and artists to draw things. So, we replace the tool with deep neural networks and we have D that is the discriminator and we have G that is the generator. The generator receives some latent input some noise variable z and from the noise variable and the parameters, it produces some image. The discriminator then tries to figure out whether this was a real or fake image. So, the output of the discriminator is going to be 1 for real and 0 for fake.
好吧,无监督的深度学习部分生成对抗网络来自GAN玩以下游戏的关键思想:您有一个生成器和一个鉴别器。 现在,生成器可能会争辩说是某人生成了虚假图像。 然后,必须辨别出生成器实际上是生成的是真实的还是假的。 因此,鉴别者可以决定是假的还是真实的,并且为了训练鉴别者,他可以访问许多真实的数据观察结果。 因此,判别器的结果就是输入是真实的还是假的。 好吧,当然,这很难问个人和艺术家画画。 因此,我们用深度神经网络代替了该工具,并且D是鉴别符,G是生成器。 发生器接收一些潜在的输入一些噪声变量z,并从噪声变量和参数中产生一些图像。 然后,鉴别者试图弄清楚这是真实图像还是伪图像。 因此,鉴别器的输出对于真实将为1,对于伪造为0。
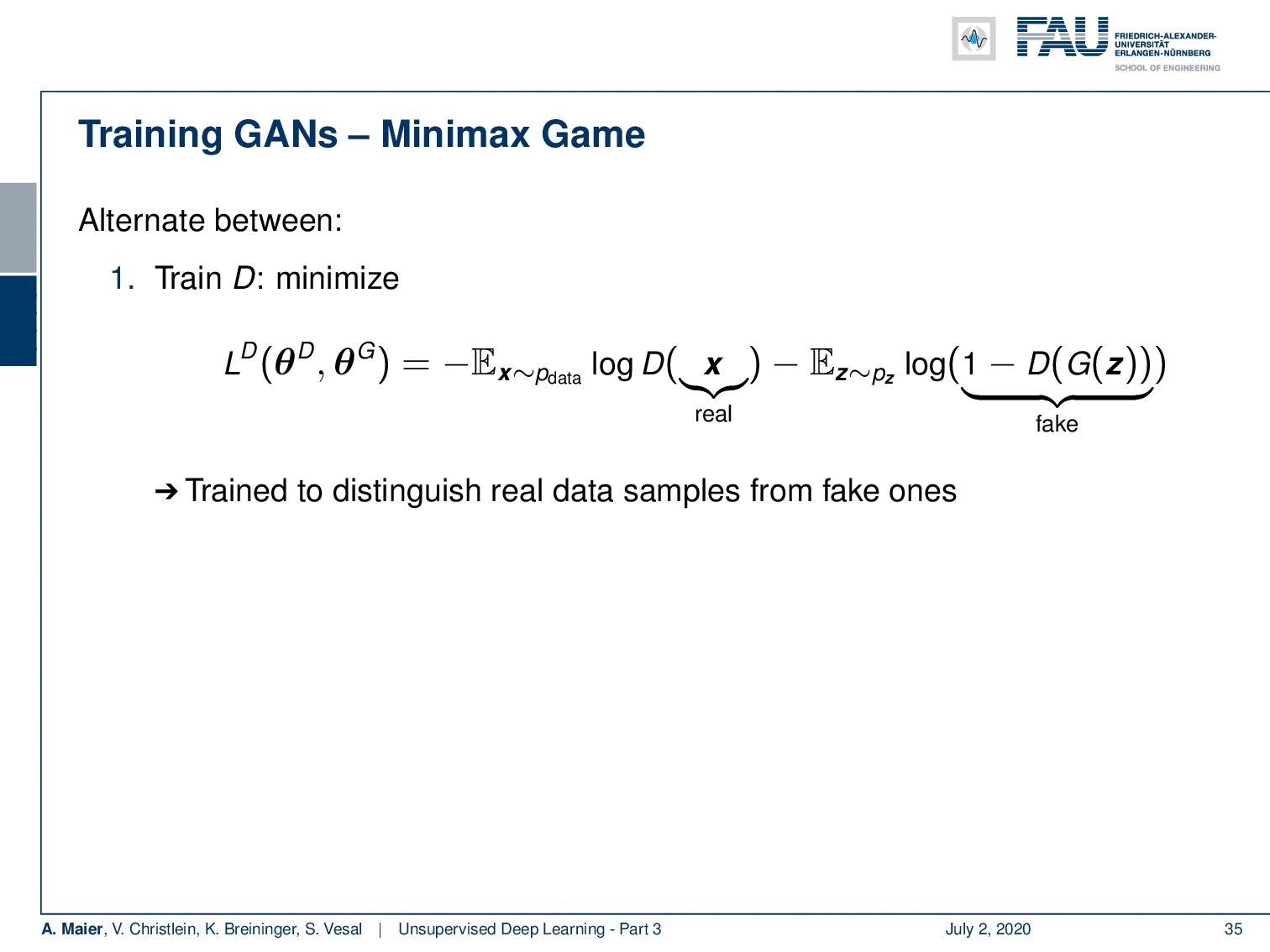
Once we have found this kind of neural network representation, we are also able to describe a loss. The loss of our discriminator is to minimize the following function that is dependent on the parameters of the discriminator and the parameters of the generator. It is essentially minimizing the expected value of x from the data. This is simply the logarithm of the output of our discriminator for real samples minus the expected value of some generated noise and that is the logarithm of 1 minus the discriminator of the generator of some noise. So, it’s