一、重写equals方法
package myself;
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override //重写equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Student s = (Student) obj;
if(this.name.equals(s.name) && this.age==s.age) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
第二种简化重写equals方法
package myself;
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name,int age) {
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override //重写equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//为了提高效率
if(this==obj) {
return true;
}
//为了提高程序健壮性
//这时候我们要判断一个对象,要判断它是不是某个类的对象
//记住一个各式:对象名 instanceof 类名, 表示判断对象名是不是该类的一个对象
if(!(obj instanceof Student)){
return false;
}//如果是就继续执行下面代码
Student s = (Student) obj;
return this.name.equals(name) && this.age==age ;
}
}
二、重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age;
}
}
三、String类的常见操作
package school;
public class StringClass {
public StringClass() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
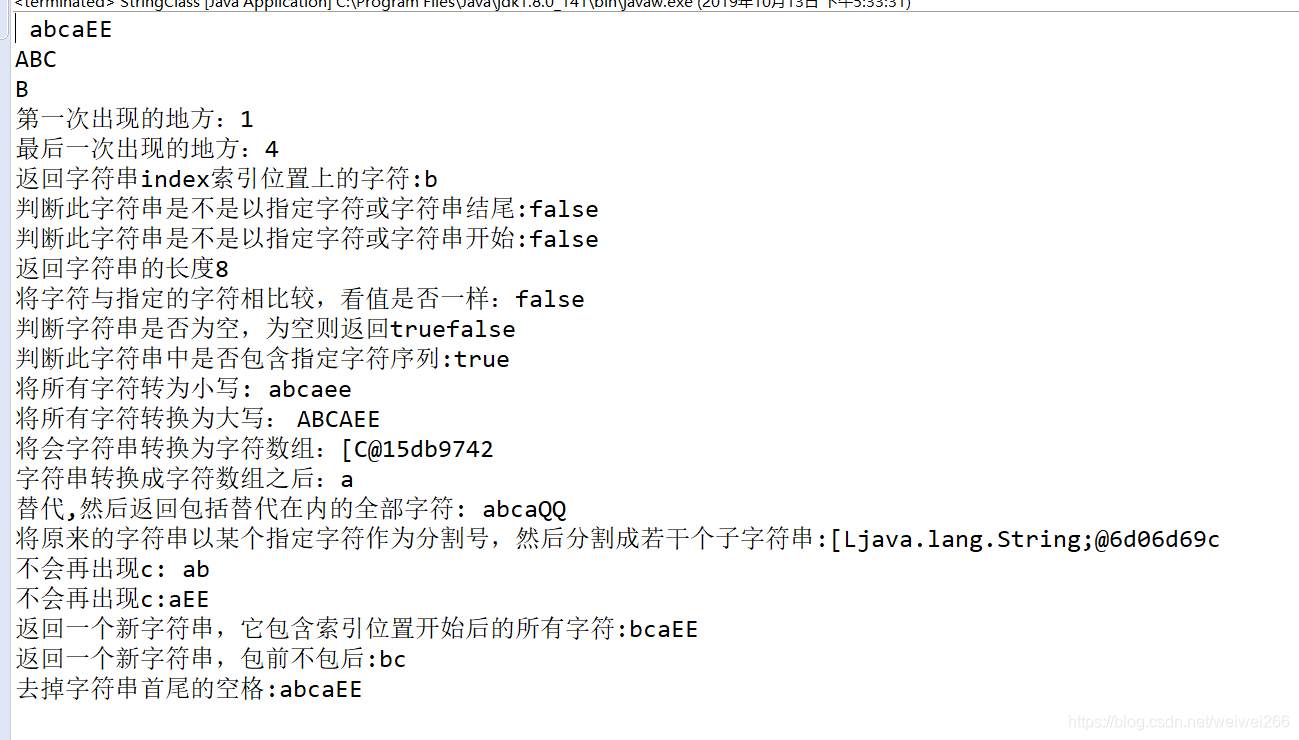
String str = new String(" abcaEE ");//这里首尾各有一个空格,也算是两个个字符
char[] strarray = new char[] {'A','B','C'};
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(strarray);
System.out.println(strarray[1]);
//返回指定字符第一次出现的索引位置
System.out.println("第一次出现的地方:"+str.indexOf("a"));
//返回指定字符最后一次出现的索引位置
System.out.println("最后一次出现的地方:"+str.lastIndexOf("a"));
//返回字符串index索引位置上的字符。
System.out.println("返回字符串index索引位置上的字符:"+str.charAt(2));
//判断此字符串是不是以指定字符或字符串结尾,是则返回true,否在返回false。
System.out.println("判断此字符串是不是以指定字符或字符串结尾:"+str.endsWith("a"));
//判断此字符串是不是以指定字符或字符串开始,是则返回true,否在返回false。
System.out.println("判断此字符串是不是以指定字符或字符串开始:"+str.startsWith("b"));
//返回字符串的长度。
System.out.println("返回字符串的长度"+str.length());
//将字符与指定的字符相比较,看值是否一样,一样则返回true。
System.out.println("将字符与指定的字符相比较,看值是否一样:"+str.equals("abca" ));
//判断字符串是否为空,为空则返回true。
System.out.println("判断字符串是否为空,为空则返回true"+str.isEmpty());
//判断此字符串中是否包含指定字符序列。
System.out.println("判断此字符串中是否包含指定字符序列:"+str.contains("ca"));
//将所有字符转为小写
System.out.println("将所有字符转为小写:"+str.toLowerCase());
//将所有字符转换为大写
System.out.println("将所有字符转换为大写:"+str.toUpperCase());
//将会字符串转换为字符数组
System.out.println("将会字符串转换为字符数组:"+str.toCharArray());
//因为转换成了字符数组,所有可以用下标[i]读出。
System.out.println("字符串转换成字符数组之后:"+str.toCharArray()[1]);
//替代,然后返回包括替代在内的全部字符
System.out.println("替代,然后返回包括替代在内的全部字符:"+str.replace("E","Q"));
//将原来的字符串以某个指定字符作为分割号,然后分割成若干个子字符串
//若分割符号是原字符串中的,则分割后,此分割号不再在原来字符串中
System.out.println("将原来的字符串以某个指定字符作为分割号,然后分割成若干个子字符串:"+str.split("c"));//以原字符串中的c作为分割号
System.out.println("不会再出现c:"+str.split("c")[0]);//不会再出现c
System.out.println("不会再出现c:"+str.split("c")[1]);//不会再出现c
//返回一个新字符串,它包含索引位置开始后的所有字符。
System.out.println("返回一个新字符串,它包含索引位置开始后的所有字符:"+str.substring(2));
//返回一个新字符串,包前不包后。
System.out.println("返回一个新字符串,包前不包后:"+str.substring(2, 4));
//去掉字符串首尾的空格
System.out.println("去掉字符串首尾的空格:"+str.trim());
}
}
(1)、结果
四、StringBuffer(字符串缓冲区)

