转载地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangfei/p/5229434.html
在做自动化测试时,数据驱动是一个很重要的概念,当数据与脚本分离后,面对茫茫多的数据,管理数据又成了一个大问题,而数据源又可能面对多个,就跟在开发过程中,有时候要连接MYSQL,有时候又要连接SQL SERVER一样,如何做到快速切换?下面的示例中,我们将从一个数据源开始,一步步的演示下去:
一. 用外部文件做数据驱动的基本写法
1.1 我们在做数据驱动时,把数据存储在JAVA的属性文件中:data.properties
|
1
2
|
username=testpassword=123456 |
1.2 解析properties文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public
class PropertiesHandler { private
static Properties loadPropertiesFile(String filePath){ Properties p =
new Properties(); InputStream in =
null; try
{ in =
new FileInputStream(new
File(filePath)); p.load(in); }
catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try
{ if(in !=
null){ in.close(); } }
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return
p; } /** * 将property转换成Map * @param key * @return */ @SuppressWarnings({
"rawtypes",
"unchecked" }) public
static Map<String, String> getPropertyData(String filePath){ try{ return
new HashMap<String, String>((Map)PropertiesHandler.loadPropertiesFile(filePath)); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return
new HashMap<String, String>(); } public
static void
main(String[] args) { System.out.println(PropertiesHandler.getPropertyData("file/data.properties")); }} |
1.3 写一个TestBase类,里面用来存放TestNg的DataProvider
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public
class TestBase { @DataProvider public
Object[][] dataProvider(){ return
this.getTestData(); } private
Object[][] getTestData(){ PropertiesData testData =
new PropertiesData(); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object; } } |
可以看出,我只要有一个类,能够提供出一个数据类型为:List<Map<String, String>>的数据对象,就能够转换成Object[][]的二维数组,就能够提供给测试方法运行了。
1.4 在1.3中出现了一个PropertiesData类,现在来实现这个类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
class PropertiesData { public
List<Map<String, String>> getTestMethodData(){ List<Map<String, String>> list =
new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>(); list.add(PropertiesHandler.getPropertyData("file/data.properties")); return
list; } } |
1.5 以上中有数据解析类,有数据加载类,有数据提供的基础类,于是我们再结合测试方法,把这三个基础类给融合在一起,就形成了一个外部文件来做数据源的完整示例了:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
class TestDemo extends
TestBase{ @Test(dataProvider="dataProvider") public
void testDemo(Map<String, String> param){ System.out.println(param.get("username")); System.out.println(param.get("password")); } } |
1.6 以上的运行结果输出为:
二. 属性文件换成txt文件的实现
2.1 如果有多个数据源,我想用txt来存放数据,txt里面存放一个json串:data.txt
|
1
2
3
4
|
{ "username":"test", "password":"123456"} |
2.2 读出这个txt文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
public
class FileUtils { public
static String readFile(String fileName) { InputStream is =
null; StringBuffer sb =
new StringBuffer(); try
{ is =
new FileInputStream(fileName); byte[] byteBuffer =
new byte[is.available()]; int
read = 0; while((read = is.read(byteBuffer)) != -1){ sb.append(new
String(byteBuffer, 0, read)); } }
catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try
{ if(is!=null){ is.close(); } }
catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return
sb.toString(); } public
static void
main(String[] args) { System.out.println(FileUtils.readFile("file/data.txt")); } } |
2.3 将读取出来的JSON串进行解析(这里需要用到一个JAR包,gson.jar)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public
class TxtData { public
List<Map<String, String>> getTestMethodData(){ List<Map<String, String>> list =
new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>(); String data = FileUtils.readFile("file/data.txt"); Gson gson =
new Gson(); Map<String, String> dataMap = gson.fromJson(data,
new TypeToken<Map<String, String>>(){}.getType()); list.add(dataMap); return
list; } } |
2.4 将TxtData类给用上,即将TestBase类里的用到PropertiesData类的地方换成TxtData类即可
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
Object[][] getTestData(){ TxtData testData =
new TxtData(); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object;} |
2.5 运行TestDemo测试类后,发现结果与之前用PropertiesData类出现的结果一模一样。
三. 用接口来实现
3.1 上面的两种数据源,在把数据源里的内容给加载出来且加载出来的数据类型为:List<Map<String, String>>后,只需要把TestBase类里的数据源加载类给替换一个即可,那如此一来,我们可以利用JAVA里面的interface来重构我们的代码,首先当然得要有一个interface
|
1
2
3
|
public
interface DataInterface { public
List<Map<String, String>> getTestMethodData();} |
3.2 我们的PropertiesData类与TxtData类当然要实现这个接口了
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public
class PropertiesData implements
DataInterface{ public