trained to distinguish real data samples from fake ones. Now, if you want to train the generator you minimize the loss of the generator that is the negative loss of the discriminator. So, the generator minimizes the probability of the discriminator being correct. You train to generate domain images to fool D. Optionally, you can run k steps of one player for every step of the other player and the equilibrium is a saddle point of the discriminator loss.
一旦找到了这种神经网络表示形式,我们就能够描述损失。 鉴别器的损失是使取决于鉴别器参数和发生器参数的以下功能最小化。 从本质上讲,它是从数据中最小化x的期望值。 这仅是我们的鉴权器对真实样本的输出的对数减去一些产生的噪声的期望值,也就是1的对数减去某些噪声的生成器的对数。 因此,它经过训练可以区分真实数据样本和假数据样本。 现在,如果您要训练发电机,则可以将发电机的损耗(即鉴别器的负损耗)降至最低。 因此,生成器将鉴别器正确的可能性降到最低。 您训练以生成要欺骗D的域图像。(可选)您可以对一个参与者的每一步运行k步,而对另一参与者的每一步进行平衡,则均衡是鉴别器损失的鞍点。
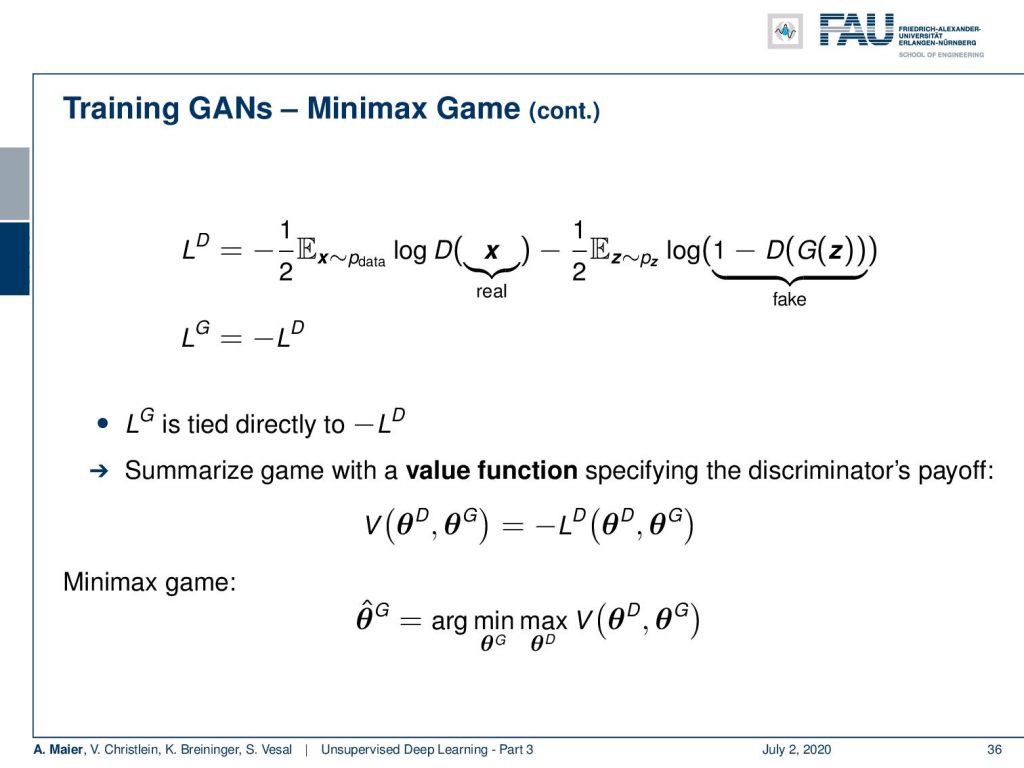
If you look into this in more detail, you can find that the loss of the generator is directly tied to the negative loss of the discriminator. So, you can summarize this game with a value function specifying the discriminator’s payoff that is given as V. This is the negative loss of the discriminator and this then results in the following minimax game: So the optimal parameter set of the generator can be determined by maximizing V with respect to the discriminator nested into a minimization of the parameters of G with respect to the same value function.
