delete和truncate的区别:
相同点:都可以删掉所有表记录,不改变表的结构
不同点:truncate会重新设置自增列的计数器,归零
truncate不会影响事务
delete删除问题:
InnoDB自增列会重1开始(存在内存中,断电丢失)
MyISAM继续从上一个自增量开始(存在文件中,不会丢失)

去重 distinct
select distinct studentNo from student
与、或、非:and、or、not(&&、||、!=)

模糊查询

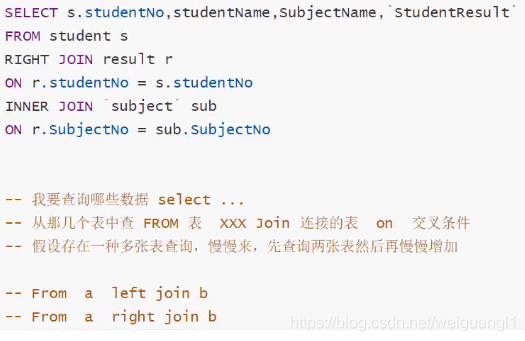
联表查询
on和where的区别:(有效率的区别)
on条件是生成临时表时的条件,无论on的条件是否为真,左表的数据都会 返回,只是右表数据这是都会变成null,这是Left Join的特性(Right Join同)
所以当使用left join和right join时不能使用where,因为此时表还没有建立
where是在临时表创建完后根据条件进行筛选




连接了多张表时,两张两张相连就行
自连接
自己的表和自己连接,核心是一张表拆成两张一样的表
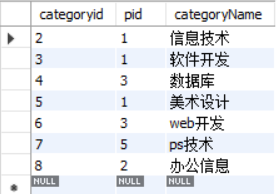
select a.`categoryName` as '父栏目',b.`categoryName` as '子栏目' from school.category as a,school.category as b
where a.categoryid=b.pid;
分页limit和排序orderby
排序:升序Asc,降序Desc
order by 字段 排序方式
select s.studentno,s.studentname,subjectname,studentresult from school.student as s right join school.`subject` as sub on s.gradeid=sub.gradeid
and sub.subjectname='数据库结构-2' inner join school.result as r on s.studentno=r.studentno
order by studentresult desc;
分页:limit
语法:limit 起始下标(起始数据),页面大小
limit 0,5 第1-5条数据
limit 1,5 第2-5条数据
limit 5,5 第6-5条数据
网站中的第N页 limit (N-1)pageSize,pageSize
select s.studentno,s.studentname,subjectname,studentresult
from school.student as s
inner join school.`subject` as sub on sub.gradeid=s.gradeid
inner join school.result as r on s.studentno=r.studentno
where sub.subjectname='C语言-2'
order by studentresult desc
limit 0,4;
子查询
where语句里面嵌套语句
例题:查询课程为C语言-2并且分数不小于80的同学的学号和姓名
select s.studentno,s.studentname from school.student s
inner join school.result r on r.studentno=s.studentno
where studentresult >= 80 and subjectno=(
select subjectno from school.`subject` where subjectname='C语言-2')
order by s.studentno asc;
select studentno,studentname from student
where studentno in(
select studentno from result where studentresult>=50 and subjectno=(
select subjectno from `subject` where subjectname='C语言-2' )
);
分组和过滤
select subjectname,avg(studentresult),max(studentresult),min(studentresult)
from `subject` as sub inner join result r on sub.subjectno=r.subjectno
group by r.subjectno
having avg(studentresult)>80;-- having也是用来过滤,但是是过滤分组后的结果,这里不能用where代替
 SQL操作详解
SQL操作详解




















 397
397

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








