目录
1. 网络爬虫
1.1 网络爬虫的合法性
1.2 网络爬虫前置技术
1.3 目标网站进行调研
1.3.1 robots.txt
1.3.2 网站所使用的技术
1.3.3 网站地图
1.3.4 估算网站大小
1.3.5 网站所有者
1.4 网络爬虫的通用流程
1.5 爬取脚本样例
《自然语言处理实战入门》 ---- 第二课 :网络爬虫简介 https://edu.youkuaiyun.com/course/play/20769/259542 本文为上述课程的讲稿
我们平时做自然语言处理,机器学习,都是希望能够有丰富的训练数据集,这样才能获取质量上乘的模型。在大数据时代,处理数据已经不再是是问题了,spark,hadoop ,Elastic search提供了海量甚至巨量的分布式数据处理方法。问题是没有数据怎么办?在合理合法 的前提下自然语言处理 的语料和其他机器学习模型训练数据需要的图片等等各类数据,我们其实都是可以通过网络爬虫的方式进行积累的。
1.网络爬虫
网络爬虫(Web Spider)又称网络蜘蛛、网络机器人,是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本。
网络爬虫按照系统结构和实现技术,大致可分为一下几种类型:
通用网络爬虫:就是尽可能大的网络覆盖率,如 搜索引擎(百度、雅虎和谷歌等…)。
聚焦网络爬虫:有目标性,选择性地访问万维网来爬取信息。
增量式网络爬虫:只爬取新产生的或者已经更新的页面信息。特点:耗费少,难度大
深层网络爬虫:通过提交一些关键字才能获取的Web页面,如登录或注册后访问的页面。
注:实际工作中通常是几种爬虫技术结合实现。
1.1 网络爬虫的合法性
网络爬虫及其使用时法律所允许的内容仍然处于建设当中。
爬虫所带来风险主要体现在以下3个方面:
1、违反网站意愿,例如网站采取反爬措施后,强行突破其反爬措施;2、爬虫干扰了被访问网站的正常运营;3、爬虫抓取了受到法律保护的特定类型的数据或信息。
那么作为爬虫开发者,如何在使用爬虫时避免进局子的厄运呢?
1、严格遵守网站设置的robots协议;2、在规避反爬虫措施的同时,需要优化自己的代码,避免干扰被访问网站的正常运行;3、在设置抓取策略时,应注意编码抓取视频、音乐等可能构成作品的数据,或者针对某些特定网站批量抓取其中的用户生成内容;4、在使用、传播抓取到的信息时,应审查所抓取的内容,如发现属于用户的个人信息、隐私或者他人的商业秘密的,应及时停止并删除。
1.2 网络爬虫前置技术
常用爬虫库:
urllib
requests
selenium
scrapy爬虫框架
其中,urllib、requests用来获取URL对应的原始响应内容;而selenium通过加载浏览器驱动,获取浏览器渲染之后的响应内容,模拟程度更高。考虑效率、当然能使用urllib、requests等解决的尽量不用selenium,因为后者因需要加载浏览器而导致效率较低。
在数据解析方面相应的库包括:
lxml
html5lib
html.parser
beautifulsoup4
re
pyquery
lxml 兼容html 和xml 都可以解析,底层用c语言编写,解析速度很快 html5lib兼容性非常好、能够像web浏览器一样解析html页面、Creates valid HTML5 html.parser 是python自带的解析器
beautifulsoup4 一般是将html 解析为soup文档,一般是网页解析首选。非结构化的信息提取用re ,正则表达式 PyQuery 是 Python 仿照 jQuery 的严格实现。语法与 jQuery 几乎完全相同
对于数据解析,主要是从相应页面里提取所需的数据,常用方法有:
xpath路径表达式
CSS选择器
正则表达式
其中,xpath路径表达式、CSS选择器主要用于提取结构化的数据。而正则表达式主要用于提取非结构化的数据。
数据的存储:MySQL、MongoDB、Redis
对于数据抓取,涉及的过程主要是模拟浏览器向服务器发送构造好的http请求,常见类型有:get/post。
1.3 目标网站进行调研
下面我们以csdn 为例进行目标网站的调研
1.3.1 robots.txt
Robots协议(也称为爬虫协议、机器人协议等)的全称是“网络爬虫排除标准”(Robots Exclusion Protocol),网站通过Robots协议告诉搜索引擎哪些页面可以抓取,哪些页面不能抓取。
https://www.youkuaiyun.com/robots.txt
User-agent: *
Disallow: /scripts
Disallow: /public
Disallow: /css/
Disallow: /images/
Disallow: /content/
Disallow: /ui/
Disallow: /js/
Disallow: /scripts/
Disallow: /article_preview.html*
Disallow: /tag/
Disallow: /*?*
Sitemap: http://www.youkuaiyun.com/article/sitemap.txt
上述定义的含义为,可以使用用户代理,但是不要爬取一下罗列的这些链接。
1.3.2 网站所使用的技术
1. 网站是通过什么样的技术搭建的
builtwith 网站技术信息查询工具,检查网站构建的技术类型。
import builtwith
builtwith.parse("https://www.youkuaiyun.com")
{
'web-servers': ['OpenResty', 'Nginx'],
'programming-languages': ['Lua'],
'javascript-frameworks': ['Modernizr', 'jQuery'],
'web-frameworks': ['Twitter Bootstrap']
}
2. 网站是通过什么样的技术开发的
wappalyzer大名鼎鼎的网站技术分析插件基于Node.js构建,可以分析目标网站所采用的平台构架、网站环境、服务器配置环境、JavaScript框架、编程语言等参数