如果您对此进行更详细的研究,您会发现发生器的损耗与鉴别器的负损耗直接相关。 因此,您可以使用值函数来概括该游戏,该函数指定以V给出的鉴别器的收益。这是鉴别器的负损失,因此导致以下最小极大游戏:因此,可以确定发生器的最佳参数集通过相对于鉴别器最大化V,嵌套到相对于相同值函数的G参数最小化。

So, let’s have a look at the optimal discriminator. There a key assumption is that is both densities are nonzero everywhere. Otherwise, some input values would never be trained and the discriminator would have undetermined behavior in those areas. Then you solve with respect to the gradient of the discriminator loss with respect to the discriminator to be zero. You can find the optimal discriminator for any data distribution and any model distribution in the following way: the optimal discriminator is the distribution of the data divided by the distribution of the data plus the distribution of the model over your entire input domain of x. Unfortunately, this optimal discriminate is theoretical and unachievable. So, it’s key for GANs to have an estimation mechanism. You can use supervised learning to estimate this ratio. Then this leads to the problem of underfitting and overfitting.
因此,让我们看一下最佳鉴别器。 一个关键的假设是,两个密度在各处都不都是零。 否则,将永远不会训练某些输入值,并且判别器在那些区域中的行为不确定。 然后,根据鉴别器损耗相对于鉴别器的梯度为零进行求解。 您可以通过以下方式找到任何数据分布和模型分布的最佳判别器:最佳判别器是数据的分布除以数据分布再加上模型在整个x输入域上的分布。 不幸的是,这种最佳区分是理论上无法实现的。 因此,GAN具有评估机制的关键。 您可以使用监督学习来估计此比率。 然后,这会导致拟合不足和拟合过度的问题。
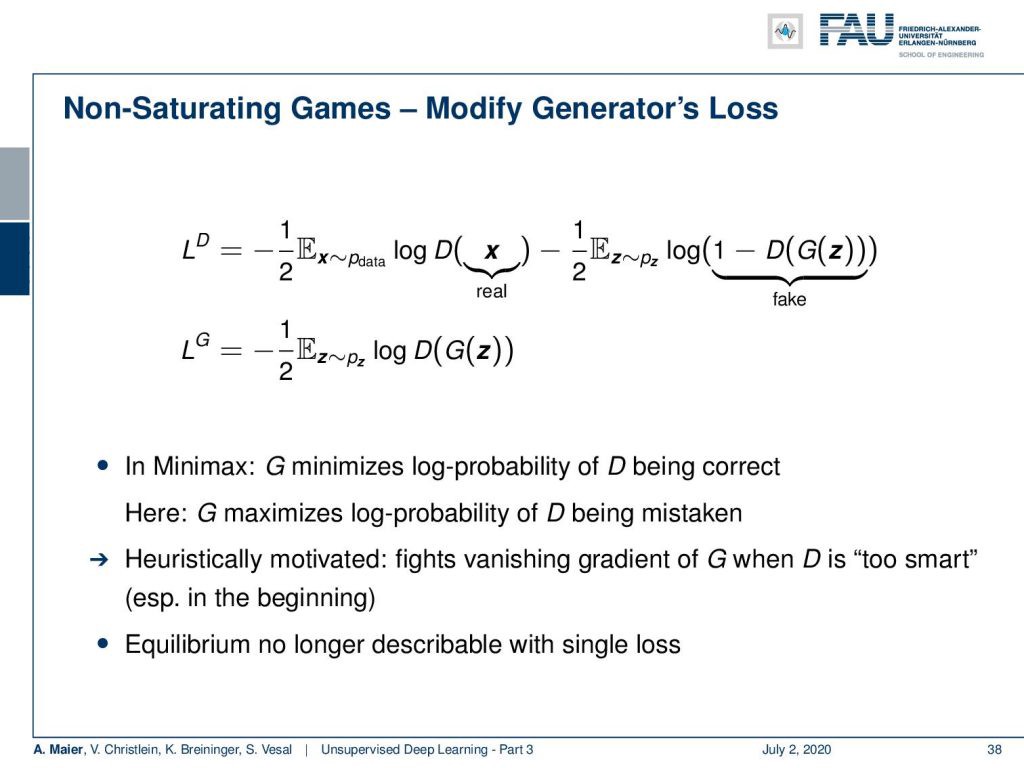
