策略模式:
定义一系列算法,把他们一个个封装起来,并使他们可以互相替换(不同情况下处理方式需改变时,替换处理算法)。该模式的算法可以独立于使用它的程序代码而变化(扩展子类化算法)。
UML关系类图
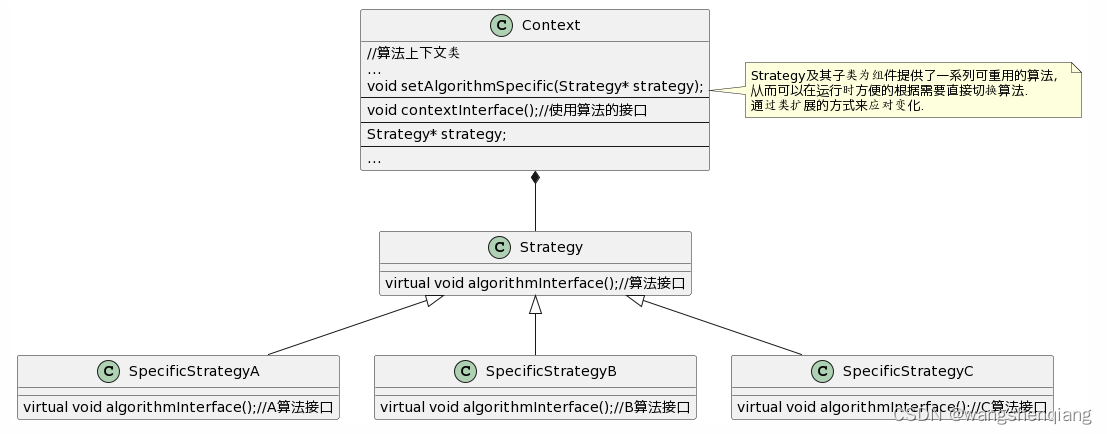
(代码和类图略有出入,因为第一稿的指针使用的是原始方法,当前使用的C++11以上版本的智能指针,避免直接new创建堆对象,减少内存泄漏的风险)。
使用算法的类 WorkContext
workcontext.h
#ifndef WORKCONTEXT_H
#define WORKCONTEXT_H
#include <memory>
class BaseStrategy;
using BaseStrategy_ptr = std::shared_ptr<BaseStrategy>;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/// \brief The WorkContext class
/// 策略模式
/// 定义一系列算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并使它们可以互相替换(变化)。
/// 该模式是的算法可以独立于使用它的程序代码(WorkContext)而变化(扩展,子类化)。
/// 使用算法的WorkContext类是稳定的,而不同的算法可以独立实现。
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class WorkContext
{
public:
WorkContext();
~WorkContext();
//也可以作为类构造的参数,这里单独用一个接口进行设置
void setAlgorithm(BaseStrategy_ptr algorithm);
void working();
private:
BaseStrategy_ptr m_algorithm;
};
#endif // WORKCONTEXT_H
workcontext.cpp
#include "workcontext.h"
#include "basestrategy.h"
#include <iostream>
WorkContext::WorkContext()
: m_algorithm(nullptr)
{
}
WorkContext::~WorkContext()
{
std::cout << "WorkContext::~WorkContext" << std::endl;
}
void WorkContext::setAlgorithm(BaseStrategy_ptr algorithm)
{
m_algorithm = algorithm;
}
void WorkContext::working()
{
if(m_algorithm) m_algorithm->algorithmInterface();
}
算法抽象类 BaseStrategy
basestrategy.h
#ifndef BASESTRATEGY_H
#define BASESTRATEGY_H
class BaseStrategy
{
public:
BaseStrategy();
virtual ~BaseStrategy();
virtual void algorithmInterface();
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class SpecificStrategyA : public BaseStrategy
{
public:
SpecificStrategyA();
virtual ~SpecificStrategyA();
virtual void algorithmInterface();
};
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
class SpecificStrategyB : public BaseStrategy
{
public:
SpecificStrategyB();
virtual ~SpecificStrategyB();
virtual void algorithmInterface();
};
#endif // BASESTRATEGY_H
basestrategy.cpp
#include "basestrategy.h"
#include <iostream>
BaseStrategy::BaseStrategy(){
}
BaseStrategy::~BaseStrategy(){
}
void BaseStrategy::algorithmInterface(){
std::cout << "BaseStrategy::algorithmInterface" << std::endl;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SpecificStrategyA::SpecificStrategyA()
: BaseStrategy(){
}
SpecificStrategyA::~SpecificStrategyA(){
std::cout << "SpecificStrategyA::~SpecificStrategyA" << std::endl;
}
void SpecificStrategyA::algorithmInterface(){
std::cout << "SpecificStrategyA::algorithmInterface" << std::endl;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
SpecificStrategyB::SpecificStrategyB()
: BaseStrategy(){
}
SpecificStrategyB::~SpecificStrategyB(){
std::cout << "SpecificStrategyB::~SpecificStrategyB" << std::endl;
}
void SpecificStrategyB::algorithmInterface(){
std::cout << "SpecificStrategyB::algorithmInterface" << std::endl;
}
main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include "workcontext.h"
#include "basestrategy.h"
#include <memory>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
{
std::shared_ptr<WorkContext> worker = std::make_shared<WorkContext>();
{//第一版需求只支持SpecificStrategyA
std::shared_ptr<BaseStrategy> stategy = std::make_shared<SpecificStrategyA>();
worker->setAlgorithm(stategy);
worker->working();
}
{//第二版需求:既需要支持SpecificStrategyA,又需要支持SpecificStrategyB
std::shared_ptr<BaseStrategy> stategyA = std::make_shared<SpecificStrategyA>();
worker->setAlgorithm(stategyA);
worker->working();
std::shared_ptr<BaseStrategy> stategyB = std::make_shared<SpecificStrategyB>();
worker->setAlgorithm(stategyB);
worker->working();
}
}
return a.exec();
}
主要应用在根据不同条件(未来可能存在其他不确定条件),进行不同操作的代码;使用模式的方法进行类扩展,从而避免直接进行代码改动。
遵循:对修改封闭,对扩展开放的原则。





 文章介绍了策略模式如何封装算法,允许在运行时替换不同处理方式,通过BaseStrategy和其子类如SpecificStrategyA、SpecificStrategyB实现。展示了如何在WorkContext中使用这些策略,并使用C++11智能指针管理内存,遵循封闭-扩展原则。
文章介绍了策略模式如何封装算法,允许在运行时替换不同处理方式,通过BaseStrategy和其子类如SpecificStrategyA、SpecificStrategyB实现。展示了如何在WorkContext中使用这些策略,并使用C++11智能指针管理内存,遵循封闭-扩展原则。
















&spm=1001.2101.3001.5002&articleId=133359032&d=1&t=3&u=4134145829dc424e9aff66f6900b3cab)
 1451
1451

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








