视频地址
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xE41137Qy?p=1
目录
对象
P01-面向对象概念-1 1:09:22
P02-面向对象概念-2 52:28
P03-方法的重载 48:38
P04-对象的创建和使用 47:41
P05-对象和引用 39:50
P06-this关键字 30:16
三大特性
P01-封装 1:14:55
P02-继承关系 1:27:13
P03-方法的覆盖 27:08
P10-super关键字 1:07:04
P11-单继承 16:49
P12-继承习题课 42:11
对象
P01-面向对象概念-1 1:09:22
一、 面向对象思想
1.对象组成:
1)属性 对象有什么
2)方法 对象能做什么 对外提供的行为
2.对象之间的关系
1) is a 汽车与车关系 继承关系
2) has a 汽车与发动机的关系 关联关系 一个对象是另一个对象的属性
3) use a 司机开汽车 依赖关系 一个对象调用另一个对象的方法
3.面向对象思想
面对需求, 找出解决问题的对象, 让对象之间建立适当的关系
二、 面向对象编程思想
模拟现实世界,用计算机中的对象,模拟现实世界中的对象
抽象:
用计算机中类型的概念,对象现实世界中类的概念
类: 对象共性的抽象,
三、 如何定义一个JAVA类
类包含: 属性,方法,构造方法
属性 :
成员变量特点
1) 成员变量有默认值 (0: 数值的7种 false boolean null 对象类型 )
2) 成员变量作用范围,整个类
3)成员变量与局部变量可以同名
方法: 行为 函数
方法声明: 修饰符 返回值 方法名(参数列表) 异常
方法实现{}
构造方法:特殊方法
1) 没有返回值类型
2) 方法名必须与类名相同,包括大小写
3) 不允许手工调用
4)如果类没有定义任何构造方法,编译器自动提供默认无参构造方法
P02-面向对象概念-2 52:28
在这里插入代码片
P03-方法的重载 48:38

方法重载:(也叫编译时多态)
1. 参数个数不同
2. 参数类型不同
3. 参数类型排列不同
4. 构造方法也可以重载
为什么有重载的存在
重载的作用: 一个类的同一行为,由于参数不同,造成的实现差异,对对象的调用者是屏蔽的
P04-对象的创建和使用 47:41
对象的创建过程:
1. 分配堆空间 属性被赋值为 默认值
2. 初始化属性 属性被赋值为 初始值
3. 调用构造方法 属性被赋值为 构造参数
package day6;
public class TestClass{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s =new Student();
System.out.println(s.name);
System.out.println(s.age);
System.out.println(s.score);
s.eat();
}
}
class Student{
String name;
int age;
double score;
public Student(){}
public Student(String name){
this.name=name;
}
void eat(){
System.out.println("eating ....");
}
void sleep(){
System.out.println("sleeping ... ");
}
}
P05-对象和引用 39:50

对象都是存储在堆空间内的
String是引用类型,要注意String不是8种基本类型
成员变量 VS 局部变量
简单变量 VS 引用
简单变量: 8中基本类型 存储值 作为函数的参数时候, 实参 形参 值相同
引用: 存储地址 作为函数参数时候 , 实参形参 地址相同 ,指向同一对象
package day7;
public class TestReference{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=10;
int b=a;
b++;
System.out.println(a); // 10
MyClass mc1 =new MyClass();
MyClass mc2 =mc1;
mc2.value++;
System.out.println(mc1.value); //21
MyClass mc3 =new MyClass();
changeValue(mc3);
System.out.println(mc3.value); //21
}
static void changeValue(MyClass mc){
mc.value++;
}
}
class MyClass{
int value=20;
}
P06-this关键字 30:16
this 代表对象自己 就是当前对象
对this 调用,必须是构造器第一个语句 ,见下图

面向对象三大特性
P01-封装 1:14:55


对象有明确的边界,对象边界对对象内部数据起到保护作用,隔离作用
可以利用修饰符,定义类的属性,方法 是否能被外部访问
public
private
默认 属性或方法只能被同包的
访问方法: get属性名(); set属性名();
对于boolean类型,get方法用is方法替换,如:getMale() 通常用isMale();
现实中文一个女生年龄:女生通过getAge()方法返回年龄
1. 认识的人问此女生 会回答你,可能偏小
2. 生病时,医生问此女生 回答一定真实
3. 陌生人问此女生 女生会回答,滚 ,流氓 ....
这就是封装了,如果没有封装,直就是age 属性的公共方法了;
最简单的方式访问类
公共属性的方式
package day8;
public class TestEncapsulation{
public static void main(String[] args){
CredictCard card=new CredictCard();
System.out.println(card.password);
card.password ="654321";
System.out.println(card.password);
}
}
class CredictCard{
String password="123456";
}
通过方法访问
属性私有化
属性访问通过方法完成,可以在方法中增加验证身份逻辑,来保护数据本身

