前言
我们都知道Vue 2中用的diff算法是双端Diff。而Vue 3的其中一个特性就是把底层的diff算法改成了快速Diff。
与字面意思一样,快速diff是目前已知的最快的diff算法。
本文将带大家解剖一下快速diff的原理。
预处理
在真正进入Diff之前,快速Diff会先执行一段”预处理“的前置操作。目的是先把可以直接排除的项去掉,降低diff的操作量。这个思路来自与unix等操作系统的文件内容diff,举个例子:
welcome to Guangdong, i hope you have a great travel.
welcome to Beijing, i hope you have a great travel.
上方的2行文中,在diff时会先从左边开始对比。一直到Guangdong和Beijing,发现不一样就停止。然后从右边开始找发现右边也是一直到Guangdong和Beijing才不同。因此,就找出了不同点Guangdong和Beijing。
预处理本质上是为了”对齐“,diff是一个繁琐的过程,涉及到新增,删除,改顺序,替换等操作。但无论是什么操作,最后新旧两组节点应该都要长度一样。即如果新比旧长,就要把新的多出部分新增补齐,如果是旧比新长,就要把旧的多出部分删除对齐。
Vue 3中的预处理
了解完上述的理论背景之后,我们来看一下在Vue 3中是怎么实现的。假设现在有下图的两组新旧节点组:
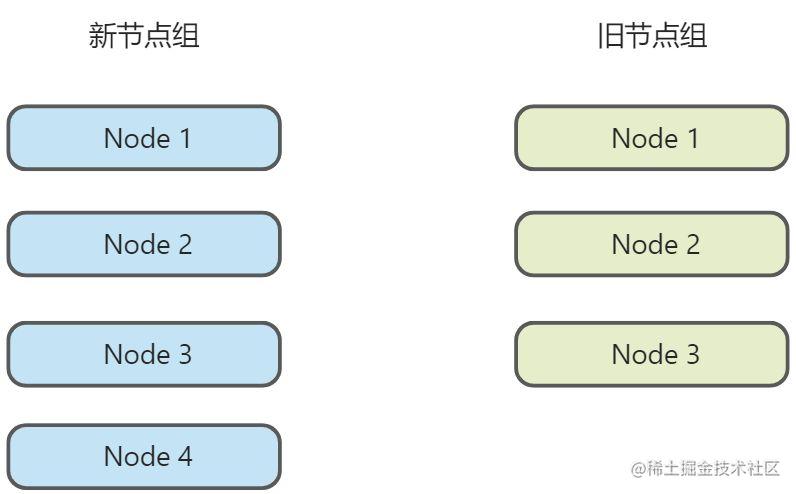
按照快速diff的预处理,我们会先扫描两组的前后内容:
function patchKeyedChildren(n1, n2, container) {// 拿到两组Children节点组const newChildren = n2.childrenconst oldChildren = n1.children// 用j定义头索引let j = 0let oldVNode = oldChildren[j]let newVNode = newChildren[j]// 开始扫描头部// while 循环向后遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {// 调用 patch 函数更新patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)j++oldVNode = oldChildren[j]newVNode = newChildren[j]}// ========================================// 开始处理尾部// 由于尾部跟头部不同,它们可能不一样。因此需要定义各自的索引let oldEnd = oldChildren.length - 1let newEnd = newChildren.length - 1oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]// 开始扫描尾部// while 循环向前遍历,直到遇到拥有不同 key 值的节点为止while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {// 调用 patch 函数更新patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)oldEnd--newEnd--oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]}// ...}
我把代码相关的描述写在注释中,大家可以看到现在我们通过j,oldEnd和newEnd作为索引,和两个while循环实现了两组节点组的头尾处理。处理完之后节点应该是这样的:
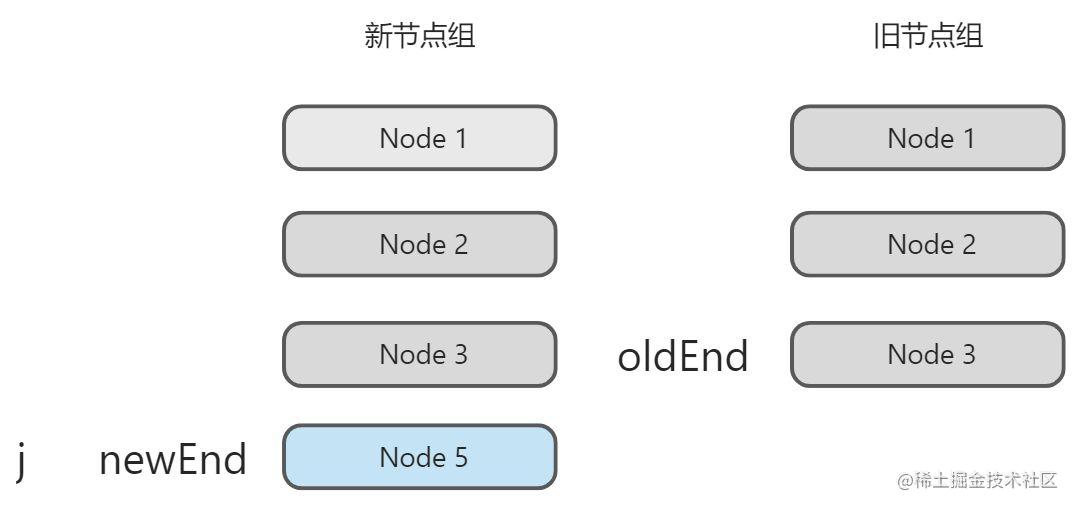
增删节点
根据这个思路,如果两个内容是一致的,在预处理阶段就能处理完了。但很多时候并不会那么顺利,如我们上面的例子中,新节点组中的Node5 就是一个新的节点,需要我们有一个插入新节点操作。同样,如果是旧节点组中有额外的节点,则需要一个删除旧节点的操作。