List<Map<String, String>> getTestMethodData(){ List<Map<String, String>> list =
new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>(); list.add(PropertiesHandler.getPropertyData("file/data.properties")); return
list; } } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public
class TxtData implements
DataInterface{ public
List<Map<String, String>> getTestMethodData(){ List<Map<String, String>> list =
new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>(); String data = FileUtils.readFile("file/data.txt"); Gson gson =
new Gson(); Map<String, String> dataMap = gson.fromJson(data,
new TypeToken<Map<String, String>>(){}.getType()); list.add(dataMap); return
list; } } |
3.3 然后在TestBase里就要有所改变了,即产生数据加载的类对象要发生改变,我们在TestBase里新加一个方法(这是产生类对象的一种新的方式)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
DataInterface getDataInstance(String key){ DataInterface data =
null; try
{ data = (DataInterface) Class.forName(key).newInstance(); }
catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return
data;} |
3.4 TestBase类里的getTestData()方法就要重新的改变一下了
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
Object[][] getTestData(){ DataInterface testData =
this.getDataInstance("com.test.testdata.PropertiesData"); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object;} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
Object[][] getTestData(){ DataInterface testData =
this.getDataInstance("com.test.testdata.TxtData"); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object;} |
3.5 再次运行TestDemo,即可发现结果仍然是一样的。所以,这时候只需要改变数据加载类的路径即可了。
四. 将数据加载类的路径可配置化
4.1 这时候,我们就可以想着把数据加载类的路径写在配置文件中了config.properties
|
1
|
DataSource=com.test.testdata.TxtData |
4.2 加载config文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public
class Config { public
static String DATA_SOURCE; static{ Map<String, String> map = PropertiesHandler.getPropertyData("config/config.properties"); DATA_SOURCE = map.get("DataSource"); } } |
4.3 将TestBase里的getTestData()方法再改进一下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
private
Object[][] getTestData(){ DataInterface testData =
this.getDataInstance(Config.DATA_SOURCE); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object;} |
4.4 再次运行TestDemo类,结果仍然是一样的。到此为止,我们已实现了去更改配置文件里面的内容,来选择加载数据源。
五. 多数据源的切换
5.1 如果一个测试类里有两个测试方法,那么在配置文件里配置好数据源后,就表示这两个测试方法都将会加载同样的数据源,但如果我们希望一个测试方法用属性文件的数据源,另一个方法用TXT的数据源,这个如何办?也就是需要实现在全局配置化后,局部可再次选择数据源。我将会利用到JAVA里的注解,来实现。所以我们先定义一个DataSource的注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public
@interface DataSource { String value();} |
5.2 解析该注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public
class DataSources { public
static String getDataSource(Method method){ DataSource ds = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class); if(ds !=
null){ return
ds.value(); } return
null; } } |
5.3 该注解的使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@DataSource("com.test.testdata.PropertiesData")@Test(dataProvider="dataProvider")public
void testDemo(Map<String, String> param){ System.out.println(param.get("username")); System.out.println(param.get("password"));} |
5.4 TestBase类里的getTestData()方法再次的更改,要利用上这个注解解析出来的值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
private
Object[][] getTestData(Method method){ String sourceKey = DataSources.getDataSource(method); if(sourceKey==null){ sourceKey = Config.DATA_SOURCE; } DataInterface testData =
this.getDataInstance(sourceKey); List<Map<String, String>> listData = testData.getTestMethodData(); Object[][] object =
new Object[listData.size()][]; for
(int
i = 0; i < listData.size(); i++) { object[i] =
new Object[]{listData.get(i)}; } return
object;} |
这段代码可以看到,如果测试方法标注DataSource,则会以标注的注解值为准,否则则会以全局配置的值为准。
5.5 在TestDemo里多加一个测试方法,以示区别
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public
class TestDemo extends
TestBase{ @DataSource("com.test.testdata.PropertiesData") @Test(dataProvider="dataProvider") public
void testDemo(Map<String, String> param){ System.out.println(param.get("username")); System.out.println(param.get("password")); } @Test(dataProvider="dataProvider") public
void testDemo1(Map<String, String> param){ System.out.println(param.get("username")); System.out.println(param.get("password")); } } |
上面的测试类中,两个测试方法,一个用了全局的配置数据源值,一个用了注解数据源值。大家可以运行的看看结果。
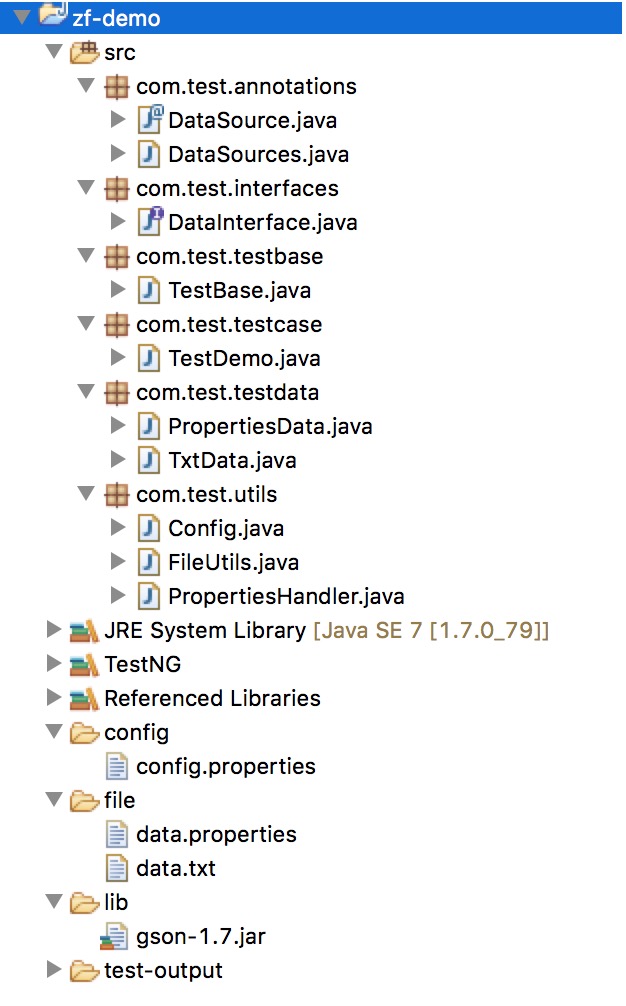
六. 工程结构图:
至于源码,大家自行的拷贝粘贴吧,也当作是一种知识的巩固。
























 1366
1366

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