1、
package school;
public class String_Buffer {
public String_Buffer() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// StringBuffer类和String类最大的区别在于它的内容和长度都是可以改变的。
//StringBuffer类似一个字符容器,当在其中添加或删除字符时,并不会产生新的StringBuffer对象。
StringBuffer s1=new StringBuffer("hello");
StringBuffer s2=new StringBuffer("aaa");
//在字符串"hello"后面连接" world";
StringBuffer s3=s1.append(" world");
//在字符串"hello"索引1的位置插入"b";
StringBuffer s4=s2.insert(1, "b");
StringBuffer s5=new StringBuffer("co");
//删除字符串“co”索引1的位置。
StringBuffer s6=s5.deleteCharAt(1);
StringBuffer s7=new StringBuffer("ABCD");
//删除字符串,包左不包右。
StringBuffer s8=s7.delete(0, 3);
StringBuffer s9=new StringBuffer("我爱你");
//从索引0开始,不包含索引2位置开始替换,也就是把“我爱”替换为"哈喽亚"。
StringBuffer s10=s9.replace(0, 2, "哈喽亚");
StringBuffer s11=new StringBuffer("我是你爸");
//setCharAt(index,ch)方法是一个无返回值的,
//所有不能把s11.setCharAt(3, '妈')再赋值给一个变量。
s11.setCharAt(3, '妈');
StringBuffer s12=new StringBuffer("ABC");
//将字符串倒序。
StringBuffer s13=s12.reverse();
System.out.println("在字符串\"hello\"后面连接\" world\":"+s3);
System.out.println("在字符串\"aaa\"索引1的位置插入\"b\":"+s4);
System.out.println("删除字符串“co”索引1的位置:"+s6);
System.out.println("删除字符串,包左不包右。:"+s8);
System.out.println("从索引0开始,不包含索引2位置开始替换,也就是把“我爱”替换为\"哈喽亚\":"+s10);
System.out.println("不能把s11.setCharAt(3, '妈')再赋值给一个变量。:"+s11);
System.out.println("字符串倒序。:"+s13);
}
}
2、结果

五、System类
**1、System类的arraycopy()方法**
package school;
public class System_test {
public System_test() {
// System类的方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System类的方法:拷贝数组
int[] s1= {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] s2= {6,7,8,9};
//第一个参数s1是源数组,第二个参数3是源数组从索引位置几开始拷贝。
//第三个参数s2是目标数组,第四个参数是目标数组从索引位置几开始拷贝。
System.arraycopy(s1,3,s2,2,2);
for(int i=0;i<s2.length;i++) {
System.out.println(i+":"+s2[i]);
}
}
}
**2、结果**