Now, what else can we do? We can do non-saturating games where we modify the generator’s loss. Then, in this example, we are no longer using the same function for both. Instead, we have a new loss for the generator where we simply compute the expected value of the logarithm of the discriminator of the generator given some input noise. In minimax, G minimizes the log probability of D being correct. In this solution, G minimizes the log probability of D being mistaken. It’s heuristically motivated because it fights the vanishing gradient of G when D is too smart. This is particularly a problem in the beginning. However, the equilibrium is no longer describable using a single loss.
现在,我们还能做什么? 我们可以做非饱和游戏,在此我们可以修改生成器的损失。 然后,在此示例中,我们不再为两者使用相同的功能。 取而代之的是,我们对发生器产生了新的损失,在这种情况下,只要输入噪声,我们就可以简单地计算出发生器鉴别器对数的期望值。 在minimax中,G使D正确的对数概率最小。 在此解决方案中,G使D被错误记录的对数概率最小。 启发式动机是因为当D太聪明时,它可以克服G消失的梯度。 一开始这尤其是一个问题。 但是,不再使用单个损失来描述平衡。
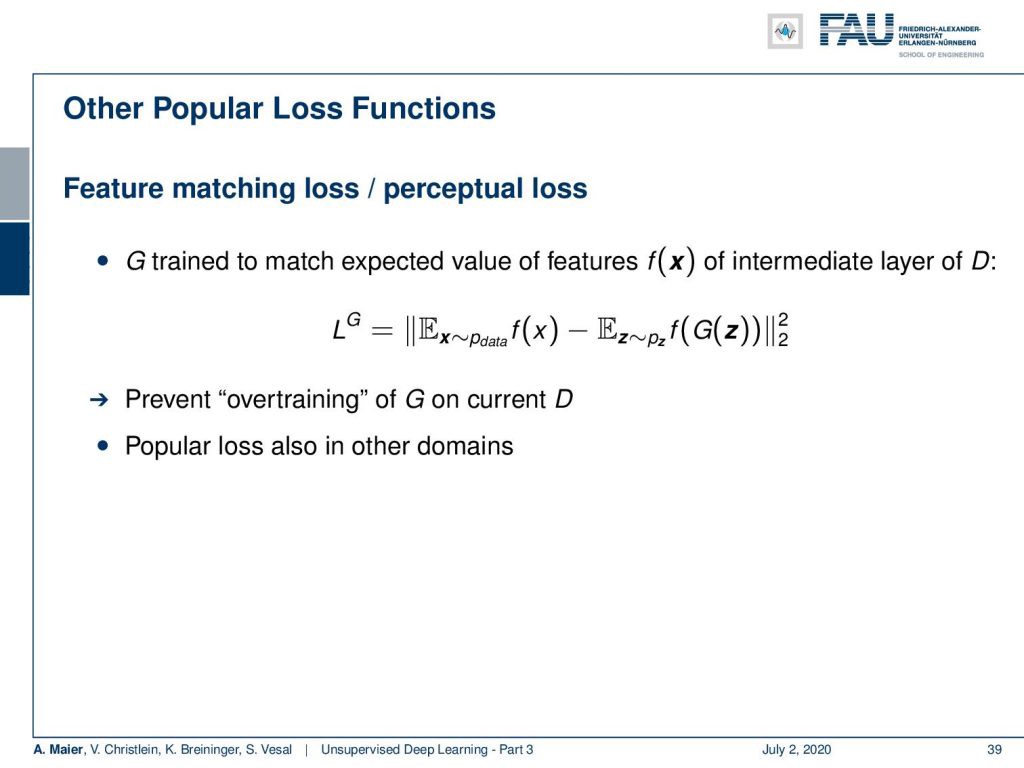
So, there are a lot of things like extensions that are quite popular like the feature matching loss or the perceptual loss. Here, G is trying to match the expected value of features f(x) of some intermediate layer of D. You’ve seen this already that f can be for example some other network and some layer 3 or layer 5 representation. Then, you want the expected values of these representations to be the same given for real inputs as well as for generated noise images. So, here you want to prevent the overtraining of the generator on the current discriminator. By the way, this is also a popular loss in many other domains.