package day8;
public class TestEncapsulation{
public static void main(String[] args){
CredictCard card=new CredictCard();
// System.out.println(card.password);
// card.password ="654321";
// System.out.println(card.password);
System.out.println( card.getPassword());
card.setPassword("654321");
System.out.println( card.getPassword());
}
}
class CredictCard{
private String password="123456";
public String getPassword(){
// could do someting to protect the access ,such as role
// 只有 管理员 && 用户本身可以访问此方法 ,其他用户不可以访问此方法,(下同)
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password){
this.password =password;
}
}
P02-继承关系 1:27:13
20201228 55:50
子类 is a 父类 父类 – 子类 一般 – 特殊 父类有什么 ,子类就有什么
继承: 从可重用的角度,可扩展角度,子类自动继承父类,可以在父类基础上扩展
LSP:里氏代换原则 : 将父类替换为子类时,依然合乎逻辑
LSP 的经典案例: 长方形 , 正方形 ,
数学老师教:正方形 is a 特殊的长方形
计算机老师: 正方形 is a 特殊的矩形
长方形 is a 特殊的矩形
父类: 一定个各种子类的抽象,将子类的共性提炼出来形成的。
没有继承前的定义
package day8;
public class TestInheritance{
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
class Animal{
int age;
char gender;
public void eat(){
}
public void sleep(){
}
}
class Dog{
int age;
char gender;
public void eat(){
}
public void sleep(){
}
public void shout(){
}
}
dog 继承 了 animal ,下面是示例
package day8;
public class TestInheritance2{
public static void main(String[] args){
Animal2 ani= new Dog2();
ani.eat();
}
}
class Animal2{
int age;
char gender;
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eating by Animal2 ");
}
public void sleep(){
}
}
class Dog2 extends Animal2{
//int age;
//char gender;
@Override
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eating by Dog2 ");
}
//public void sleep(){
//}
public void shout(){
}
}
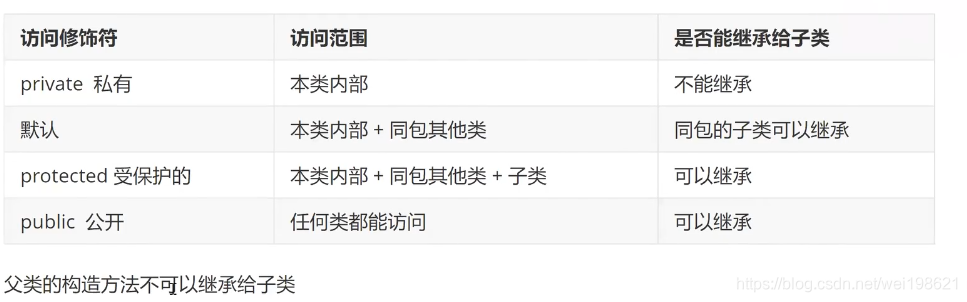
属性方法,访问符
private 本类
default 本类,同包
protected 本类,同包,子类
public all
P03-方法的覆盖 27:08
方法的覆盖
子类用自己的方法实现,替换父类的方法实现,覆盖==重写
P10-super关键字 1:07:04
视频地址
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xE41137Qy?p=10
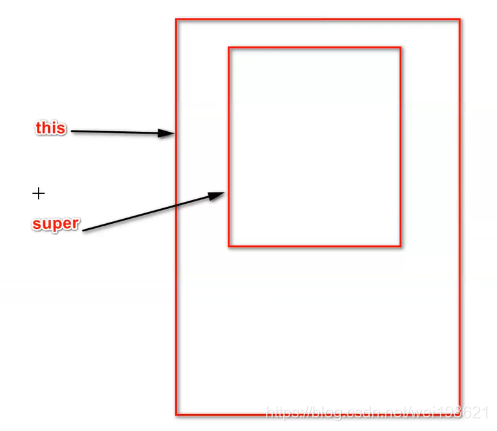
super
super 与 this 对照着学习,
this
-
super引用指向父类对象的属性、方法
super.m;
super.method(); -
super用在构造方法中,构造父类对象,必须是构造方法的第一条语句
- 程序员主动在构造方法第一行写了super()
- 程序员主动在构造方法第一行写了this() 真正执行的还是super();
- 构造方法的第一行 不是super 也不是this ,编译器自动为此构造方法添加super()
===> 任何一个类的构造方法,第一行一定是super()
最先执行的一定是 构造父类对象
构造子类对象,必须先构造父类对象 ,如果子类没有明确盗用父类哪个构造方法,用super调用无参的
编写类的时候,要给类添加无参构造函数
package day8;
public class TestSuper{
public static void main(String[] args){
//ClassB clsb=new ClassB();
//clsb.method();
new B();
System.out.println("----------");
new B(22,33);
}
}
class ClassA{
int m=10;
public void method(){
System.out.println("method by ClassA ");
}
}
class ClassB extends ClassA{
int m=20;
public void method(){
super.method(); // 子类 调用父类中被覆盖的方法
System.out.println("method by ClassB ");
}
public void print(){
System.out.println(this.m); //20
System.out.println(super.m); //10 子类 调用父类 被覆盖的属性
}
}
class A {
public A(){
System.out.println("A()");
}
public A(String s){
System.out.println("A(String)");
}
}
class B extends A {
// type1
public B(){
super(); // super 用在构造方法中,表示构造父类对象 // 利用父类的无参构造方法创建父类对象
System.out.println("B()");
}
// type2
public B(int a){
this(); // this() ; 表示 public B() .... ,所以明面上构造方法首行是this,实际构造方法首行还是super();
System.out.println("B(int)");
}
//type3 the method 2 is same
public B(int a,int b){
System.out.println("B(int,int)"); //构造方法首行,不是this ,也不是 super ,编译器自动给该狗脏方法添加一个super();
}
/*public B(int a,int b){
super();
System.out.println("hehe");
}*/
}
//父类标准写法 无参构造函数虽然系统自动提供,但是最好手动写
class Super{
public Super(){}
}
//子类标准写法 子类 无参构造函数 使用super调用父类无参构造函数 ;
class Sub extends Super{
public Sub(){
super();
}
}
// 程序员自己的写法
class MyClass{
int a=10;
int b;
String s="abc";
public MyClass(){
System.out.println("hehe");
}
}
// 编译器的执行顺序
class MyClassAfterCompile{
int a;
int b;
String s;
public MyClassAfterCompile(){
super();
a=10;
s="abc"
System.out.println("hehe");
}
}
/*
对象创建过程
0)分配堆空间 对象所需空间一次性分配好 ,属性赋值默认值
1) 创建父类对象 super();
2)初始化属性 a=10;
3)执行构造方法的剩余语句 System.out.println("hehe");
*/

