如果使用过mybatis generator的人,你就知道了,这个插件自动生成example,就采用的是Builder模式来构建查询条件。
Joshua Bloch著的《Effective Java》中指示:遇到多个构造器参数时需要考虑构建器。
传统的方式是通过构造函数重载的方式,那么什么时候会出现问题呢?构造函数如果有5个参数还可以容忍,如果有10个参数,怎么办呢?不停的重载?
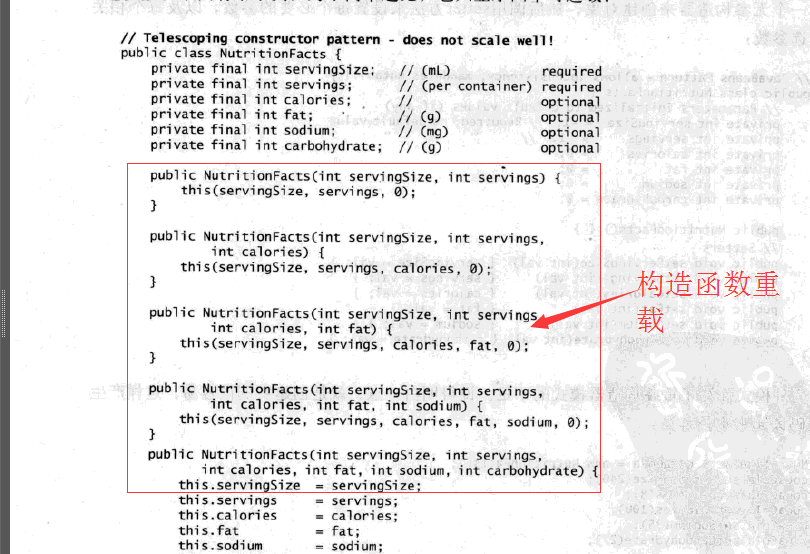
怎么解决这个问题,让它容易扩展呢?这里就采用了Builder模式.
看下面实例VmParams 这个JAVABean有很多属性,但是我们给他定义个private构造函数,也就是说VmParams我们不让它直接实例。那么谁来做呢?
- 找到build()方法,它返回的是VmParams对象,也就是说这个VmParams的构造交给了buid()
- 找到private VmParams构造函数,可以看到参数是builder。而VmParams的属性基本都是由builder赋值的,可以想象这些属性的set值在builder对象中肯定有一份。
- 果不其然,我们看静态内部类Builder,有相同的属性。
/**
* 模板参数
*
* @author dzm
*/
public class VmParams {
/**
* 包名路径
*/
private final String packagePath;
/**
* 模块路径
*/
private final String modulePath;
/**
* js路径
*/
private final String jsPath;
/**
* jsp路径
*/
private final String jspPath;
private Bean bean;
private final Annotation annotation;
/**
* 数据库连接配置
*/
private final JDBCConnectionConfiguration jdbcConfig;
/**
* 产生代码bean的列表
*/
private final List<String> beanNameList;
/**
* 子表清单
*/
private final List<String> subBeanNameList;
/**
* 子表类清单
*/
private List<ClassBean> subClassBeanList;
/**
* 订单头
*/
private final String mainBean;
/**
* 左表
*/
private final String left;
/**
* 右表
*/
private final String right;
/**
* 额外的参数
*/
private final Map<String, Object> extras;
private VmParams(Builder builder) {
//
this.annotation = builder.annotation;
this.packagePath = builder.packagePath;
this.modulePath = builder.modulePath;
this.jsPath = builder.jsPath;
this.jspPath = builder.jspPath;
this.jdbcConfig = builder.jdbcConfig;
this.beanNameList = builder.beanNameList;
this.subBeanNameList = builder.subBeanNameList;
this.mainBean = builder.mainBean;
this.left = builder.left;
this.right = builder.right;
this.extras = builder.extras;
_subBean2Class(subBeanNameList);
}
private void _subBean2Class(List<String> subBeanNameList){
if (!CheckEmptyUtil.isEmpty(subBeanNameList)){
this.subClassBeanList = new ArrayList<ClassBean>();
for (String subBeanName:this.subBeanNameList){
ClassBean classBean = new ClassBean();
classBean.setClassPath(subBeanName);
classBean.setBigName(StringUtil.getLastChar(subBeanName));
classBean.setLittleName(StringUtil.toLowerCaseFirstOne(classBean.getBigName()));
this.subClassBeanList .add(classBean);
}
}
}
/**
* 将参数交给构建器
*
* @author dzm
*/
public static class Builder {
private Annotation annotation;
private String packagePath;
private String modulePath;
private String jsPath;
private String jspPath;
private JDBCConnectionConfiguration jdbcConfig;
private List<String> beanNameList;
private List<String> subBeanNameList;
private String mainBean;
private String left;
private String right;
private Map<String, Object> extras;
public Builder() {
}
/**
* 添加额外的参数
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public Builder addExtra(String key, Object value) {
if (null == extras) {
extras = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
extras.put(key, value);
return this;
}
/**
* 添加subbean
*
* @param subBeanName
* @return
*/
public Builder addSubBeanName(String subBeanName) {