因此,有很多诸如扩展之类的东西很流行,例如特征匹配损失或感知损失。 在这里,G试图匹配D的某个中间层的特征f( x )的期望值。您已经看到,f可以例如是其他网络和第3层或第5层表示形式。 然后,您希望这些表示的期望值与实际输入以及生成的噪声图像的期望值相同。 因此,在这里您要防止发电机在当前鉴别器上过度训练。 顺便说一句,这在许多其他领域也是一种普遍的损失。
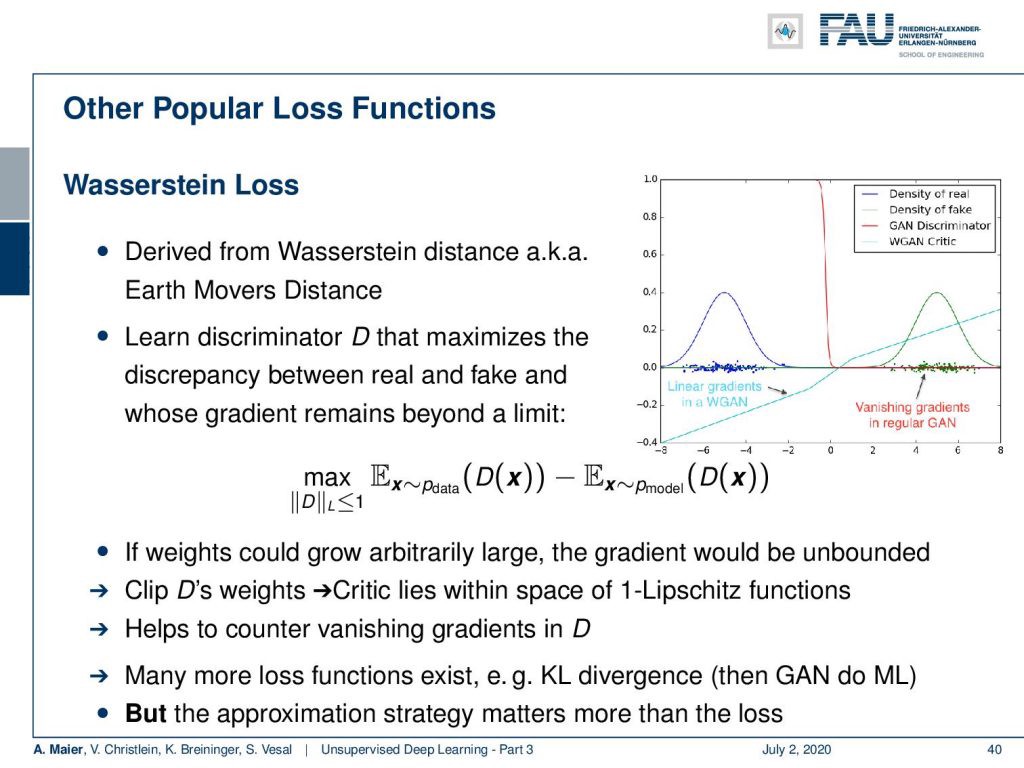
What else can be done? Well, there’s the so-called Wasserstein loss. It’s derived from the Wasserstein distance which is also known as the earth movers distance. Here, you learn a discriminator that maximizes the discrepancy between the real and fake samples, and at the same time, you restrict the gradient to stay behind a certain limit. So, you essentially limit the gradient towards a specific Lipschitz constant which is the maximum slope of the gradient. Here, in the image on the right-hand side, you can see that out of the red discrimination curve which saturated very quickly, you can then create a discriminator that has this non-saturated loss. This way, you will always be able to find good gradients, even in areas where you’re already saturated with your discriminator. Again, this helps to counter vanishing gradients in the discriminator. Many more loss functions exist like the KL divergence. Then, the GANs actually do maximum likelihood, but the approximation strategy matters much more than the loss.