docker pull wappalyzer/cli
docker run wappalyzer/cli https://www.youkuaiyun.com
{
"urls": [
"https://www.youkuaiyun.com/"
],
"applications": [
{
"name": "Modernizr",
"confidence": "100",
"version": "2.8.3",
"icon": "Modernizr.svg",
"website": "https://modernizr.com",
"categories": [
{
"12": "JavaScript Frameworks"
}
]
},
{
"name": "OpenResty",
"confidence": "100",
"version": "",
"icon": "OpenResty.png",
"website": "http://openresty.org",
"categories": [
{
"22": "Web Servers"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Bootstrap",
"confidence": "100",
"version": "",
"icon": "Bootstrap.svg",
"website": "https://getbootstrap.com",
"categories": [
{
"18": "Web Frameworks"
}
]
},
{
"name": "jQuery",
"confidence": "100",
"version": "1.9.1",
"icon": "jQuery.svg",
"website": "https://jquery.com",
"categories": [
{
"12": "JavaScript Frameworks"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Nginx",
"confidence": "0",
"version": "",
"icon": "Nginx.svg",
"website": "http://nginx.org/en",
"categories": [
{
"22": "Web Servers"
}
]
},
{
"name": "Lua",
"confidence": "0",
"version": "",
"icon": "Lua.png",
"website": "http://www.lua.org",
"categories": [
{
"27": "Programming Languages"
}
]
}
],
"meta": {
"language": null
}
}
detectem检查网站构建的技术类型,旨在成为wappalyzer的python版本
docker pull scrapinghub/splash
pip install detectem
det https://www.youkuaiyun.com/
[{'name': 'jquery', 'version': '1.9.1'}, {'name': 'jquery', 'version': '1.12.4'}, {'name': 'modernizr', 'version': '2.8.3'}]
1.3.3 网站地图
主要用途
1.为搜索引擎蜘蛛提供可以浏览整个网站的链接简单的体现出网站的整体框架出来给搜索引擎看;2.为搜索引擎蜘蛛提供一些链接,指向动态页面或者采用其他方法比较难以到达的页面;3.作为一种潜在的着陆页面,可以为搜索流量进行优化:如果访问者试图访问网站所在域内并不存在的URL,那么这个访问者就会被转到“无法找到文件”的错误页面,而网站地图可以作为该页面的“准”内容。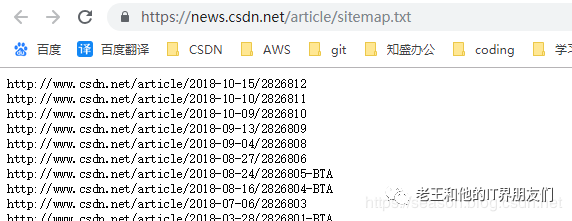
1.3.4 估算网站大小
使用google
site:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wangyaninglm
google 的爬虫估算我的博客页面数量在500左右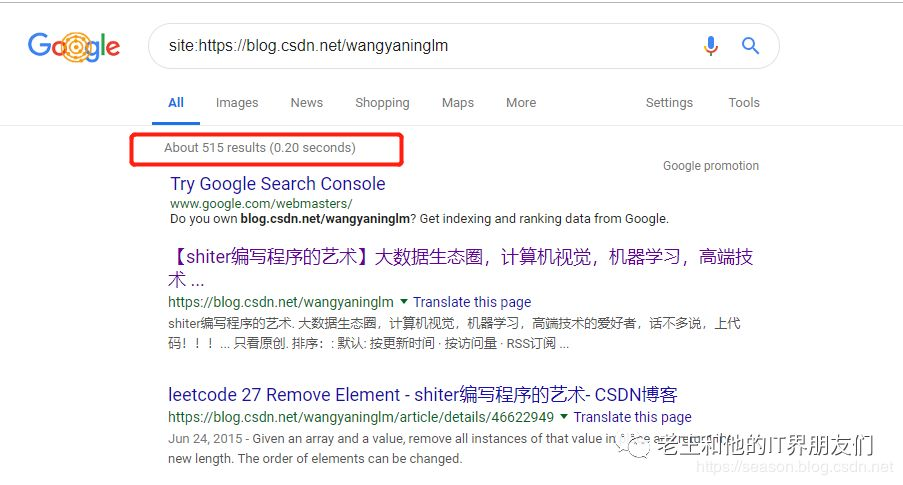
1.3.5 网站所有者
我们可以看到csdn 的域名应该是部署绑定在阿里云上面的,这个域名1999年就注册了,可以说相当早了
>>> print(whois.whois('www.youkuaiyun.com'))
{
"domain_name": [
"youkuaiyun.com",
"youkuaiyun.com"
],
"registrar": "Alibaba Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd.",
"whois_server": "grs-whois.hichina.com",
"referral_url": null,
"updated_date": "2019-03-12 10:56:11",
"creation_date": "1999-03-11 05:00:00",
"expiration_date": "2021-03-11 04:00:00",
"name_servers": [
"VIP3.ALIDNS.COM",
"VIP4.ALIDNS.COM"
],
"status": [
"clientTransferProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientTransferProhibited",
"clientUpdateProhibited https://icann.org/epp#clientUpdateProhibited"
],