//父类标准写法 无参构造函数虽然系统自动提供,但是最好手动写
class Super{
public Super(){}
}
//子类标准写法 子类 无参构造函数 使用super调用父类无参构造函数 ;
class Sub extends Super{
public Sub(){
super();
}
}
P11-单继承 16:49
一个类只能有一个直接父类
class C extends B
class B extends A
java 为什么要单继承,为了保证类之间的树状结构
P12-继承习题课 42:11
//super 用法一 用在构造方法中,设置父类属性
// super 用法二 普通方法中 ,用于调用父类方法
package day9;
public class TestEmployee{
public static void main(String[] args){
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int birthMonth;
public Employee(String name,int birthMonth){
super();
this.name=name;
this.birthMonth = birthMonth;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
if(this.birthMonth==month) return 100;
return 0;
}
}
class SalariedEmployee extends Employee{
private double salary;
public SalariedEmployee(String name,int birthMonth,double salary){
super(name,birthMonth); //super 用法一 用在构造方法中,设置父类属性
this.salary=salary;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
return this.salary +super.getSalary(month); // super 用法二 普通方法中 ,用于调用父类方法
}
}
class HourlyEmployee extends Employee{
private double salaryPerHour;
private int hours;
public HourlyEmployee(String name,int birthMonth,double salaryPerHour,int hours){
super(name,birthMonth);
this.salaryPerHour =salaryPerHour;
this.hours = hours;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
return this.salaryPerHour * hours +super.getSalary(month);
}
}
class SalesEmployee extends Employee{
private int sales;
private int rate;
public SalesEmployee(String name,int birthMonth,double sales,int rate){
super(name,birthMonth);
this.sales =sales;
this.rate = rate;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
return this.sales*this.rate +super.getSalary(month);
}
}
class BasedPlusSalesEmployee extends SalesEmployee{
private double basedSalary;
public SalesEmployee(String name,int birthMonth,double sales,int rate,double basedSalary){
super(name,birthMonth,sales,rate);
this.basedSalary =basedSalary;
}
public double getSalary(int month){
return this.basedSalary +super.getSalary(month);
}
}





 该博客围绕Java面向对象编程展开,介绍了面向对象概念、方法重载、对象创建与使用等对象相关知识,还阐述了面向对象三大特性,包括封装、继承关系、方法覆盖等,同时讲解了this和super关键字的使用,以及单继承的规则和相关习题。
该博客围绕Java面向对象编程展开,介绍了面向对象概念、方法重载、对象创建与使用等对象相关知识,还阐述了面向对象三大特性,包括封装、继承关系、方法覆盖等,同时讲解了this和super关键字的使用,以及单继承的规则和相关习题。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