还有什么可以做的? 好吧,这就是所谓的Wasserstein损失。 它源自Wasserstein距离,也称为推土机距离。 在这里,您将学习一个鉴别器,该鉴别器可以使真实样本与假样本之间的差异最大化,同时,您可以将梯度限制在一定限度内。 因此,您实际上将梯度限制在特定的Lipschitz常数上,该常数是梯度的最大斜率。 在这里,在右侧的图像中,您可以看到在很快Swift饱和的红色辨别曲线中,您可以创建一个具有这种非饱和损耗的鉴别器。 这样一来,即使在已经充满识别器的区域中,您也始终可以找到良好的渐变。 同样,这有助于抵消鉴别器中消失的梯度。 存在更多的损失函数,例如KL散度。 然后,GAN确实具有最大的可能性,但是近似策略比损失要重要得多。

So, how do we evaluate GANs? Well, we can, of course, look at the image and say: “Yeah, they look realistic! Or not?” But this is kind of intractable for large data sets. So, you have to use a score for images. One idea is the inception score.
那么,我们如何评估GAN? 好吧,我们当然可以看一下图像说:“是的,它们看起来很逼真! 或不?” 但这对于大型数据集来说是很难处理的。 因此,您必须对图像使用分数。 一种想法是起始分数。
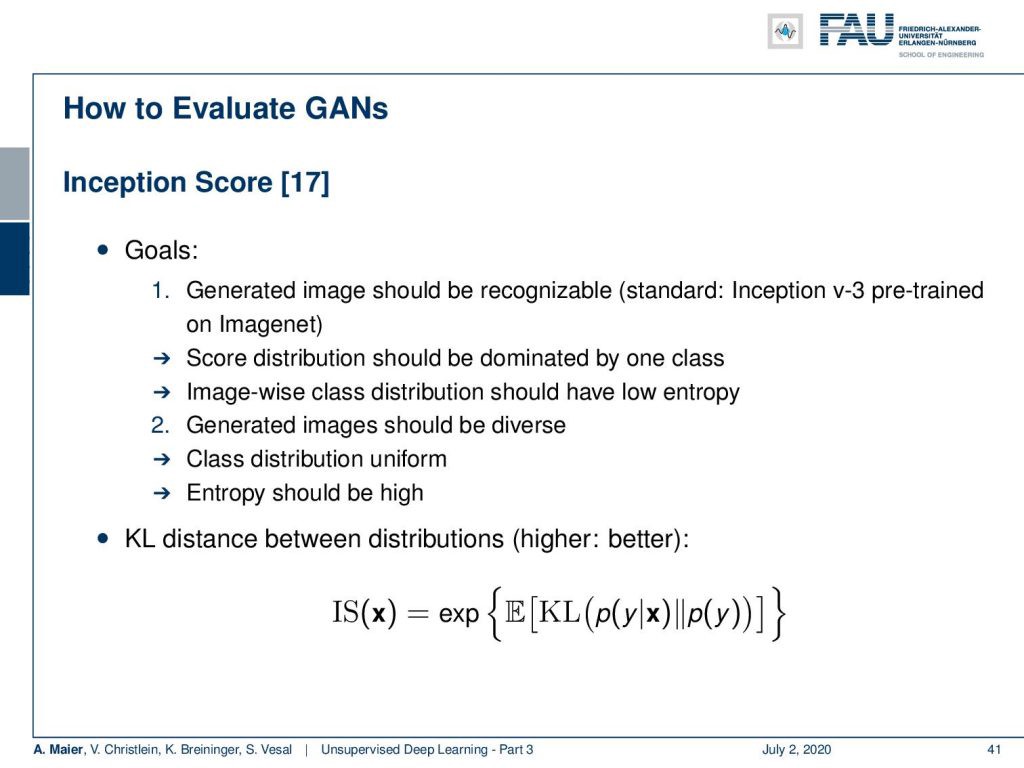
The inception score is based on two goals. One goal is that the generated images should be recognizable. So, you use, for example, an Inception v3 pre-trained Network on ImageNet and you want the score distribution to be dominated by one class. The image-wise class distribution should have low entropy. At the same time, you want the generated images to be diverse. So the overall class distribution should be more or less uniform. The entropy should be high. So, you can then express this inception score as e to the power of the expected value of the KL divergence between p(y|x) and p(y).