"emails": "DomainAbuse@service.aliyun.com",
"dnssec": "unsigned",
"name": null,
"org": null,
"address": null,
"city": null,
"state": "bei jing",
"zipcode": null,
"country": null
}
1.4 网络爬虫的通用流程
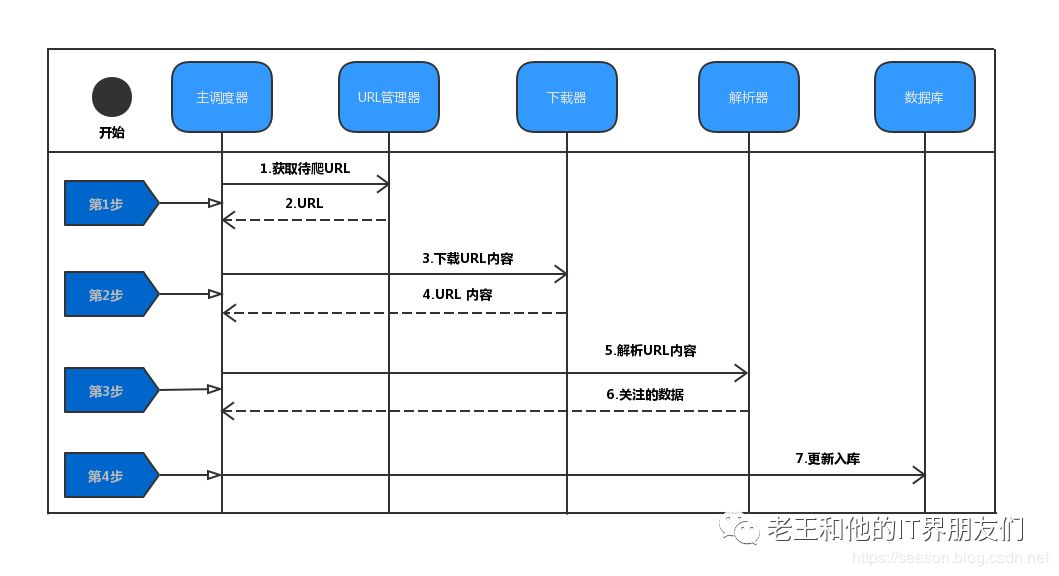
1.5 爬取脚本样例
主要步骤:
1.重试下载 互联网工程任务组(Internet Engineering Task Force)定义了Http 错误的完整列表。当download 函数遇到5xx错误码时,会递归调用函数自身进行重试。
2.设置用户代理 为了让下载网站更加可靠,避免封禁我们自己ip,避免给爬取的网站过大压力 等原因,需要设置用户代理
import re
import urllib.request
from urllib import robotparser
from urllib.parse import urljoin
from urllib.error import URLError, HTTPError, ContentTooShortError
from chp1.throttle import Throttle
def download(url, num_retries=2, user_agent='wswp', charset='utf-8', proxy=None):
""" Download a given URL and return the page content
args:
url (str): URL
kwargs:
user_agent (str): user agent (default: wswp)
charset (str): charset if website does not include one in headers
proxy (str): proxy url, ex 'http://IP' (default: None)
num_retries (int): number of retries if a 5xx error is seen (default: 2)
"""
print('Downloading:', url)
request = urllib.request.Request(url)
request.add_header('User-agent', user_agent)
try:
if proxy:
proxy_support = urllib.request.ProxyHandler({'http': proxy})
opener = urllib.request.build_opener(proxy_support)
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
resp = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
cs = resp.headers.get_content_charset()
if not cs:
cs = charset
html = resp.read().decode(cs)
except (URLError, HTTPError, ContentTooShortError) as e:
print('Download error:', e.reason)
html = None
if num_retries > 0:
if hasattr(e, 'code') and 500 <= e.code < 600:
# recursively retry 5xx HTTP errors
return download(url, num_retries - 1)
return html
def get_robots_parser(robots_url):
" Return the robots parser object using the robots_url "
rp = robotparser.RobotFileParser()
rp.set_url(robots_url)
rp.read()
return rp
def get_links(html):
" Return a list of links (using simple regex matching) from the html content "
# a regular expression to extract all links from the webpage
webpage_regex = re.compile("""<a[^>]+href=["'](.*?)["']""", re.IGNORECASE)
# list of all links from the webpage
return webpage_regex.findall(html)
def link_crawler(start_url, link_regex, robots_url=None, user_agent='wswp',
proxy=None, delay=3, max_depth=4):
""" Crawl from the given start URL following links matched by link_regex. In the current
implementation, we do not actually scrapy any information.
args:
start_url (str): web site to start crawl
link_regex (str): regex to match for links
kwargs:
robots_url (str): url of the site's robots.txt (default: start_url + /robots.txt)