新增节点
那么,我们首先要知道什么条件下才应该插入节点。根据上图我们可以得出,当j大于oldEnd且小于等于newEnd,就应该新增节点。由此我们得出代码:
// 满足两者则需要新增节点
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {// 锚点的索引const anchorIndex = newEnd + 1// 锚点元素const anchor = anchorIndex < newChildren.length ? newChildren[anchorIndex].el : null// 采用 while 循环,调用 patch 函数逐个挂载新增的节点while (j <= newEnd) {patch(null, newChildren[j++], container, anchor)}
}
这里的patch实际上是mountElement,在patch源码中有以下处理:
function patch(n1, n2, container, anchor) {
// ...
if (!n1) {mountElement(n2, container, anchor)
} else {patchElement(n1, n2)
}
//...
}
删除节点
同理可得,当j大于newEnd且 j 小于等于 oldEnd时,则需要删除节点。可以对照下图:
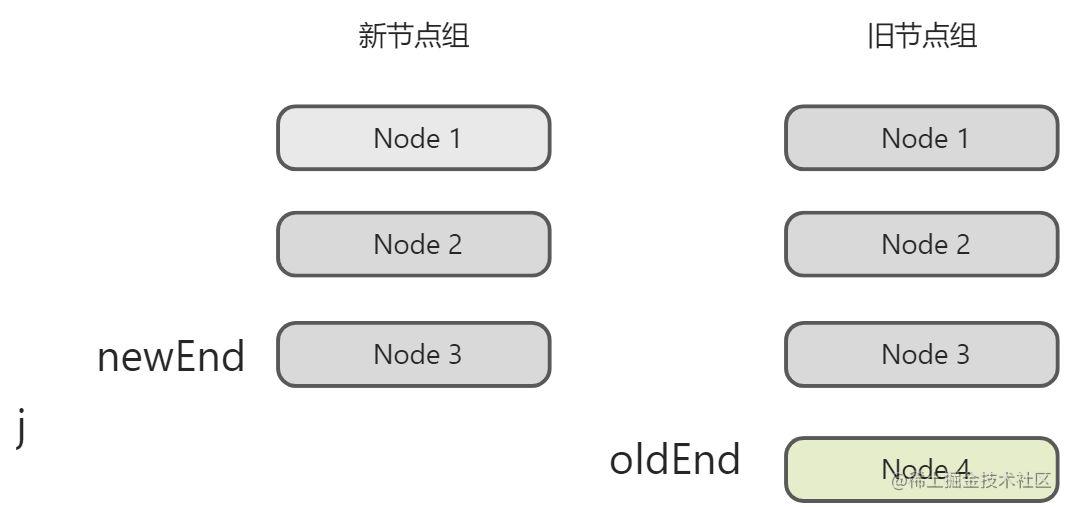
得出代码:
if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {// 省略新增节点的代码} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {// j -> oldEnd 之间的节点应该被卸载while (j <= oldEnd) {unmount(oldChildren[j++])}}
diff处理
然而,在实际开发中往往存在着更为复杂的情况。如下图,新旧两组的节点长度是一致的,但各不相同。
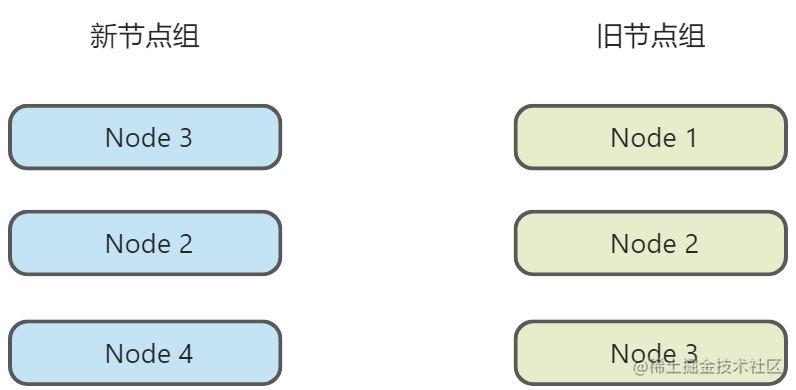
针对这种情况,如果是暴力地把3行替换显然不是最好的做法。我们最直观的感受是希望可以把Node 2和Node 3 放到对的位置,然后把Node4 替换Node 1。
快速Diff中使用了一个source数组来记录新节的位置索引,并用-1来代表需要新增的节点,整体代码如下:
// 新的一组子节点中剩余未处理节点的数量const count = newEnd - j + 1 // 构造 source 数组,并默认填充-1const source = new Array(count)source.fill(-1)// 索引从预处理后的j开始const oldStart = jconst newStart = j// moved用作标识是否需要重新排序let moved = false// pos记录上一个找到的节点的位置,用于辅助设置movedlet pos = 0// keyIndx是一个缓存表,记录新节点的key和索引的关系const keyIndex = {}// 先把新节点全部放keyIndxfor(let i = newStart; i <= newEnd; i++) {keyIndex[newChildren[i].key] = i}// 记录从旧节点中找到匹对的次数let patched = 0for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {oldVNode = oldChildren[i]if (patched < count) {// k是从keyIndex中找到的节点在新节点组中的索引const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {newVNode = newChildren[k]patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)patched++// 修改对应source中的项source[k - newStart] = i// 判断是否需要移动if (k < pos) {moved = true} else {pos = k}} else {// 没找到unmount(oldVNode)}} else {// 如果节点中的内容已经全都匹对过了,说明剩下的全是应该删除的unmount(oldVNode)}}