初始分数基于两个目标。 一个目标是生成的图像应该是可识别的。 因此,例如,您使用ImageNet上的Inception v3预训练网络,并且希望分数分布由一个类别控制。 按图像分类分布应具有较低的熵。 同时,您希望生成的图像多样化。 因此,整个班级分布应大致相同。 熵应该很高。 因此,您可以将该初始得分表示为p(y | x )和p(y)之间KL散布的期望值的幂。
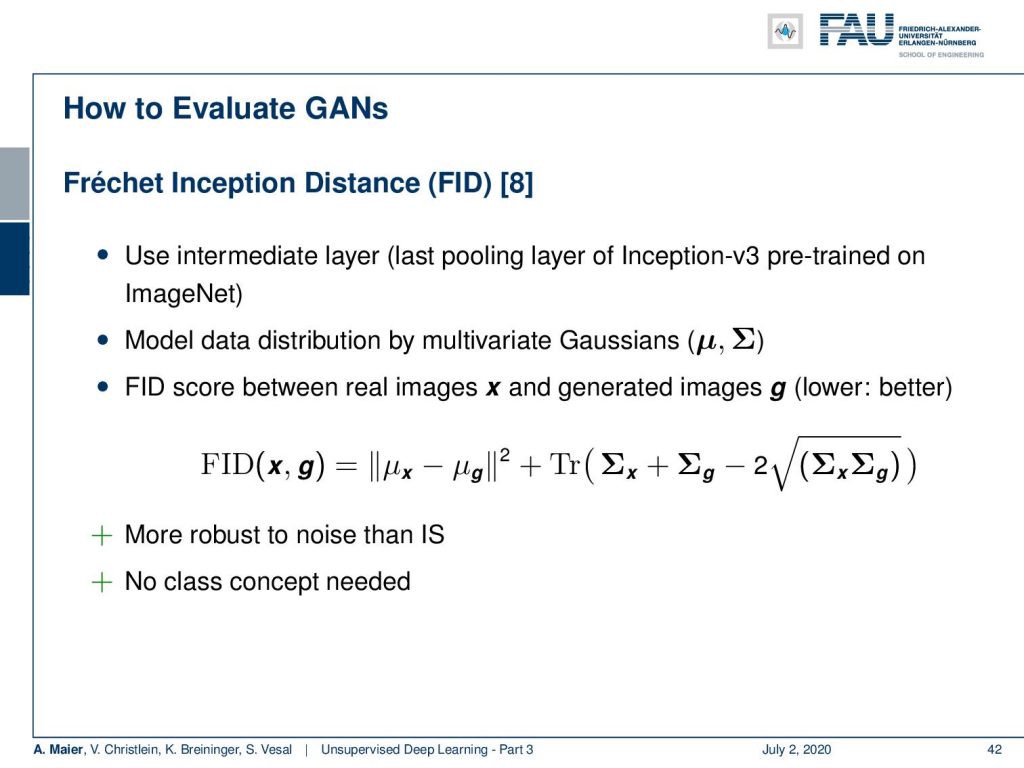
Another measurement is the Fréchet inception distance which is using an intermediate layer. So, the last pooling layer of Inception v3 pretrained on ImageNet, for example. Then, you model the data distribution by multivariate Gaussians. The FID score between the real images x and the generated images g can be expressed as the difference between the mean values of x and g in an l2 norm plus the trace of the covariance matrices of x and g minus two times the square root of covariance matrix x times covariance matrix g. This is more robust than the inception score. We don’t need the class concept. In this case, we can simply work on multivariate Gaussians in order to model the distributions.