user_agent (str): user agent (default: wswp)
proxy (str): proxy url, ex 'http://IP' (default: None)
delay (int): seconds to throttle between requests to one domain (default: 3)
max_depth (int): maximum crawl depth (to avoid traps) (default: 4)
"""
crawl_queue = [start_url]
# keep track which URL's have seen before
seen = {}
if not robots_url:
robots_url = '{}/robots.txt'.format(start_url)
rp = get_robots_parser(robots_url)
throttle = Throttle(delay)
while crawl_queue:
url = crawl_queue.pop()
# check url passes robots.txt restrictions
if rp.can_fetch(user_agent, url):
depth = seen.get(url, 0)
if depth == max_depth:
print('Skipping %s due to depth' % url)
continue
throttle.wait(url)
html = download(url, user_agent=user_agent, proxy=proxy)
if not html:
continue
# TODO: add actual data scraping here
# filter for links matching our regular expression
for link in get_links(html):
if re.match(link_regex, link):
abs_link = urljoin(start_url, link)
if abs_link not in seen:
seen[abs_link] = depth + 1
crawl_queue.append(abs_link)
else:
print('Blocked by robots.txt:', url)
使用requests的高级链接爬虫优点:
1.请求本身status_code 包含状态码 2.不需要再测试字符编码 3.对于无法处理的URL或者超时等罕见情况,都由RequestException 处理
import re
from urllib import robotparser
from urllib.parse import urljoin
import requests
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import time
class Throttle:
""" Add a delay between downloads to the same domain
"""
def __init__(self, delay):
# amount of delay between downloads for each domain
self.delay = delay
# timestamp of when a domain was last accessed
self.domains = {}
def wait(self, url):
domain = urlparse(url).netloc
last_accessed = self.domains.get(domain)
if self.delay > 0 and last_accessed is not None:
sleep_secs = self.delay - (time.time() - last_accessed)
if sleep_secs > 0:
# domain has been accessed recently
# so need to sleep
time.sleep(sleep_secs)
# update the last accessed time
self.domains[domain] = time.time()
def download(url, num_retries=2, user_agent='wswp', proxies=None):
""" Download a given URL and return the page content
args:
url (str): URL
kwargs:
user_agent (str): user agent (default: wswp)
proxies (dict): proxy dict w/ keys 'http' and 'https', values
are strs (i.e. 'http(s)://IP') (default: None)
num_retries (int): # of retries if a 5xx error is seen (default: 2)
"""
print('Downloading:', url)
headers = {'User-Agent': user_agent}
try:
resp = requests.get(url, headers=headers, proxies=proxies)
html = resp.text
if resp.status_code >= 400:
print('Download error:', resp.text)
html = None
if num_retries and 500 <= resp.status_code < 600:
# recursively retry 5xx HTTP errors
return download(url, num_retries - 1)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print('Download error:', e)
html = None
return html
def get_robots_parser(robots_url):
" Return the robots parser object using the robots_url "
rp = robotparser.RobotFileParser()
rp.set_url(robots_url)
rp.read()
return rp
def get_links(html):
""" Return a list of links (using simple regex matching)
from the html content """
# a regular expression to extract all links from the webpage
webpage_regex = re.compile("""<a[^>]+href=["'](.*?)["']""", re.IGNORECASE)
# list of all links from the webpage
return webpage_regex.findall(html)
def link_crawler(start_url, link_regex, robots_url=None, user_agent='wswp',
proxies=None, delay=3, max_depth=4):
""" Crawl from the given start URL following links matched by link_regex.
In the current implementation, we do not actually scrape any information.
args:
start_url (str): web site to start crawl
link_regex (str): regex to match for links
kwargs:
robots_url (str): url of the site's robots.txt
(default: start_url + /robots.txt)
user_agent (str): user agent (default: wswp)
proxies (dict): proxy dict w/ keys 'http' and 'https', values
are strs (i.e. 'http(s)://IP') (default: None)
delay (int): seconds to throttle between requests
to one domain (default: 3)
max_depth (int): maximum crawl depth (to avoid traps) (default: 4)
"""
crawl_queue = [start_url]
# keep track which URL's have seen before
seen = {}
if not robots_url:
robots_url = '{}/robots.txt'.format(start_url)
rp = get_robots_parser(robots_url)
throttle = Throttle(delay)
while crawl_queue:
url = crawl_queue.pop()
# check url passes robots.txt restrictions
if rp.can_fetch(user_agent, url):
depth = seen.get(url, 0)
if depth == max_depth:
print('Skipping %s due to depth' % url)
continue
throttle.wait(url)
html = download(url, user_agent=user_agent, proxies=proxies)
if not html:
continue
# TODO: add actual data scraping here
# filter for links matching our regular expression
for link in get_links(html):
if re.match(link_regex, link):
abs_link = urljoin(start_url, link)
if abs_link not in seen:
seen[abs_link] = depth + 1
crawl_queue.append(abs_link)
else:
print('Blocked by robots.txt:', url)
def main():
'''
主函数,测试网页下载
:return:
'''
url = 'https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wangyaninglm/article/details/51912766'
print(download(url))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
参考文献
1.深入探讨:爬虫究竟是合法还是违法的?
2.6大项目快速掌握Python爬虫与反爬虫应用
P.S 号外号外,公众号听众800人了,感谢各位厚爱!
这一期给大家推送一些最近看到的好玩的文章,再次感谢。





















 2428
2428

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