六、Math类的方法
package school;
public class Math_test {
public Math_test() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Math类的方法
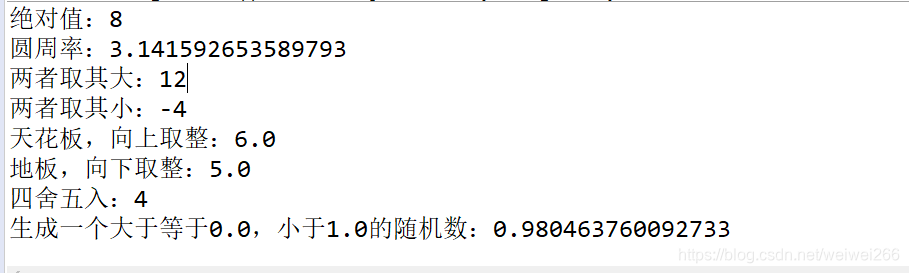
System.out.println("绝对值:"+Math.abs(-8));
System.out.println("圆周率:"+Math.PI);
System.out.println("两者取其大:"+Math.max(12, 10));
System.out.println("两者取其小:"+Math.min(-4, -1));
System.out.println("天花板,向上取整:"+Math.ceil(5.6));
System.out.println("地板,向下取整:"+Math.floor(5.6));
System.out.println("四舍五入:"+Math.round(4.49));
System.out.println("生成一个大于等于0.0,小于1.0的随机数:"+Math.random());
}
}
2、结果
七、Random类及其方法

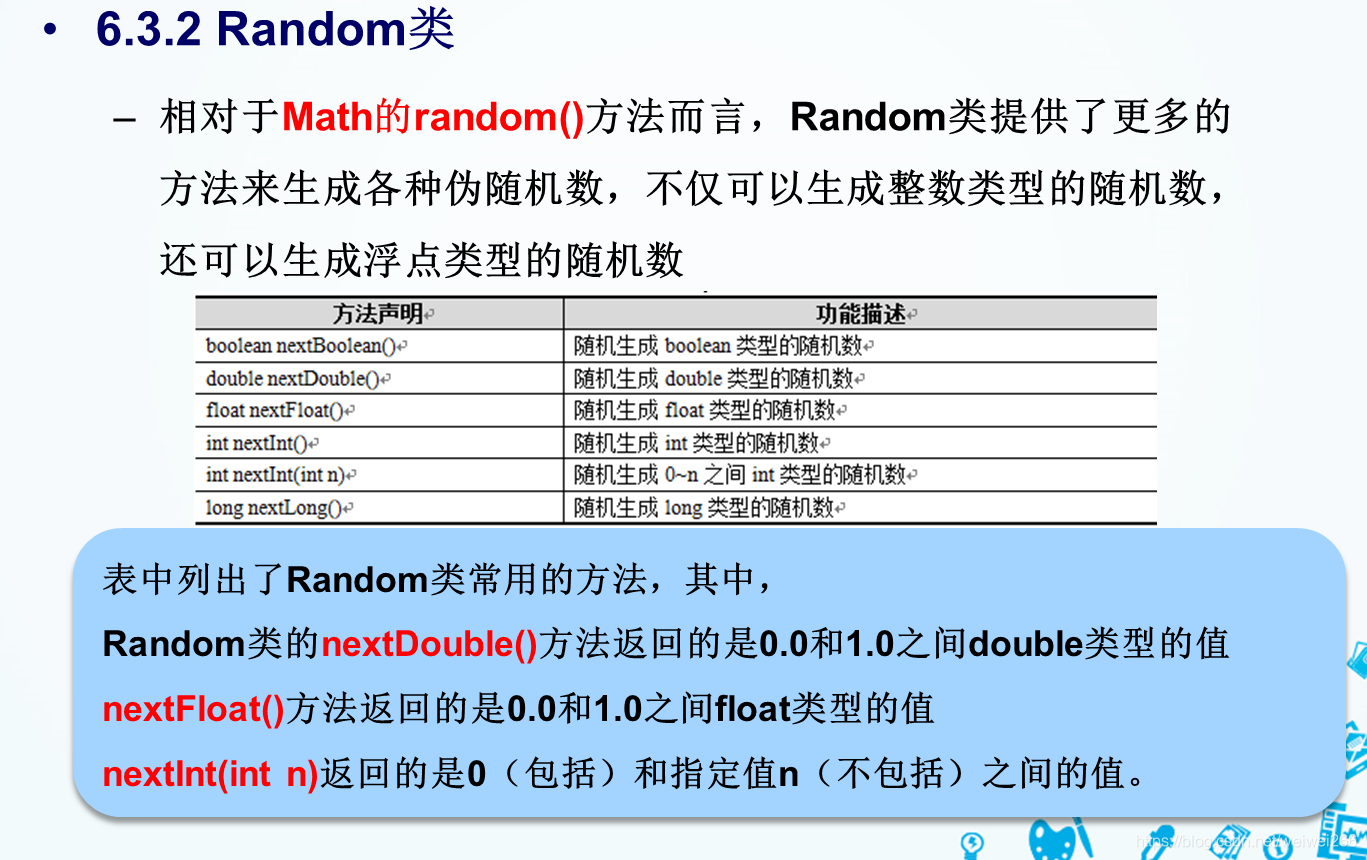
3、代码
package school;
import java.util.*;
public class Random_test {
public Random_test() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Random类的方法
//不传入种子,默认以当前时间为种子。
Random r1=new Random();
//随机生成10个[0,100)之间的整数。
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
System.out.print(r1.nextInt(100)+" ");
}
}
}
八、Calendar类及其方法
1、 Calendar类是一个抽象类,不可以被实例化,在程序中需要调用其静态方法getInstance()来得到一个Calendar对象,然后调用其相应的方法,
package school;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Calendar_class {
public Calendar_class() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Calendar类及其方法
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
int year = c1.get(Calendar.YEAR);//获取年
int month = c1.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1;//获取月,月要+1
int day = c1.get(Calendar.DATE);//获取日
int hour = c1.get(Calendar.HOUR);//获取时
int minute = c1.get(Calendar.MINUTE);//获取分
int second = c1.get(Calendar.SECOND);//获取秒
System.out.println(year+"年"+month+"月"+day+"日 下午"+hour+"时"+minute+"分"+second+"秒");
}
}
结果