另一个度量是使用中间层的弗雷谢特起始距离。 因此,例如,在ImageNet上对Inception v3的最后一个池化层进行了预训练。 然后,通过多元高斯模型对数据分布进行建模。 实像x和生成的图像g之间的FID分数可以表示为l2范数中x和g的平均值之差加上x和g的协方差矩阵的迹线减去协方差平方根的两倍矩阵x乘方差矩阵g 。 这比初始分数更健壮。 我们不需要类的概念。 在这种情况下,我们可以简单地处理多元高斯模型以对分布进行建模。
A big advantage of GANs is that they are able to generate samples in parallel. There are very few restrictions. For example, compared to the Boltzmann machines that have plenty of restrictions: You don’t need a Markov chain in this model. There are also no variational bounds needed. GANs are known to be asymptotically consistent since the model families are universal function approximators. So, this was a very first introduction to GANs.
GAN的一大优势在于它们能够并行生成样本。 限制很少。 例如,与具有很多限制的Boltzmann机器相比:在此模型中不需要马尔可夫链。 也没有变化的界限。 由于模型族是通用函数逼近器,因此已知GAN渐近一致。 因此,这是GAN的第一个介绍。

In the next video, we want to talk a bit about more advanced GAN concepts like the conditional GANs where we can also start and modeling constraints and conditions into the generation process. People also looked into a very cool technique that is called the cycle GAN which allows unpaired to domain translation. So, you can translate images from day to night. You can even translate horses to zebras and zebras to horses. So, a very, very cool technique coming up. I hope you enjoyed this video and I’m looking forward to seeing you in the next one. Thank you very much!
在下一个视频中,我们想谈一些更高级的GAN概念,例如条件GAN,我们还可以在其中开始并将约束和条件建模到生成过程中。 人们还研究了一种称为循环GAN的非常酷的技术,该技术允许不配对的域翻译。 因此,您可以将图像白天转换为晚上。 您甚至可以将马翻译成斑马,再将斑马翻译成马。 因此,出现了一种非常非常酷的技术。 希望您喜欢这个视频,并期待在下一个视频中见到您。 非常感谢你!

If you liked this post, you can find more essays here, more educational material on Machine Learning here, or have a look at our Deep LearningLecture. I would also appreciate a follow on YouTube, Twitter, Facebook, or LinkedIn in case you want to be informed about more essays, videos, and research in the future. This article is released under the Creative Commons 4.0 Attribution License and can be reprinted and modified if referenced. If you are interested in generating transcripts from video lectures try AutoBlog.
如果你喜欢这篇文章,你可以找到这里更多的文章 ,更多的教育材料,机器学习在这里 ,或看看我们的深入 学习 讲座 。 如果您希望将来了解更多文章,视频和研究信息,也欢迎关注YouTube , Twitter , Facebook或LinkedIn 。 本文是根据知识共享4.0署名许可发布的 ,如果引用,可以重新打印和修改。 如果您对从视频讲座中生成成绩单感兴趣,请尝试使用AutoBlog 。
链接 (Links)
Link — Variational Autoencoders: Link — NIPS 2016 GAN Tutorial of GoodfellowLink — How to train a GAN? Tips and tricks to make GANs work (careful, noteverything is true anymore!) Link - Ever wondered about how to name your GAN?
链接 —可变自动编码器: 链接 — Goodfellow的NIPS 2016 GAN教程链接 —如何训练GAN? 使GAN正常工作的提示和技巧(小心,什么都没了!) 链接 -是否想知道如何命名GAN?
翻译自: https://towardsdatascience.com/unsupervised-learning-part-3-7b15038bb884
无监督学习 k-means




 本文深入探讨了无监督学习中的生成对抗网络(GANs),介绍了GANs的基本原理,包括生成器与鉴别器的游戏,以及如何通过不同策略优化训练过程。文章还讨论了评估GANs性能的方法,如初始分数和Frechet初始距离。
本文深入探讨了无监督学习中的生成对抗网络(GANs),介绍了GANs的基本原理,包括生成器与鉴别器的游戏,以及如何通过不同策略优化训练过程。文章还讨论了评估GANs性能的方法,如初始分数和Frechet初始距离。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