if (null == subBeanNameList) {
subBeanNameList = new ArrayList<String>();
}
subBeanNameList.add(subBeanName);
return this;
}
/**
* 添加bean
*
* @return
*/
public Builder addBeanName(String beanName) {
if (null == beanNameList) {
beanNameList = new ArrayList<String>();
}
beanNameList.add(beanName);
return this;
}
public Builder setAnnotation(Annotation annotation) {
this.annotation = annotation;
return this;
}
public Builder setPackagePath(String packagePath) {
this.packagePath = packagePath;
return this;
}
public Builder setModulePath(String modulePath) {
this.modulePath = modulePath;
return this;
}
public Builder setJsPath(String jsPath) {
this.jsPath = jsPath;
return this;
}
public Builder setJspPath(String jspPath) {
this.jspPath = jspPath;
return this;
}
public Builder setJdbcConfig(JDBCConnectionConfiguration jdbcConfig) {
this.jdbcConfig = jdbcConfig;
return this;
}
public Builder setMainBean(String mainBean) {
this.mainBean = mainBean;
return this;
}
public Builder setLeft(String left) {
this.left = left;
return this;
}
public Builder setRight(String right) {
this.right = right;
return this;
}
/**
* 构建参数
*
* @return
*/
public VmParams build() {
return new VmParams(this);
}
}
public Bean getBean() {
return bean;
}
public void setBean(Bean bean) {
this.bean = bean;
}
public Annotation getAnnotation() {
return annotation;
}
public String getPackagePath() {
return packagePath;
}
public String getModulePath() {
return modulePath;
}
public String getJsPath() {
return jsPath;
}
public String getJspPath() {
return jspPath;
}
public JDBCConnectionConfiguration getJdbcConfig() {
return jdbcConfig;
}
public List<String> getBeanNameList() {
return beanNameList;
}
public List<String> getSubBeanNameList() {
return subBeanNameList;
}
public String getMainBean() {
return mainBean;
}
public String getLeft() {
return left;
}
public String getRight() {
return right;
}
public Map<String, Object> getExtras() {
return extras;
}
public List<ClassBean> getSubClassBeanList() {
return subClassBeanList;
}
public void setSubClassBeanList(List<ClassBean> subClassBeanList) {
this.subClassBeanList = subClassBeanList;
}
}
为什么认为Builder模式对参数构建有很大优势呢,我们看看他怎么调用的.
参数构建都是Builder一直那么"."下去,如果增加参数,那么增加一个set就可以了,
是不是很方便。
VmParams vmParams = new VmParams.Builder()
.setJsPath(jsPath).setJspPath(jspPath).setModulePath(modulePath).setPackagePath(packagePath)
.setJdbcConfig(getJdbcConfig())
.addBeanName(SmsEmployee.class.getName())
.addBeanName(SmsEmployeeSchedule.class.getName())
.build();
虽然Builder模式构建对象优势很明显,开销姑且不论,对构造对象变得冗长。
因此它在有很多参数或者你认为将来可能会有很多参数的时候使用。
如果有人看过温昱的《一线架构师实践指南》,
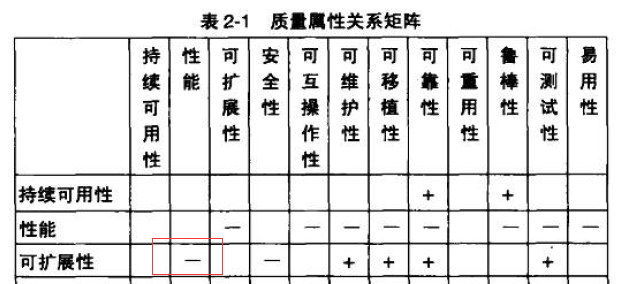
可扩展性与性能是冲突的,增加了可扩展性,那么势必就会牺牲性能。
在某性能十分注重性能地方,Builder模式可能有问题,但是一般做应用系统或者非大数据的系统,基本都合适。估计什么是十分注重性能,这个很难定义。所以尽可大胆使用。
如果你看过极光推送的sdk代码,他们用的里面也有Builder模式。有兴趣可以看看。





 本文详细介绍了Builder模式的应用场景和实现方式,特别是在参数众多时的优势。通过一个具体的JavaBean构造实例,展示了如何利用Builder模式简化对象创建过程。
本文详细介绍了Builder模式的应用场景和实现方式,特别是在参数众多时的优势。通过一个具体的JavaBean构造实例,展示了如何利用Builder模式简化对象创建过程。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