在遍历完旧节点之后,情况大致如下:
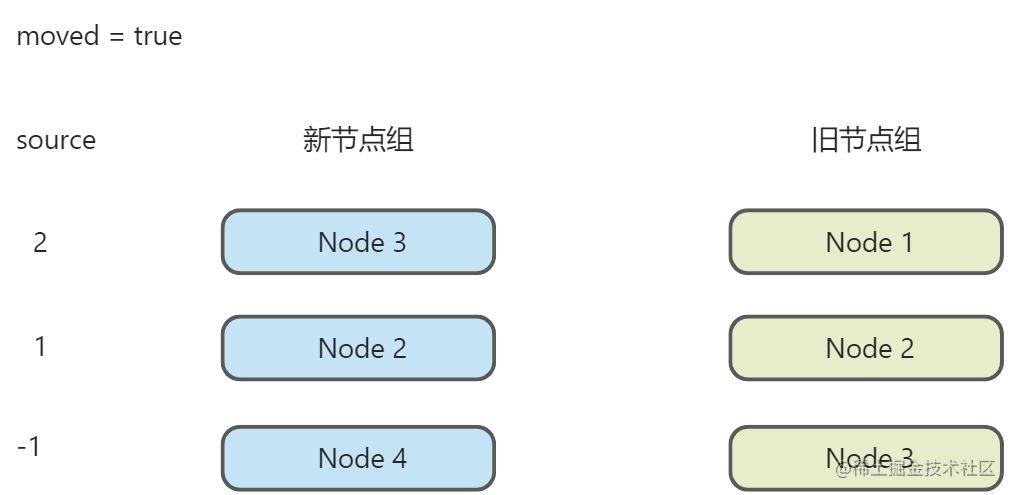
我们就可以根据moved判断出是否需要重选排序。排序的代码如下:
if (moved) {// lis是一个排序函数把source变成一个递增数组。const seq = lis(source)// s 指向最长递增子序列的最后一个值let s = seq.length - 1let i = count - 1for (i; i >= 0; i--) {if (source[i] === -1) {// 说明索引为 i 的节点是全新的节点,应该将其挂载// 该节点在新 children 中的真实位置索引const pos = i + newStartconst newVNode = newChildren[pos]// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引const nextPos = pos + 1// 锚点const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length? newChildren[nextPos].el: null// 挂载patch(null, newVNode, container, anchor)} else if (i !== seq[j]) {// 说明该节点需要移动// 该节点在新的一组子节点中的真实位置索引const pos = i + newStartconst newVNode = newChildren[pos]// 该节点下一个节点的位置索引const nextPos = pos + 1// 锚点const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length? newChildren[nextPos].el: null// 移动insert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)} else {// 当 i === seq[j] 时,说明该位置的节点不需要移动// 并让 s 指向下一个位置s--}}}
整体代码
删除注释,整体贴一遍代码。
function patchKeyedChildren(n1, n2, container) {const newChildren = n2.childrenconst oldChildren = n1.childrenlet j = 0let oldVNode = oldChildren[j]let newVNode = newChildren[j]while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)j++oldVNode = oldChildren[j]newVNode = newChildren[j]}let oldEnd = oldChildren.length - 1let newEnd = newChildren.length - 1oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]while (oldVNode.key === newVNode.key) {patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)oldEnd--newEnd--oldVNode = oldChildren[oldEnd]newVNode = newChildren[newEnd]}if (j > oldEnd && j <= newEnd) {const anchorIndex = newEnd + 1const anchor = anchorIndex < newChildren.length ? newChildren[anchorIndex].el : nullwhile (j <= newEnd) {patch(null, newChildren[j++], container, anchor)}} else if (j > newEnd && j <= oldEnd) {while (j <= oldEnd) {unmount(oldChildren[j++])}} else {const count = newEnd - j + 1 const source = new Array(count)source.fill(-1)const oldStart = jconst newStart = jlet moved = falselet pos = 0const keyIndex = {}for(let i = newStart; i <= newEnd; i++) {keyIndex[newChildren[i].key] = i}let patched = 0for(let i = oldStart; i <= oldEnd; i++) {oldVNode = oldChildren[i]if (patched < count) {const k = keyIndex[oldVNode.key]if (typeof k !== 'undefined') {newVNode = newChildren[k]patch(oldVNode, newVNode, container)patched++source[k - newStart] = iif (k < pos) {moved = true} else {pos = k}} else {unmount(oldVNode)}} else {unmount(oldVNode)}}if (moved) {const seq = lis(source)let s = seq.length - 1let i = count - 1for (i; i >= 0; i--) {if (source[i] === -1) {const pos = i + newStartconst newVNode = newChildren[pos]const nextPos = pos + 1const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length? newChildren[nextPos].el: nullpatch(null, newVNode, container, anchor)} else if (i !== seq[j]) {const pos = i + newStartconst newVNode = newChildren[pos]const nextPos = pos + 1const anchor = nextPos < newChildren.length? newChildren[nextPos].el: nullinsert(newVNode.el, container, anchor)} else {s--}}}}}
总结
可以看出快速Diff的核心代码并不多,逻辑也很容易理解。相比双端Diff,快速Diff需要处理的边际条件会更少。其中最大的特点就是预处理以及source数组的妙用。学习快速Diff不仅可以让我们对Vue3 有更深刻的了解,同时在我们的业务开发中,这些核心思考也为我们提供开发思路。
如果你觉得本文对你有一点帮助,麻烦给我点个赞吧~~ 谢谢
最后
为大家准备了一个前端资料包。包含54本,2.57G的前端相关电子书,《前端面试宝典(附答案和解析)》,难点、重点知识视频教程(全套)。



有需要的小伙伴,可以点击下方卡片领取,无偿分享





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