/---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------/
题目:一项工程从2008.8.8开始,假设100天后竣工,请问具体的竣工日期是哪一天?
package school;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Calendar_class2 {
public Calendar_class2() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 一项工程从2008.8.8开始,假设100天后竣工,请问具体的竣工日期是哪一天?
Calendar c2= Calendar.getInstance();
c2.set(2008, 8, 8);
c2.add(Calendar.DATE, 100);
int year = c2.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = c2.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int day = c2.get(Calendar.DATE);
System.out.println("竣工时间为:"+year+"年"+month+"月"+day+"日");
}
}
结果

九、DateFormat类及其方法
package day01;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class DateFormat_class {
public DateFormat_class() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Date date = new Date();
//日期格式,精确到:XXXX年X月X日,星期X
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.FULL);
//日期格式,精确到:XXX年X月X日
DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.LONG);
//日期格式,精确到:XXXX-X-X
DateFormat df3 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM);
//日期格式,精确到:XX-X-X
DateFormat df4 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT);
System.out.println("FULL:"+df1.format(date));
System.out.println("LONG:"+df2.format(date));
System.out.println("MEDIUM:"+df3.format(date));
System.out.println("SHORT:"+df4.format(date));
}
}
结果

十、SimpleFormat类及其方法
JDK中提供了一个SimpleDateFormat类,该类是DateFormat类的子类。SimpleDateFormat类可以使用new关键字创建实例对象,它的构造方法接收一个格式字符串参数,表示日期格式模板
package day01;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class SimpleFormat_class {
public SimpleFormat_class() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SimpleDateFormat s1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日");
SimpleDateFormat s2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日:今天是yyyy年的第D天,E");
System.out.println(s1.format(new Date()));
System.out.println(s2.format(new Date()));
}
}
结果

说明
在创建SimpleDateFormat对象时传入日期格式模板“Gyyyy年MM月dd日:今天是yyyy年的第D天,E” ,调用SimpleDateFormat的format()方法,将Date对象格式化成如模板格式的“公元2013年09月06日:今天是2013年的第249天,星期五”字符串形式。




 本文详细探讨了JAVA高级开发的多个方面,包括重写方法、toString方法的重写、String类的操作、StringBuffer的使用、System类和Math类的重要方法、Random类的随机数生成以及Calendar类的时间处理。此外,还介绍了日期格式化的DateFormat和SimpleDateFormat类,并通过一个实际问题——计算工程竣工日期,展示了这些知识的应用。
本文详细探讨了JAVA高级开发的多个方面,包括重写方法、toString方法的重写、String类的操作、StringBuffer的使用、System类和Math类的重要方法、Random类的随机数生成以及Calendar类的时间处理。此外,还介绍了日期格式化的DateFormat和SimpleDateFormat类,并通过一个实际问题——计算工程竣工日期,展示了这些知识的应用。
















 1152
1152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








